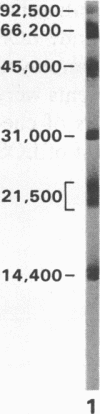
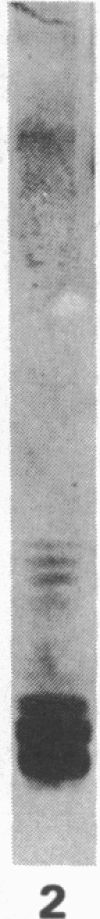
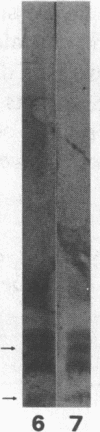
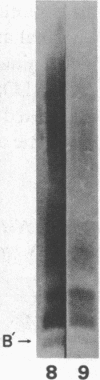
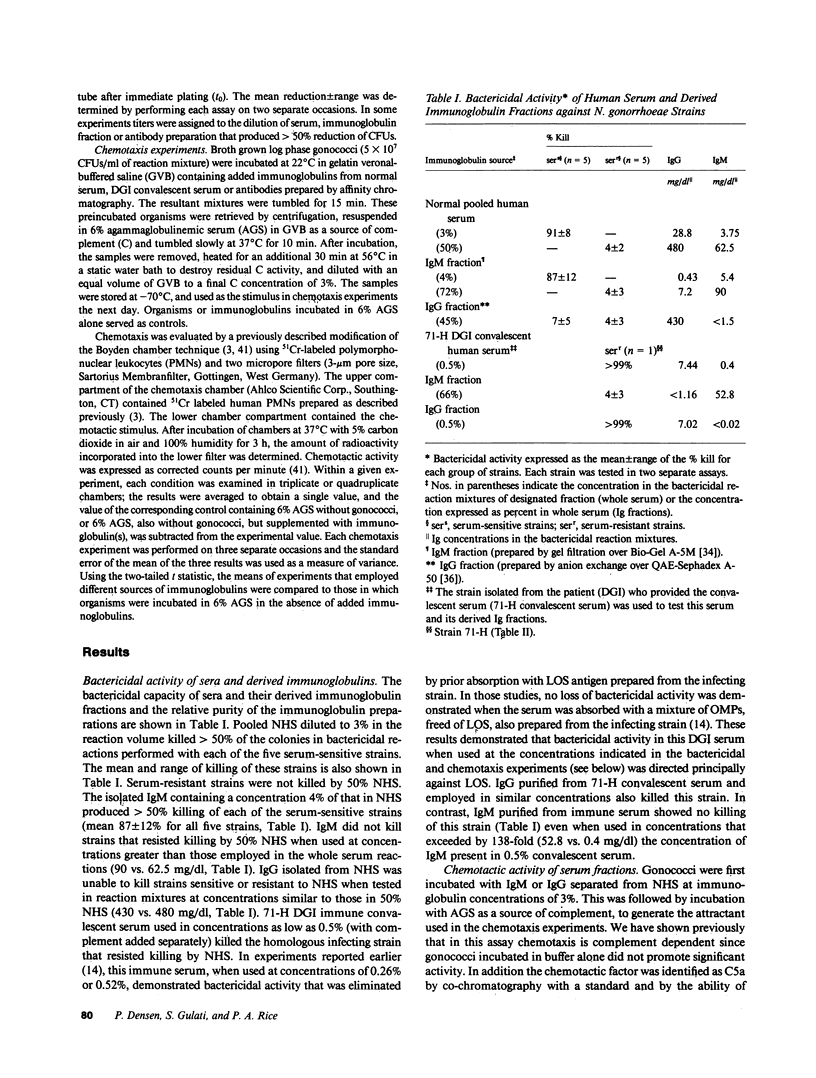
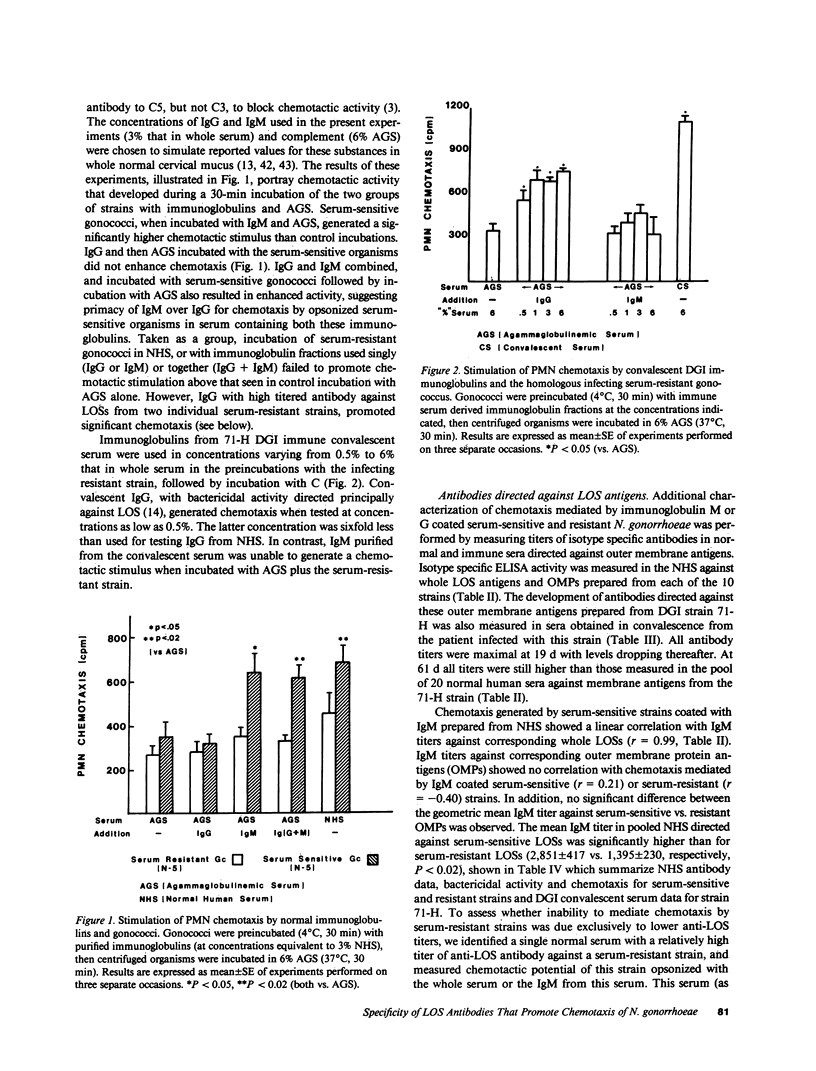
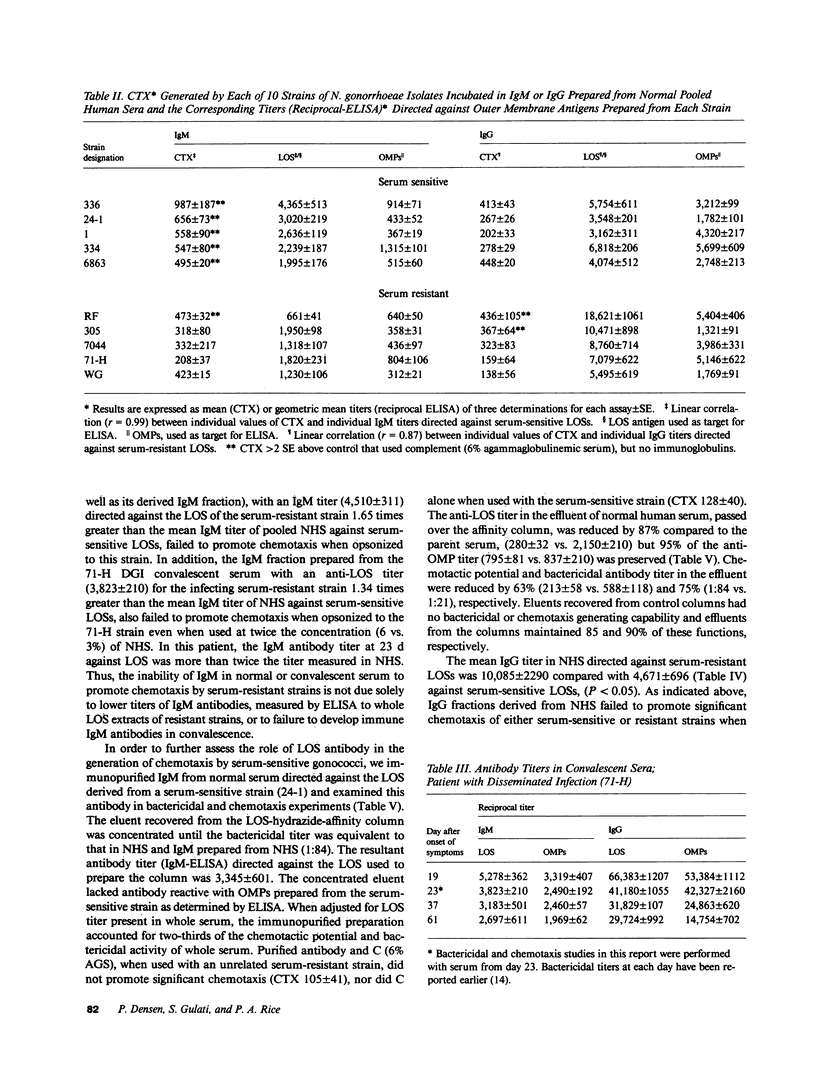
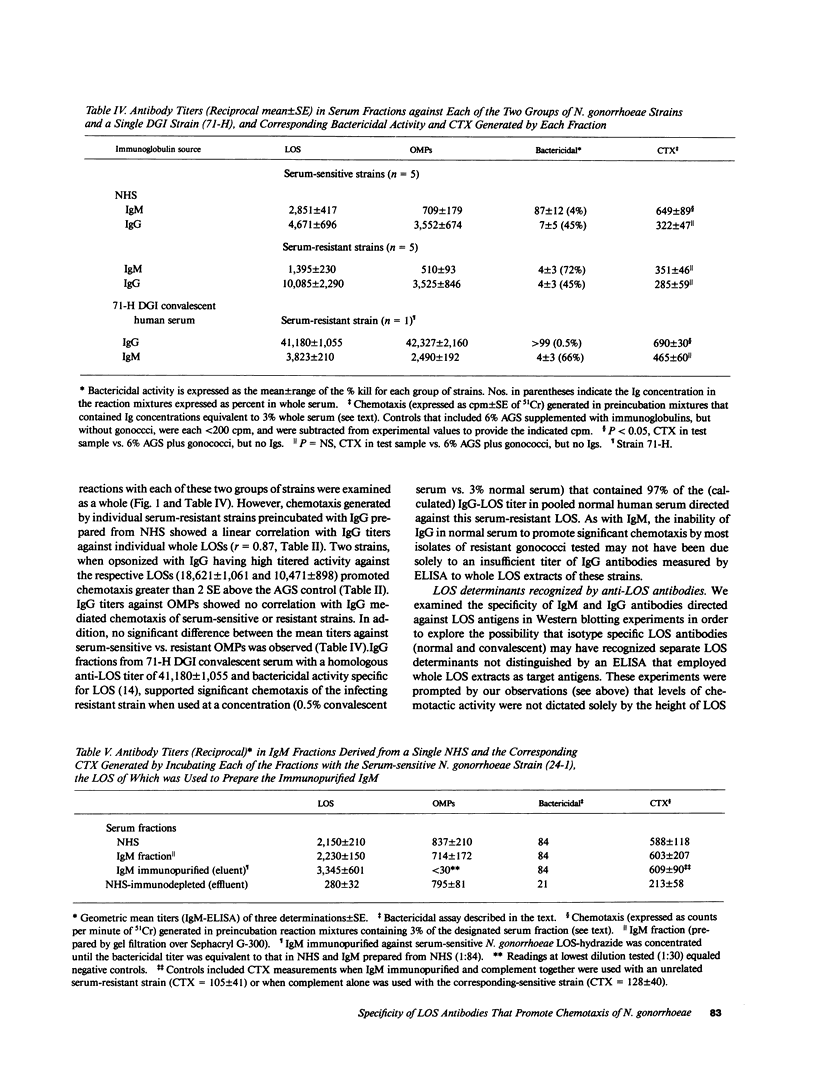
Abstract
Five strains each of Neisseria gonorrhoeae sensitive or resistant to complement (C) dependent killing by normal human serum (NHS) were examined for their ability to stimulate chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) after preincubation with NHS; or IgM or IgG derived from NHS. Serum-sensitive N. gonorrhoeae stimulated C-dependent chemotaxis when opsonized with IgM, but not IgG, however, serum-resistant strains, taken as a whole, failed to promote chemotaxis when opsonized with either isotype. IgM titers in NHS against lipooligosaccharide (LOS) antigens from individual serum-sensitive, but not serum-resistant strains, correlated with the magnitude of chemotaxis generated by the corresponding opsonized strains (r = 0.99). Western blots demonstrated that IgM and IgG from NHS recognized different antigenic determinants on LOS from serum-sensitive gonococci. IgM from NHS immunopurified against serum-sensitive LOS accounted for two-thirds of the chemotaxis promoting activity present in whole serum. IgG titers in NHS against LOS antigens from individual serum-resistant strains also correlated with magnitude of chemotaxis generated by the corresponding opsonized strains (r = 0.87), although most opsonized serum-resistant strains did not generate significantly higher magnitudes of chemotaxis than controls. In contrast, a serum-resistant isolate from a patient with disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) stimulated chemotaxis when opsonized with IgG obtained from the patient's convalescent serum. By Western blot, convalescent IgG antibody recognized an additional determinant on serum-resistant LOS not seen by normal IgG.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Gagliardi N. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of the non-serogroup antigen structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):870–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.870-874.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Westerink M. A., Morse S. A., Schneider H., Rice P. A., Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal antibody response of normal human serum to the lipooligosaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):520–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman M. J., Guerrant R. L., Murad F., Richardson S. H., Weaver D., Mandell G. L. Interaction of polymorphonuclear neutrophils with Escherichia coli. Effect of enterotoxin on phagocytosis, killing, chemotaxis, and cyclic AMP. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):227–234. doi: 10.1172/JCI108931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogadir S. P., Schimmer B. M., Myers A. R. Spectrum of the gonococcal arthritis-dermatitis syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;8(3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(79)80006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly M. C., Allen P. Z. Chemical and immunochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides from pyocin 103-sensitive and -resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Aug 16;120:171–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford C., Knapp J. S., Hale J., Holmes K. K. Asymptomatic gonorrhea in men: caused by gonococci with unique nutritional requirements. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1352–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.405742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., MacKeen L. A., Clark R. A. Dissemination of gonococcal infection is associated with delayed stimulation of complement-dependent neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):563–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.563-572.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Masi A. T. Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) and gonococcal arthritis (GCA): I. Bacteriology, epidemiology, host factors, pathogen factors, and pathology. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Feb;10(3):155–172. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(81)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnehm H. E., Pelton S. I., Gulati S., Rice P. A. Characterization of antigens from nontypable Haemophilus influenzae recognized by human bactericidal antibodies. Role of Haemophilus outer membrane proteins. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1645–1658. doi: 10.1172/JCI111872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Rietschel E. T. Isolation and analysis of the lipid A backbone. Lipid A structure of lipopolysaccharides from various bacterial groups. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Olsen D. A., Buchanan T. M. Analysis of the antigen specificity of the human serum immunoglobulin G immune response to complicated gonococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):706–709. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.706-709.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horigome T., Sugano H. A rapid method for removal of detergents from protein solution. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;130(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90605-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd R. C. 125I-peptide mapping of protein III isolated from four strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):622–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.622-631.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Drutz D. J. Perihepatitis and hepatitis as complications of experimental endocarditis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the rabbit. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):37–42. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Rice P. A., McCormick W. M. Bactericidal antibody in genital infection due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):243–251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn J., Wilchek M. A new approach (cyano-transfer) for cyanogen bromide activation of Sepharose at neutral pH, which yields activated resins, free of interfering nitrogen derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):878–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90604-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn J., Wilchek M. Procedures for the analysis of cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose or Sephadex by quantitative determination of cyanate esters and imidocarbonates. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. C., Parekh M. C., Haley J. V. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from donors of different races toward Neisseria gonorrhoeae of three different auxotypes. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;12(4):188–192. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198510000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. P., Goldenberg D. L., Rice P. A. Disseminated gonococcal infection: a prospective analysis of 49 patients and a review of pathophysiology and immune mechanisms. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Nov;62(6):395–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. J., Boettcher B. The presence of complement in human cervical mucus and its possible relevance to infertility in women with complement-dependent sperm-immobilizing antibodies. Fertil Steril. 1979 Jul;32(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)44117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank E. L., Holmes B. Chemotaxis of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes toward Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Feb;17(1):45–52. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Goldenberg D. L. Clinical manifestations of disseminated infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae are linked to differences in bactericidal reactivity of infecting strains. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Aug;95(2):175–178. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of gonococcal antigens responsible for induction of bactericidal antibody in disseminated infection. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI108867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that disseminate. Roles of blocking antibody and gonococcal outer membrane proteins. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):157–167. doi: 10.1172/JCI110589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., McCormack W. M., Kasper D. L. Natural serum bactericidal activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from disseminated, locally invasive, and uncomplicated disease. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2105–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Vayo H. E., Tam M. R., Blake M. S. Immunoglobulin G antibodies directed against protein III block killing of serum-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immune serum. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1735–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Densen P. Opsonophagocytosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: interaction of local and disseminated isolates with complement and neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIFTER S., GALLOP P. M., MICHAELS S., MEILMAN E. Analysis of hydroxamic acids and hydrazides; preparation and properties of dinitrophenyl derivatives of hydroxamic acids, oximes, hydrazides, and hydrazones. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Mandrell R. E., Jarvis G. A. Elaboration of a 3.6-kilodalton lipooligosaccharide, antibody against which is absent from human sera, is associated with serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):672–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.672-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Gonococci causing disseminated gonococcal infection are resistant to the bactericidal action of normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Ochs H. D., Buchanan T. M. Immunoglobulin class responsible for gonococcal bactericidal activity of normal human sera. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1771–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher G. F. Biochemistry of cervical mucus. Fertil Steril. 1970 Oct;21(10):697–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Mayer L. W., Tam M. R. Antigenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae outer membrane protein(s) III detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot transfer with a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):668–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.668-672.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Merril C. R., Shifrin S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. L., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Martin P. M., Smith H. Lipopolysaccharide alteration is associated with induced resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to killing by human serum. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1407–1413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Ciak J., Boslego J., McChesney D. G., Brinton C. C., Zollinger W. Antigenic specificity of antibodies in vaginal secretions during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Artenstein M. S. Cross-reactivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis and the nature of antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]