Abstract
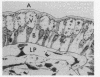
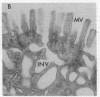
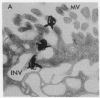
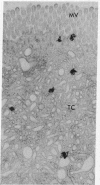
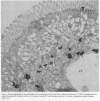
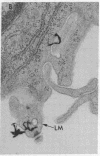
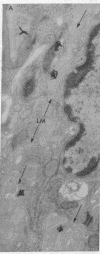
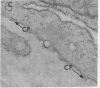
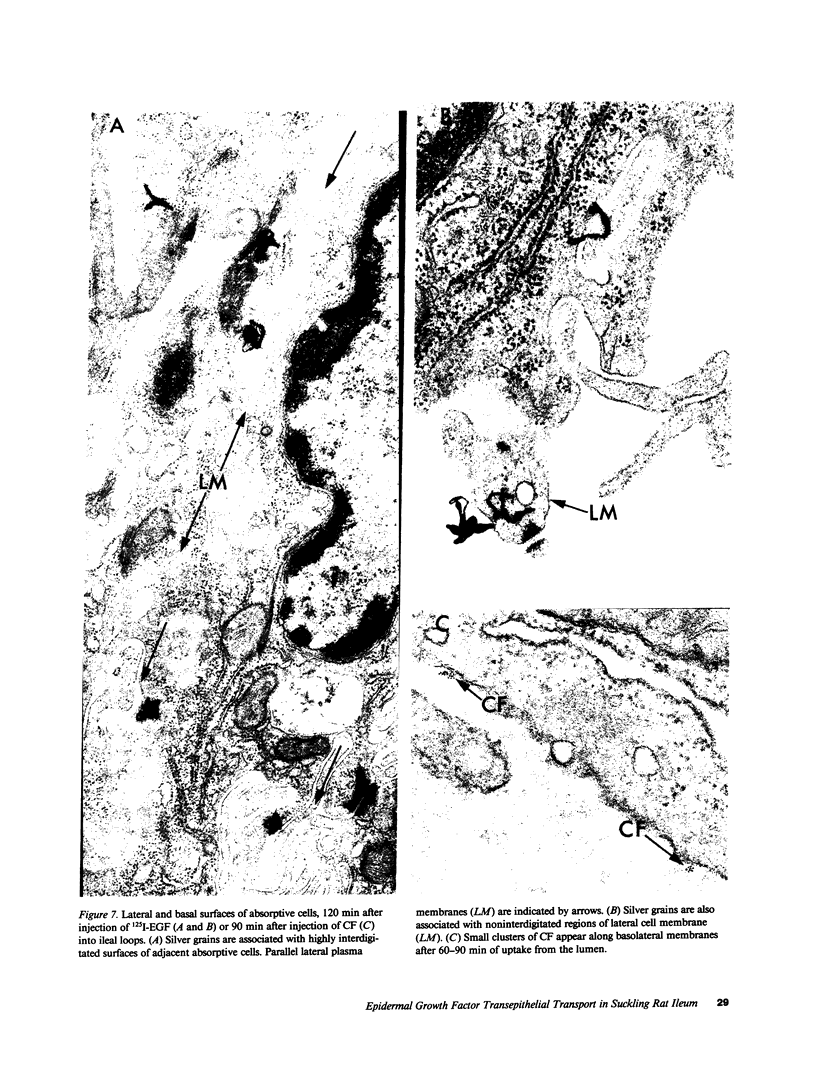
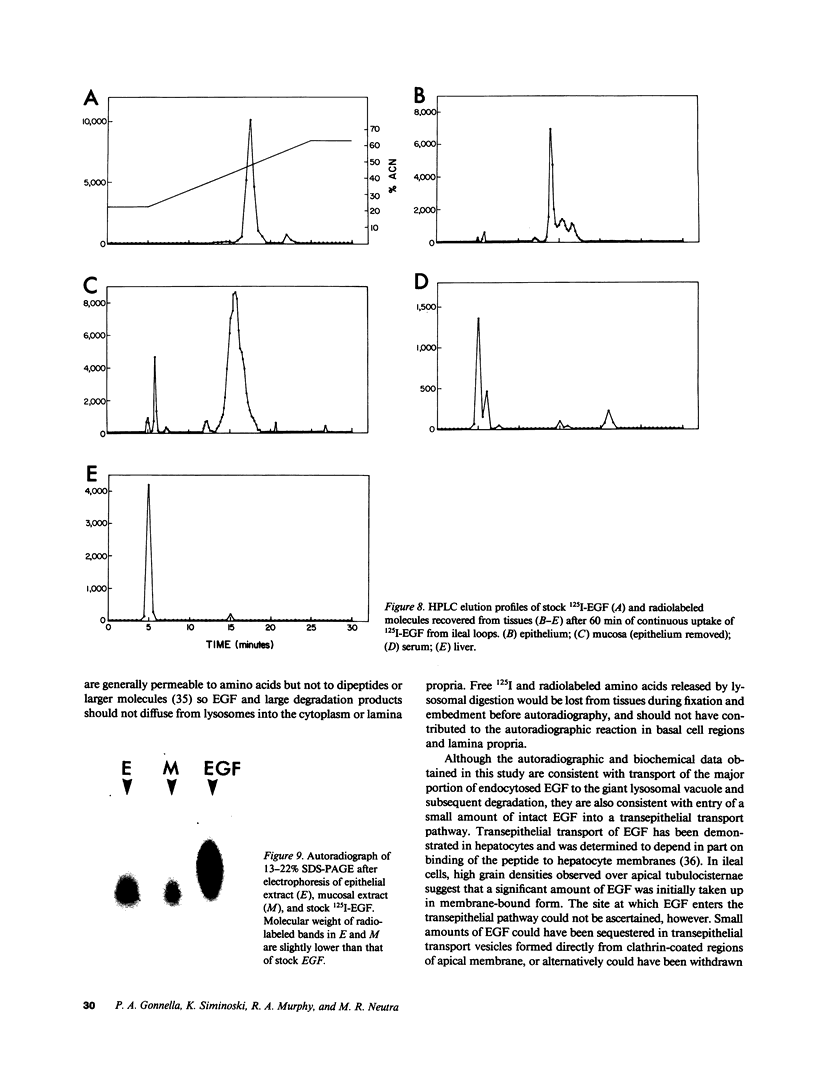
Epidermal growth factor (EGF), an acid-stable peptide present in rodent and human milk, is absorbed and promotes intestinal growth when fed to suckling rats. To determine whether absorptive cells of suckling rat ileum conduct selective transepithelial transport of EGF, we followed uptake of 125I-EGF from ileal loops by autoradiography and biochemical methods. Specific binding sites for 125I-EGF were localized by electron microscope autoradiography on apical membranes of ileal epithelial sheets in vitro. During uptake in vivo, radiolabeled molecules were concentrated in apical endosomal compartments and were also associated with lysosomal vacuoles, basolateral cell surfaces, and lamina propria. Excess cold EGF reduced basolateral label by 44% and TCA precipitable serum label by 38%. After 30 and 60 min of continuous uptake, radiolabeled molecules in epithelium, denuded mucosa, blood, and liver were analyzed under reducing conditions by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Although considerable degradation of 125I-EGF occurred after uptake from the lumen, a portion of radiolabel in epithelium and mucosa represented 125I-EGF which eluted somewhat more rapidly from C18 HPLC columns and showed a slight decrease in apparent molecular weight by SDS-PAGE. All radiolabel in blood and liver represented breakdown products. Thus, EGF is selectively transported across the ileal epithelium in suckling rats but is modified during transport. Milk EGF may accumulate in the lamina propria where it could influence growth and maturation of the suckling intestine.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamson D. R., Rodewald R. Evidence for the sorting of endocytic vesicle contents during the receptor-mediated transport of IgG across the newborn rat intestine. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):270–280. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardmore J. M., Richards R. C. Concentrations of epidermal growth factor in mouse milk throughout lactation. J Endocrinol. 1983 Feb;96(2):287–292. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0960287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes M., Cheng H. Methods for the isolation of intact epithelium from the mouse intestine. Anat Rec. 1981 Apr;199(4):565–574. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091990412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burwen S. J., Barker M. E., Goldman I. S., Hradek G. T., Raper S. E., Jones A. L. Transport of epidermal growth factor by rat liver: evidence for a nonlysosomal pathway. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1259–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO L. G., VAN TUBERGEN R. P., KOLB J. A. High-resolution autoradiography. I. Methods. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:173–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor is a major growth-promoting agent in human milk. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.6968093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Ehrenreich B. A. The uptake, storage, and intracellular hydrolysis of carbohydrates by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):201–225. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell R., Padykula H. A. A cytological study of intestinal absorption in the suckling rat. Am J Anat. 1969 Jul;125(3):291–315. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001250304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembinski A. B., Johnson L. R. Effect of epidermal growth factor on the development of rat gastric mucosa. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):90–94. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Connolly T. P., Hubbard A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor by rat hepatocytes: receptor pathway. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):24–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue-Lafitte M. E., Laburthe M., Chamblier M. C., Moody A. J., Rosselin G. Demonstration of specific receptors for EGF--urogastrone in isolated rat intestinal epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 2;114(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo-Payet N., Hugon J. S. Epidermal growth factor receptors in isolated adult mouse intestinal cells: studies in vivo and in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):194–201. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Neutra M. R. Glycoconjugate distribution and mobility on apical membranes of absorptive cells of suckling rat ileum in vivo. Anat Rec. 1985 Dec;213(4):520–528. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092130408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Neutra M. R. Membrane-bound and fluid-phase macromolecules enter separate prelysosomal compartments in absorptive cells of suckling rat ileum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):909–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Epidermal and nerve growth factors in mammalian development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:251–263. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graney D. O. The uptake of ferritin by ileal absorptive cells in suckling rats. An electron microscope study. Am J Anat. 1968 Sep;123(2):227–254. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueters A., Alm J., Lakshmanan J., Fisher D. A. Epidermal growth factor in mouse milk during early lactation: lack of dependency on submandibular glands. Pediatr Res. 1985 Aug;19(8):853–856. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198508000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J. Biochemistry of intestinal development. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Dec;33:9–16. doi: 10.1289/ehp.79339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Licko V., Van Dyke R. W., Scharschmidt B. F. Biliary secretion of fluid-phase markers by the isolated perfused rat liver. Role of transcellular vesicular transport. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):676–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI112021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo C., Ménard D. Influence of epidermal growth factor on the development of suckling mouse intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 1):28–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Planck S. R., Magun B. E. Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor. I. Acidification of 125I-epidermal growth factor in intracellular organelles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3047–3052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran J. R., Courtney M. E., Orth D. N., Vaughan R., Coy S., Mount C. D., Sherrell B. J., Greene H. L. Epidermal growth factor in human milk: daily production and diurnal variation during early lactation in mothers delivering at term and at premature gestation. J Pediatr. 1983 Sep;103(3):402–405. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80412-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Ghishan F. K., Greene H. L., Orth D. N. Effect of mouse epidermal growth factor/urogastrone on the functional maturation of rat intestine. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):940–944. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. E., Phillips T. H., Neutra M. R. Regulation of intestinal goblet cell secretion. III. Isolated intestinal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G674–G681. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planck S. R., Finch J. S., Magun B. E. Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor. II. Intracellular cleavage of the COOH-terminal region of 125I-epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3053–3057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. K., Thornburg W., Korc M., Matrisian L. M., Magun B. E., Koldovský O. Processing of epidermal growth factor by suckling and adult rat intestinal cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):G850–G855. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.6.G850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald R. Distribution of immunoglobulin G receptors in the small intestine of the young rat. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):18–32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., McHenry F. A., Salpeter E. E. Resolution of electron microscope autoradiography. IV. Application to analysis of autoradiographs. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):127–145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaudies R. P., Savage C. R., Jr Intracellular modification of 125I-labeled epidermal growth factor by normal human foreskin fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):875–882. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheving L. A., Yeh Y. C., Tsai T. H., Scheving L. E. Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, caecum, colon, and rectum of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology. 1980 May;106(5):1498–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-5-1498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminoski K., Gonnella P., Bernanke J., Owen L., Neutra M., Murphy R. A. Uptake and transepithelial transport of nerve growth factor in suckling rat ileum. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1979–1990. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Hilaire R. J., Hradek G. T., Jones A. L. Hepatic sequestration and biliary secretion of epidermal growth factor: evidence for a high-capacity uptake system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3797–3801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg W., Matrisian L., Magun B., Koldovský O. Gastrointestinal absorption of epidermal growth factor in suckling rats. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):G80–G85. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.1.G80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., VanNostrand W., McKinley D. N., Cunningham D. D. Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor and its effect on ligand-receptor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5290–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]