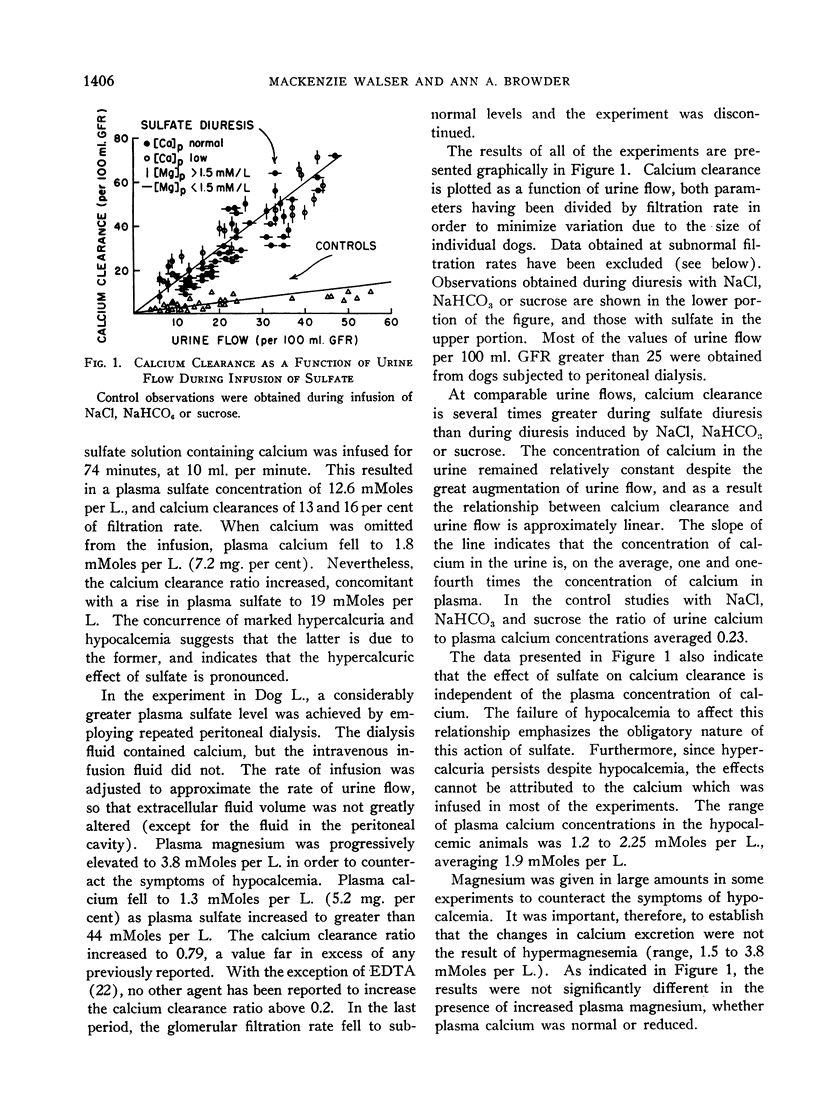
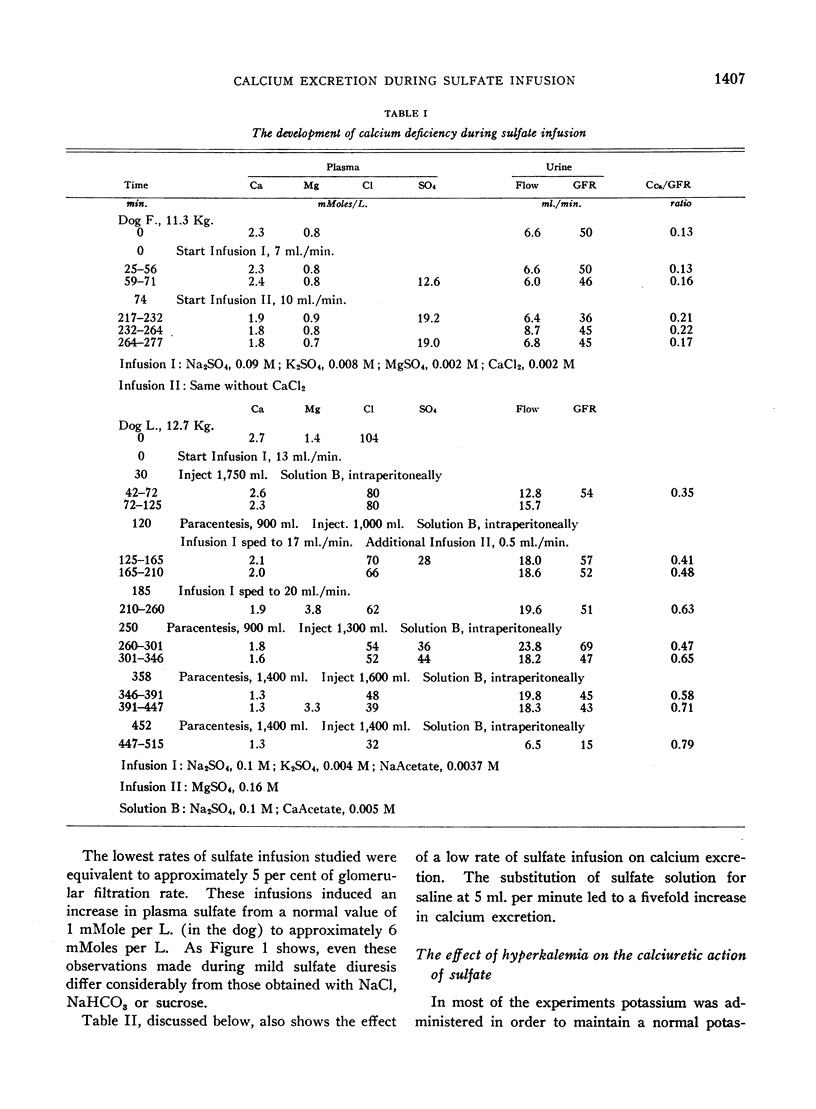
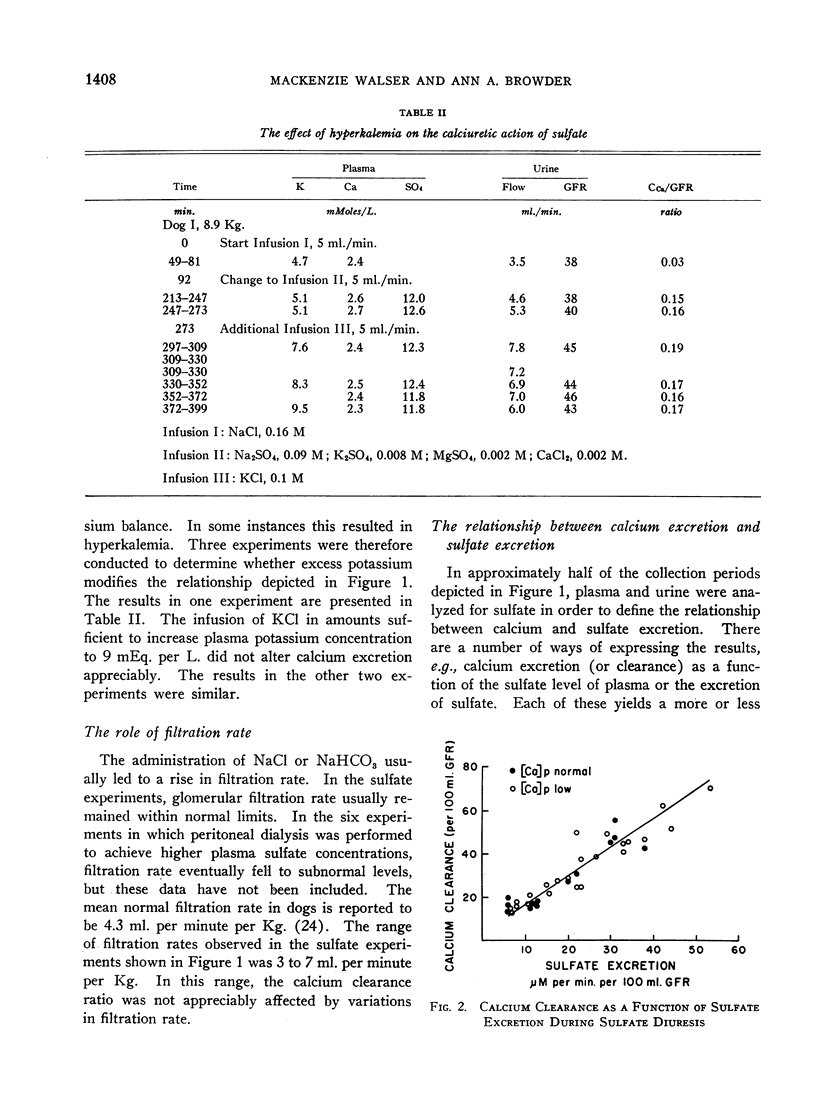
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANG T. S., FREEMAN S. Citric acid and its relation to serum and urinary calcium. Am J Physiol. 1950 Feb;160(2):330–340. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.160.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN P. S., Jr, NEUMAN W. F. Renal excretion of calcium by the dog. Am J Physiol. 1955 Mar;180(3):623–631. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHESLEY L. C., TEPPER I. Some effects of magnesium loading upon renal excretion of magnesium and certain other electrolytes. J Clin Invest. 1958 Oct;37(10):1362–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI103726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E., TRANTHAM H. V., BOWMAN R. L. An instrument and method for automatic, rapid, accurate, and sensitive titration of chloride in biologic samples. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Mar;51(3):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN S., JACOBSEN A. B., WILLIAMSON B. J. Acid-base balance and removal of injected calcium from the circulation. Am J Physiol. 1957 Nov;191(2):377–383. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLICK D., FREIER E. F., OCHS M. J. Studies in histochemistry. XLVII. Microdetermination of magnesium and its histological distribution in the adrenal in various functional states. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. F., DANIELSON E., SAHAGIAN-EDWARDS A. Use of ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid in hypercalcemic patients. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Nov;84(2):359–364. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY T. J., Jr, HILTON J. G., BERLINER R. W. Comparison of inulin and creatinine clearance in the normal dog. Am J Physiol. 1952 Oct;171(1):164–168. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.171.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., TABORSKY E., EPSTEIN F. H. Improved method for determination of inorganic sulfate in biologic fluids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Mar;91(3):480–483. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORANGE M., RHEIN H. C. Microestimation of magnesium in body fluids. J Biol Chem. 1951 Mar;189(1):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORIBARA T. Y., TEREPKA A. R., DEWEY P. A. The ultrafiltrable calcium of human serum. I. Ultrafiltration methods and normal values. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):738–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI103477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSER M., REID A. F., SELDIN D. W. A method of counting radiosulfur in liquid samples, and its application to the determination of S35 excretion following injection of S35O4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Jul;45(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTLESEY P. A continuous intravenous infusion apparatus for the unanesthetized dog. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Feb;43(2):324–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF A. V., BALL S. M. Effect of intravenous sodium sulfate on renal excretion in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1950 Feb;160(2):353–360. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.160.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



