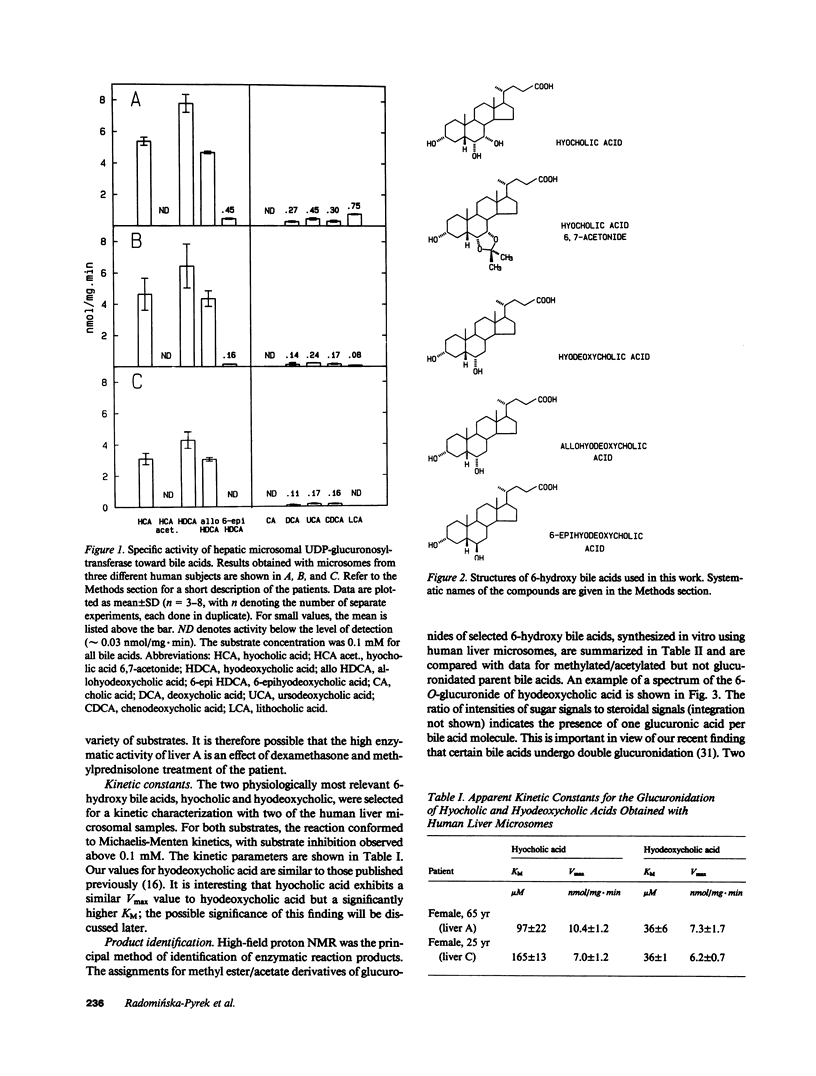
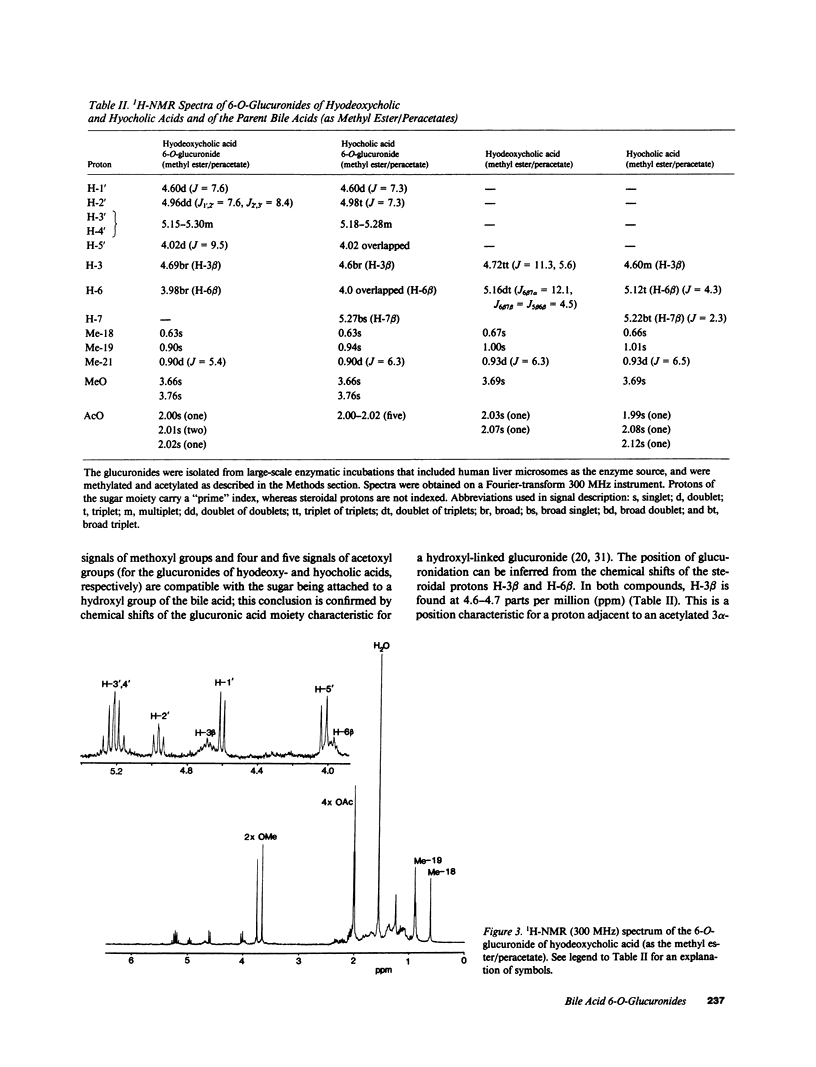
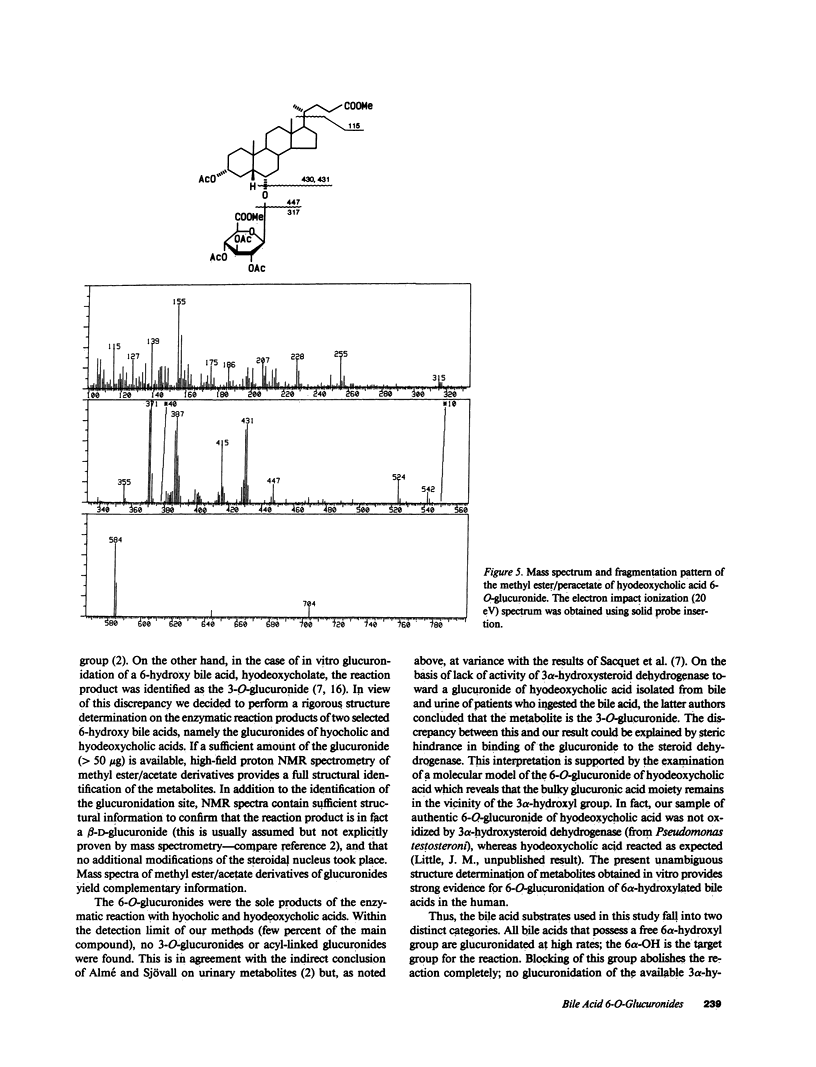
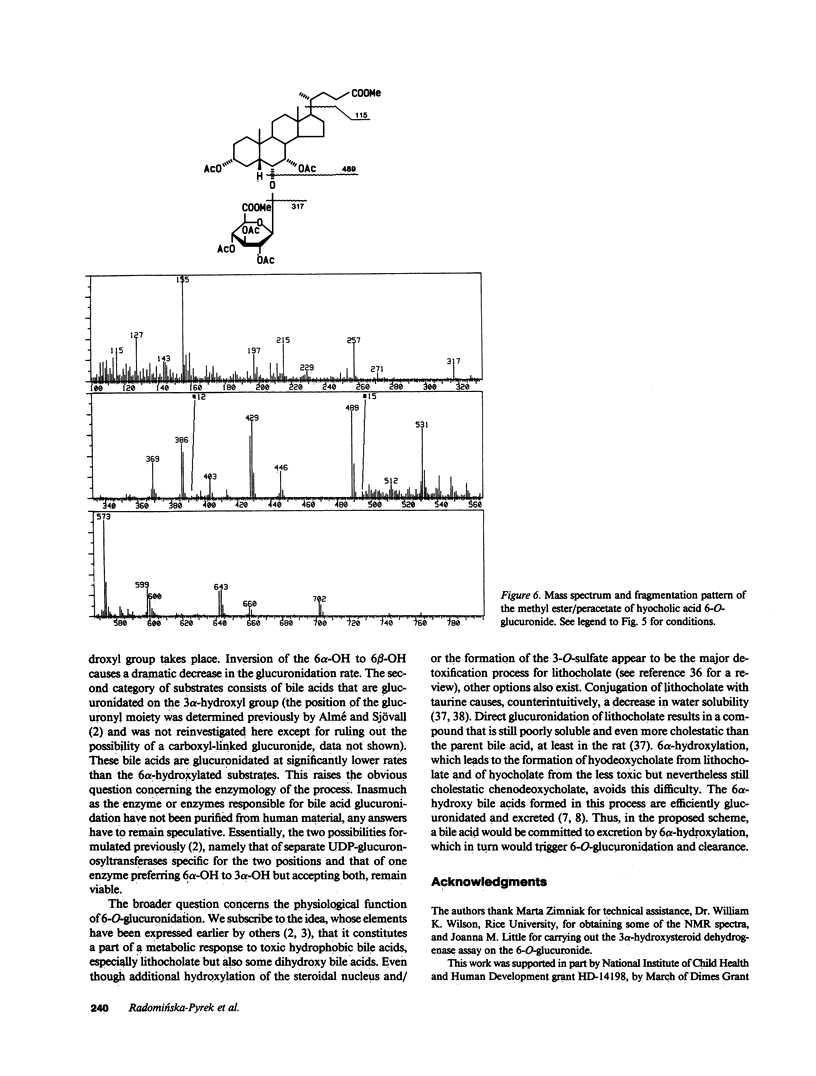
Abstract
The glucuronidation of 6-hydroxylated bile acids by human liver microsomes has been studied in vitro; for comparison, several major bile acids lacking a 6-hydroxyl group were also investigated. Glucuronidation rates for 6 alpha-hydroxylated bile acids were 10-20 times higher than those of substrates lacking a hydroxyl group in position 6. The highest rates measured were for hyodeoxy- and hyocholic acids, and kinetic analyses were carried out using these substrates. Rigorous product identification by high-field proton nuclear magnetic resonance and by electron impact mass spectrometry of methyl ester/peracetate derivatives revealed that 6-O-beta-D-glucuronides were the exclusive products formed in these enzymatic reactions. These results, together with literature data, indicate that 6 alpha-hydroxylation followed by 6-O-glucuronidation constitutes an alternative route of excretion of toxic hydrophobic bile acids.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almé B., Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J., Thomassen P. Analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids in urine using a lipophilic anion exchanger and computerized gas-liquid chromatorgaphy-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):339–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almé B., Nordén A., Sjövall J. Glucuronides of unconjugated 6-hydroxylated bile acids in urine of a patient with malabsorption. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jun 15;86(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almé B., Sjövall J. Analysis of bile acid glucuronides in urine. Identification of 3 alpha, 6 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5 beta-cholanoic acid. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Aug;13(8):907–916. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Bowen D. V. Bile acid glucuronides, III[1, 2]. Chemical synthesis and characterization of glucuronic acid coupled mono-, di- and trihydroxy bile acids. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Feb;357(2):219–224. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P. Phenobarbital-induced alterations of bile acid metabolism in cases of intrahepatic cholestasis. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Jun 1;60(11):541–549. doi: 10.1007/BF01724209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Walter K. Developmental pattern of bile acid metabolism as revealed by bile acid analysis of meconium. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Einarsson K., Hellers G. Metabolism of mono- and dihydroxylated bile acids in preparations of human liver. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;3(6):459–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb02215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J. Hydroxylation of cholic, chenodeoxycholic, and deoxycholic acids in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):1072–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A., Eisenthal R. Estimation of Michaelis constant and maximum velocity from the direct linear plot. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 14;523(1):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed E. M. Properties of acyl glucuronides: implications for studies of the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of acidic drugs. Drug Metab Rev. 1984;15(5-6):1213–1249. doi: 10.3109/03602538409033562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falany C. N., Tephly T. R. Separation, purification and characterization of three isoenzymes of UDP-glucuronyltransferase from rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Nov;227(1):248–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa S. Microbial transformation of bile acids. A unified scheme for bile acid degradation, and hydroxylation of bile acids. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1982;22(5):309–326. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630220505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. R., Hazelton G. A., Klaassen C. D. Depletion of hepatic UDP-glucuronic acid by drugs that are glucuronidated. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):610–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irshaid Y. M., Tephly T. R. Isolation and purification of two human liver UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;31(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick R. B., Falany C. N., Tephly T. R. Glucuronidation of bile acids by rat liver 3-OH androgen UDP-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6176–6180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Matern S., Schelzig C., Gerok W. Bile acid UDP-glucoronyltransferase from human liver. Properties and studies on aglycone substrate specificity. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern S., Matern H., Farthmann E. H., Gerok W. Hepatic and extrahepatic glucuronidation of bile acids in man. Characterization of bile acid uridine 5'-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase in hepatic, renal, and intestinal microsomes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):402–410. doi: 10.1172/JCI111435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelberg D. G., Chari M. V., Little J. M., Adcock E. W., Lester R. Lithocholate glucuronide is a cholestatic agent. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1172/JCI111356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parquet M., Pessah M., Sacquet E., Salvat C., Raizman A., Infante R. Glucuronidation of bile acids in human liver, intestine and kidney. An in vitro study on hyodeoxycholic acid. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter W. R., Trager W. F. Improved non-parametric statistical methods for the estimation of Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters by the direct linear plot. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):293–302. doi: 10.1042/bj1610293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomińska-Pyrek A., Zimniak P., Chari M., Golunski E., Lester R., St Pyrek J. Glucuronides of monohydroxylated bile acids: specificity of microsomal glucuronyltransferase for the glucuronidation site, C-3 configuration, and side chain length. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jan;27(1):89–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacquet E., Parquet M., Riottot M., Raizman A., Jarrige P., Huguet C., Infante R. Intestinal absorption, excretion, and biotransformation of hyodeoxycholic acid in man. J Lipid Res. 1983 May;24(5):604–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Hazelton G. A., Hall J., Watkins P. B., Klaassen C. D., Guzelian P. S. Induction of digitoxigenin monodigitoxoside UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity by glucocorticoids and other inducers of cytochrome P-450p in primary monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes and in human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8270–8275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck K. E., Radominska-Pyrek A., Zimniak P., Adcock E. W., Lester R., St Pyrek J. Metabolism of 24-norlithocholic acid in the rat: formation of hydroxyl- and carboxyl-linked glucuronides and effect on bile flow. Hepatology. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):869–873. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Admirand W. Solubility of bile salts. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):265–267. doi: 10.1038/221265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield J. A., Billing B. H., Shackleton C. H. Identification of bile acids in the serum and urine in cholestasis. Evidence for 6alpha-hydroxylation of bile acids in man. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1540507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Schoenfield L. J. Induced alterations in composition of bile of persons having cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):488–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trülzsch D., Roboz J., Greim H., Czygan P., Rudick J., Hutterer F., Schaffner F., Popper H. Hydroxylation of taurolithocholate by isolated human liver microsomes. I. Identification of metabolic product. Biochem Med. 1974 Feb;9(2):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart G. J., Mossman S., Donald A., Dutton G. J. Differential stimulation of foetal rat liver uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase activity towards certain substrates after glucocorticoid treatment in culture and in utero, and during natural development [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(3):721–723. doi: 10.1042/bst0050721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



