Abstract
We hypothesized recently that arginine homeostasis is achieved in humans largely by modulating the rate of arginine degradation. We have tested this hypothesis further by measuring in vivo the whole body rate of conversion of arginine to ornithine and ornithine oxidation in six healthy young adults. Subjects received for 6 days an L-amino acid-based diet supplying an arginine-rich or arginine-free intake and on day 7, following an overnight fast, an 8-h tracer protocol (first 3 h, fast state; next 5 h, fed state) was conducted; L-[guanidino-15N2; 5,5-2H]arginine and L-[5-13C]ornithine were given as primed, constant intravenous tracers; measurements of the abundances of various isotopologs of arginine, ornithine, and citrulline in plasma were made, and from these the various kinetic parameters of the metabolism of these amino acids were derived. Arginine and ornithine fluxes were significantly (P < 0.001) reduced in the fed state with arginine-free feeding. The rates of conversion (mumol.kg-1.h-1; mean +/- SD) of plasma arginine to ornithine for arginine-rich were 12.9 +/- 2.6 and 24.7 +/- 4.8 for fast and fed states. These values were 11.1 +/- 3.5 and 9.6 +/- 1.2 (P > 0.05 and P < 0.001), respectively, with an arginine-free diet. [13C]Ornithine oxidation was reduced (P < 0.001) by 46% during the fed state when the arginine-free diet was given. The findings strengthen our hypothesis that homeostasis of arginine metabolism in the human host depends importantly upon a regulation in the rate of arginine degradation with, perhaps, little involvement in the de novo net rate of arginine synthesis.
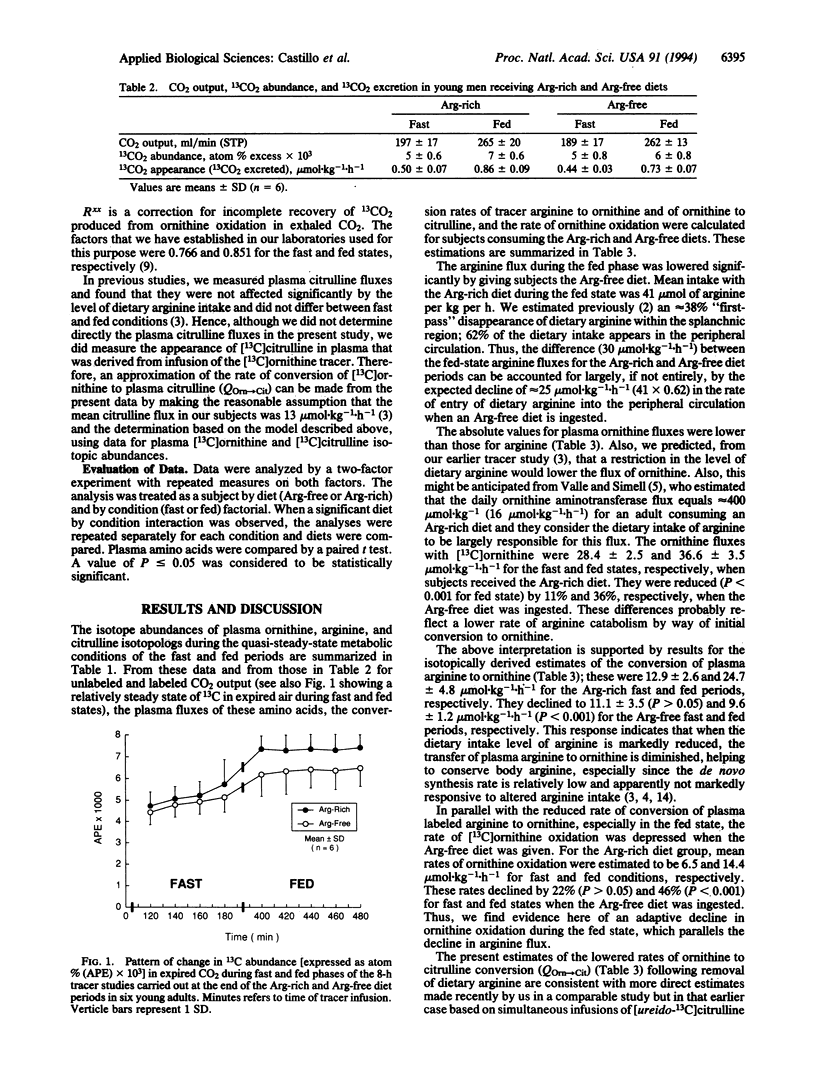
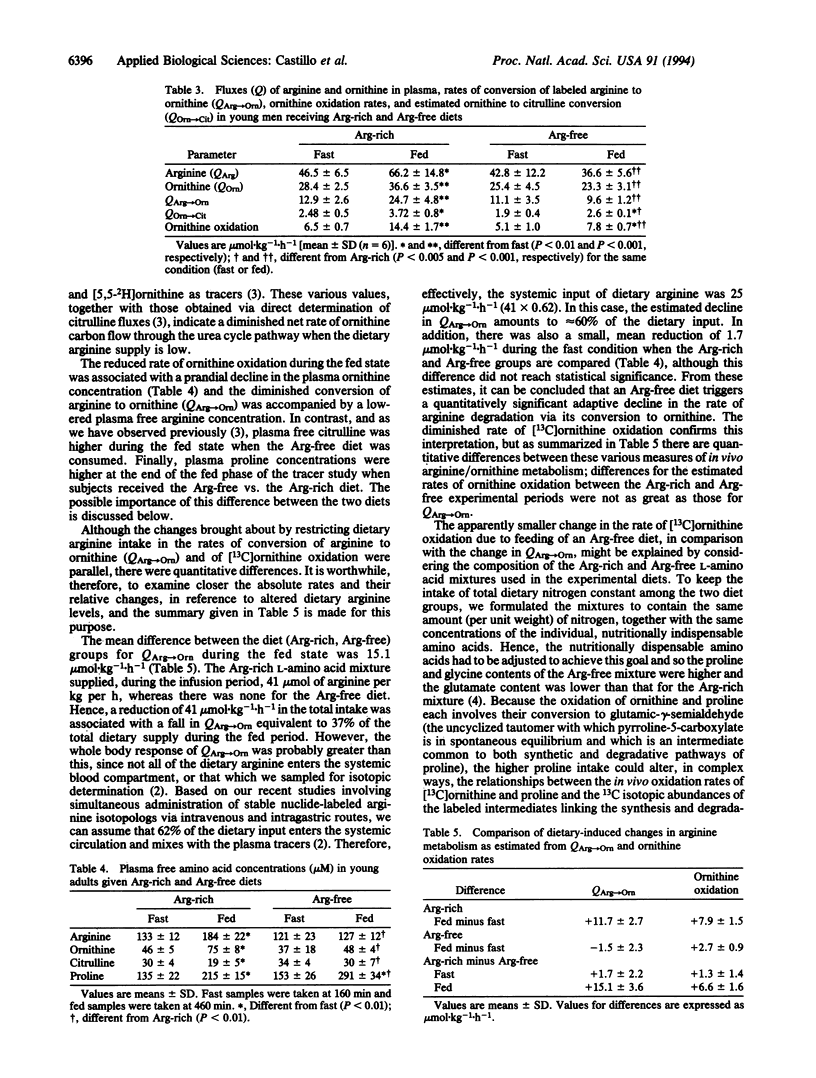
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brusilow S. W., Finkelstien J. Restoration of nitrogen homeostasis in a man with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Metabolism. 1993 Oct;42(10):1336–1339. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90135-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L., Ajami A., Branch S., Chapman T. E., Yu Y. M., Burke J. F., Young V. R. Plasma arginine kinetics in adult man: response to an arginine-free diet. Metabolism. 1994 Jan;43(1):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L., Chapman T. E., Sanchez M., Yu Y. M., Burke J. F., Ajami A. M., Vogt J., Young V. R. Plasma arginine and citrulline kinetics in adults given adequate and arginine-free diets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7749–7753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L., Chapman T. E., Yu Y. M., Ajami A., Burke J. F., Young V. R. Dietary arginine uptake by the splanchnic region in adult humans. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 1):E532–E539. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.265.4.E532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L., deRojas T. C., Chapman T. E., Vogt J., Burke J. F., Tannenbaum S. R., Young V. R. Splanchnic metabolism of dietary arginine in relation to nitric oxide synthesis in normal adult man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Bier D. M. The conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine in man. Direct measurement by continuous intravenous tracer infusions of L-[ring-2H5]phenylalanine and L-[1-13C] tyrosine in the postabsorptive state. Metabolism. 1982 Oct;31(10):999–1005. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhanakoti S. N., Brosnan J. T., Brosnan M. E., Herzberg G. R. Net renal arginine flux in rats is not affected by dietary arginine or dietary protein intake. J Nutr. 1992 May;122(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1093/jn/122.5.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grody W. W., Argyle C., Kern R. M., Dizikes G. J., Spector E. B., Strickland A. D., Klein D., Cederbaum S. D. Differential expression of the two human arginase genes in hyperargininemia. Enzymatic, pathologic, and molecular analysis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):602–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI113923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Motil K. J., Rohrbaugh D. K., Burke J. F., Young V. R., Bier D. M. Measurement of leucine metabolism in man from a primed, continuous infusion of L-[1-3C]leucine. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):E473–E479. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.5.E473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr Regulation of enzymes of urea and arginine synthesis. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:81–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.12.070192.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell J. J., Sandman R. P., Martin S. R. Gyrate atrophy of the retina: inborn error of L-ornithin:2-oxoacid aminotransferase. Science. 1978 Apr 14;200(4338):200–201. doi: 10.1126/science.635581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier V., Marks L., Wagner D. A., Hoerr R. A., Young V. R. Branched-chain amino acid interactions with reference to amino acid requirements in adult men: valine metabolism at different leucine intakes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Aug;54(2):395–401. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/54.2.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. N., Pacy P. J., Merritt H., Ford G. C., Read M. A., Cheng K. N., Halliday D. Rapid measurement of whole body and forearm protein turnover using a [2H5]phenylalanine model. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):E631–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.5.E631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt J. A., Chapman T. E., Wagner D. A., Young V. R., Burke J. F. Determination of the isotope enrichment of one or a mixture of two stable labelled tracers of the same compound using the complete isotopomer distribution of an ion fragment; theory and application to in vivo human tracer studies. Biol Mass Spectrom. 1993 Oct;22(10):600–612. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200221008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Khoury A. E., Fukagawa N. K., Sánchez M., Tsay R. H., Gleason R. E., Chapman T. E., Young V. R. Validation of the tracer-balance concept with reference to leucine: 24-h intravenous tracer studies with L-[1-13C]leucine and [15N-15N]urea. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 May;59(5):1000–1011. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/59.5.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



