Abstract
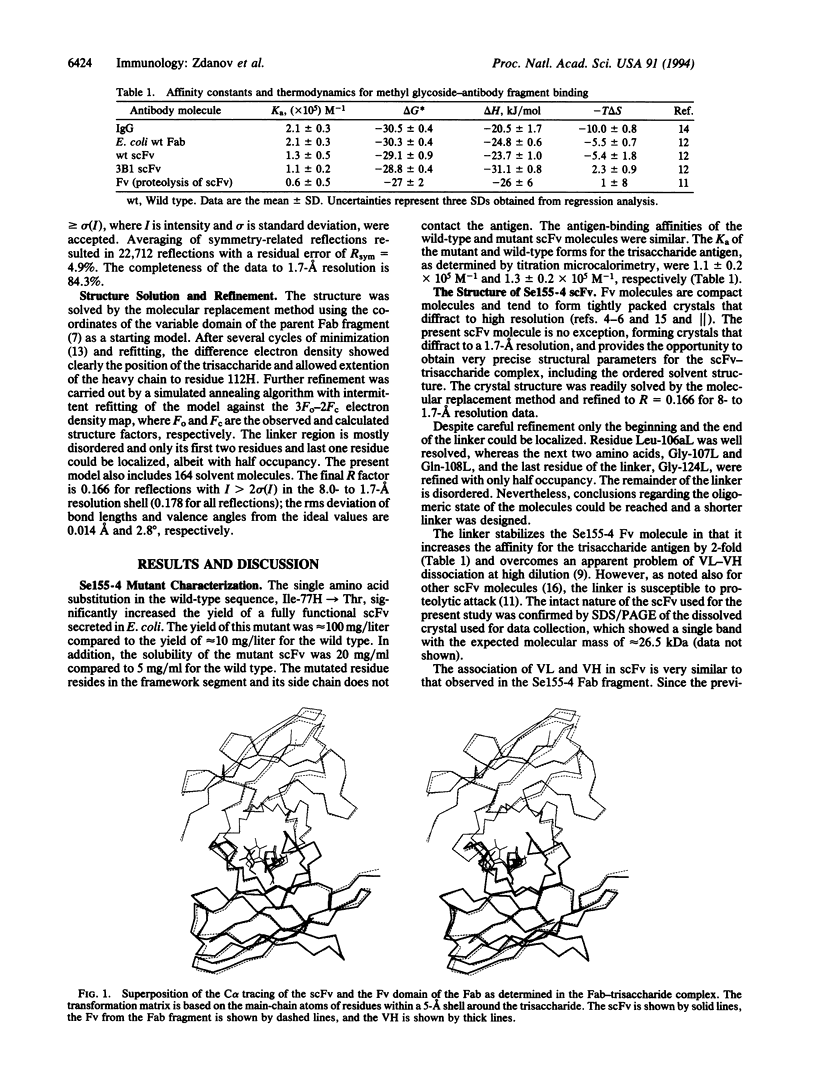
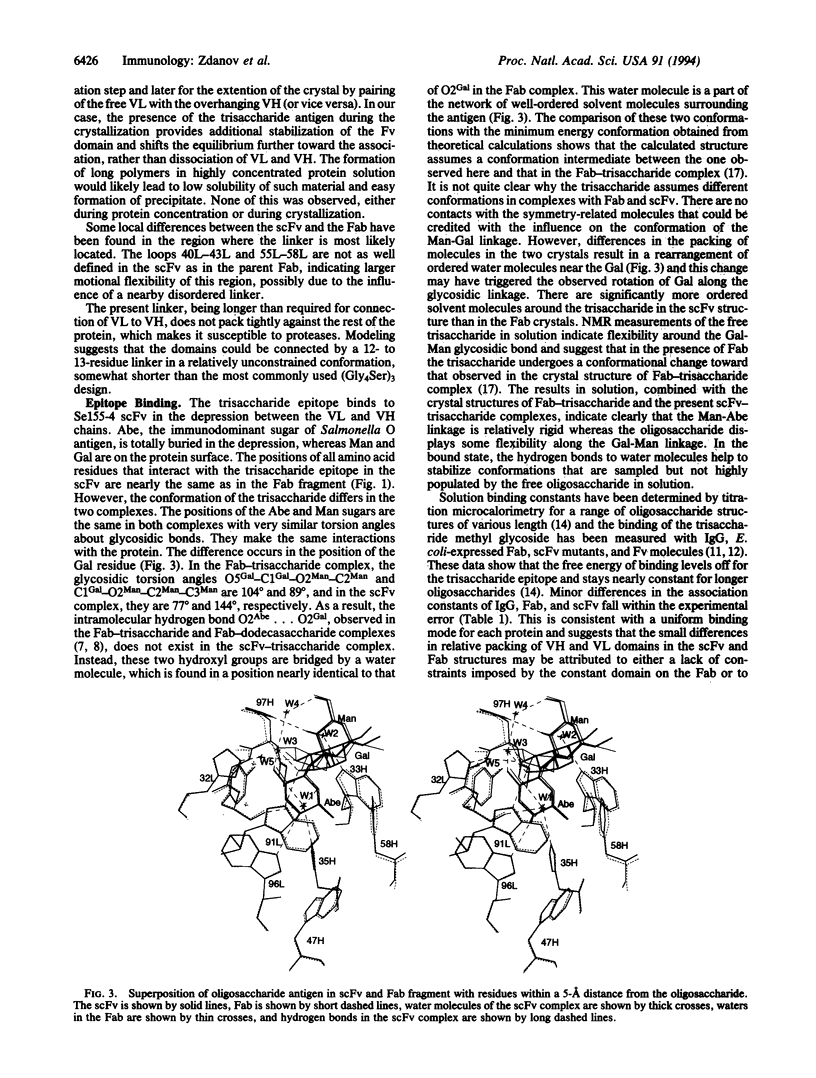
We describe here the 1.7-A resolution structure of a single-chain antibody variable domain (scFv) molecule, based on the carbohydrate-binding antibody Se155-4, complexed with the trisaccharide ligand alpha-D-Gal(1-->2)[alpha-D-Abe(1-->3)]alpha-D-Manp1-->OMe, where Abe is abequose. The scFv expressed in Escherichia coli has the variable region light chain to heavy chain polarity with the domains connected by a 19-residue linker. Although the linker is partially disordered in the crystal, the packing of the molecules suggests a monomeric state of the scFv. The carbohydrate adopts a different conformation about the Man-Gal linkage than was observed previously in the Fab-trisaccharide complex. Instead of a direct hydrogen bond between O2Abe and O2Gal, these two atoms are bridged by a water molecule in the present complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand N. N., Mandal S., MacKenzie C. R., Sadowska J., Sigurskjold B., Young N. M., Bundle D. R., Narang S. A. Bacterial expression and secretion of various single-chain Fv genes encoding proteins specific for a Salmonella serotype B O-antigen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21874–21879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat T. N., Bentley G. A., Fischmann T. O., Boulot G., Poljak R. J. Small rearrangements in structures of Fv and Fab fragments of antibody D1.3 on antigen binding. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):483–485. doi: 10.1038/347483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. E., Hardman K. D., Jacobson J. W., Johnson S., Kaufman B. M., Lee S. M., Lee T., Pope S. H., Riordan G. S., Whitlow M. Single-chain antigen-binding proteins. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3140379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M., Laver W. G., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., Tulloch P. A., Air G. M., Webster R. G. Three-dimensional structure of a complex of antibody with influenza virus neuraminidase. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):358–363. doi: 10.1038/326358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Rose D. R., Bundle D. R. Recognition of a cell-surface oligosaccharide of pathogenic Salmonella by an antibody Fab fragment. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.1713710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Wu S., Zdanov A., Bundle D. R., Rose D. R. Recognition of a carbohydrate antigenic determinant of Salmonella by an antibody. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):437–441. doi: 10.1042/bst0210437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenbrot C., Randal M., Presta L., Carter P., Kossiakoff A. A. X-ray structures of the antigen-binding domains from three variants of humanized anti-p185HER2 antibody 4D5 and comparison with molecular modeling. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 20;229(4):969–995. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Z. C., Shan L., Guddat L. W., He X. M., Gray W. R., Raison R. L., Edmundson A. B. Three-dimensional structure of an Fv from a human IgM immunoglobulin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):188–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90500-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaudemans C. P., Lerner L., Daves G. D., Jr, Kovác P., Venable R., Bax A. Significant conformational changes in an antigenic carbohydrate epitope upon binding to a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 11;29(49):10906–10911. doi: 10.1021/bi00501a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glockshuber R., Malia M., Pfitzinger I., Plückthun A. A comparison of strategies to stabilize immunoglobulin Fv-fragments. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1362–1367. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston J. S., Levinson D., Mudgett-Hunter M., Tai M. S., Novotný J., Margolies M. N., Ridge R. J., Bruccoleri R. E., Haber E., Crea R. Protein engineering of antibody binding sites: recovery of specific activity in an anti-digoxin single-chain Fv analogue produced in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5879–5883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malby R. L., Caldwell J. B., Gruen L. C., Harley V. R., Ivancic N., Kortt A. A., Lilley G. G., Power B. E., Webster R. G., Colman P. M. Recombinant antineuraminidase single chain antibody: expression, characterization, and crystallization in complex with antigen. Proteins. 1993 May;16(1):57–63. doi: 10.1002/prot.340160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rini J. M., Schulze-Gahmen U., Wilson I. A. Structural evidence for induced fit as a mechanism for antibody-antigen recognition. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):959–965. doi: 10.1126/science.1546293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A., Hendrickson W. A. The reactivity of anti-peptide antibodies is a function of the atomic mobility of sites in a protein. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):127–134. doi: 10.1038/312127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlow M., Bell B. A., Feng S. L., Filpula D., Hardman K. D., Hubert S. L., Rollence M. L., Wood J. F., Schott M. E., Milenic D. E. An improved linker for single-chain Fv with reduced aggregation and enhanced proteolytic stability. Protein Eng. 1993 Nov;6(8):989–995. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.8.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Milenic D. E., Whitlow M., Schlom J. Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res. 1992 Jun 15;52(12):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


