Abstract
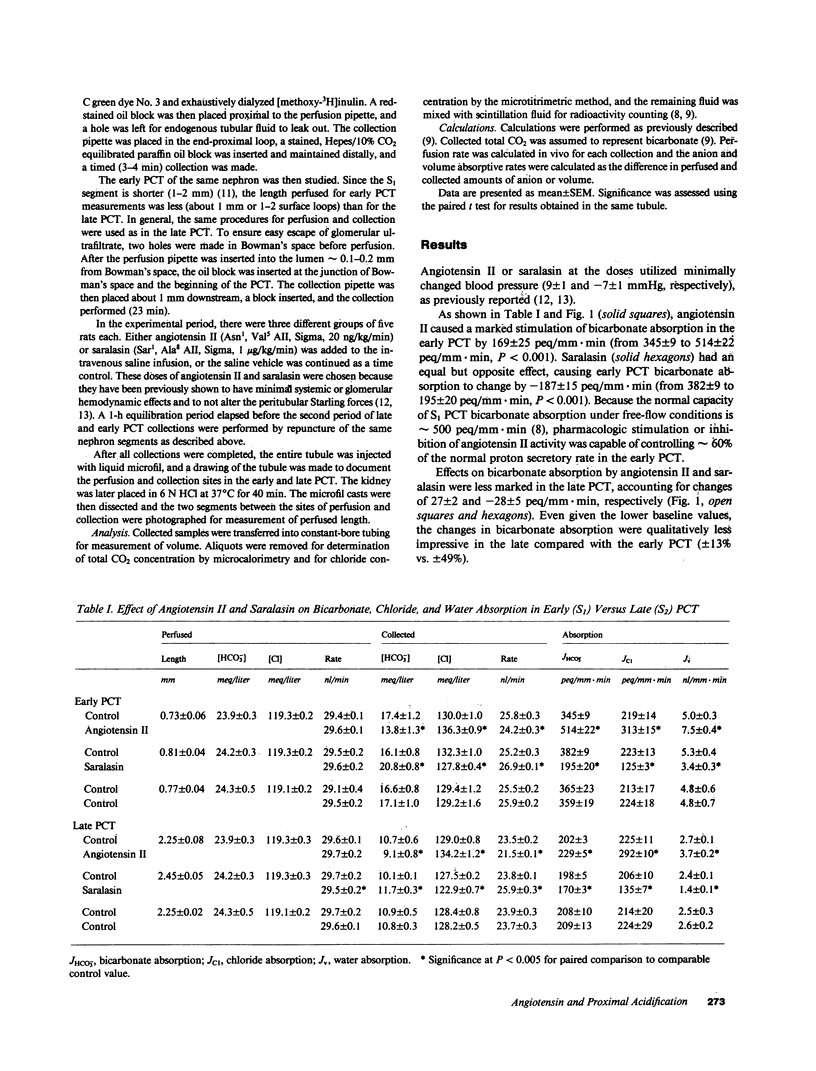
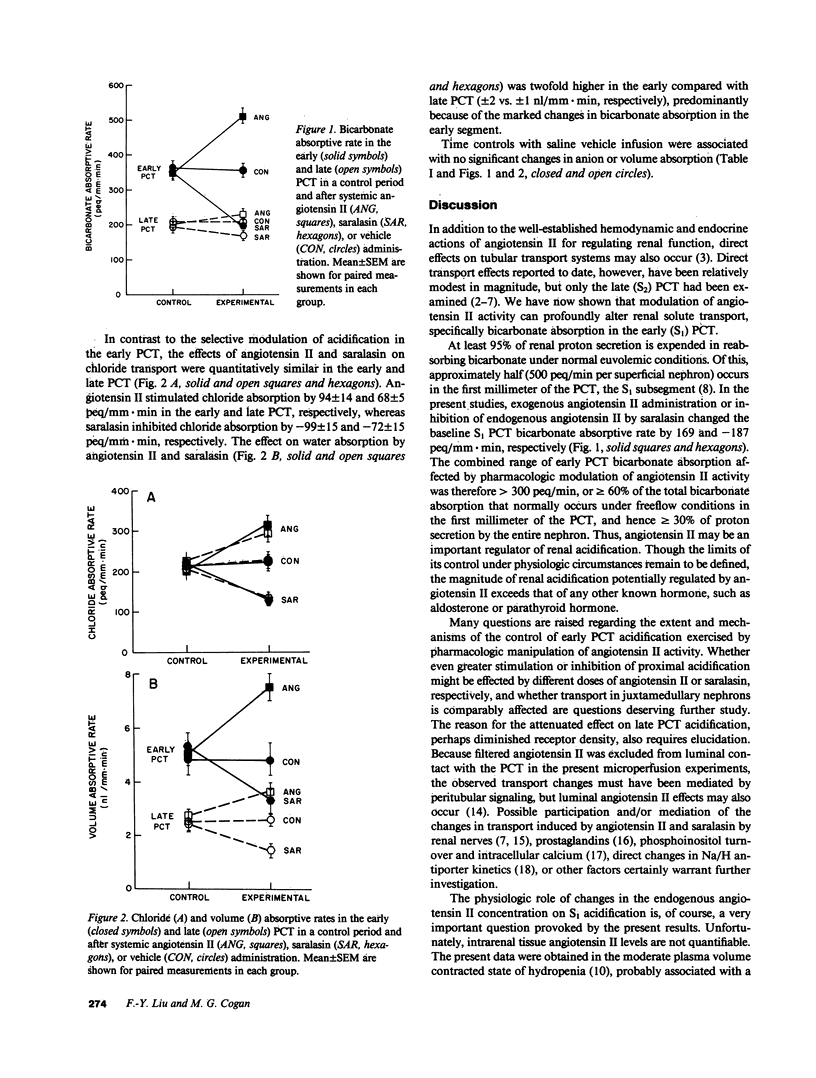
The early proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) is the site of 50% of bicarbonate reabsorption in the nephron, but its control by angiotensin II has not been previously studied. In vivo microperfusion was used in both the early and late PCT in Munich-Wistar rats. Systemic angiotensin II administration (20 ng/kg X min) or inhibition of endogenous angiotensin II activity with saralasin (1 microgram/kg X min) caused profound changes in bicarbonate absorption in the early PCT (169 +/- 25 and -187 +/- 15 peq/mm X min, respectively). Because the bicarbonate absorptive capacity of the early PCT under free-flow conditions is 500 peq/mm X min, angiotensin II administration or inhibition affected greater than 60% of proton secretion in this segment. Both agents less markedly affected bicarbonate absorption in the late PCT (+/- 28 peq/mm X min) or chloride absorption (+/- 68-99 peq/mm X min) in both the early and late PCT. Because of its potential for controlling the majority of bicarbonate absorption in the early PCT (hence greater than or equal to 30% of bicarbonate absorption in the entire nephron), angiotensin II may be a powerful physiologic regulator of renal acidification.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry C. A., Cogan M. G. Influence of peritubular protein on solute absorption in the rabbit proximal tubule. A specific effect on NaCl transport. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):506–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI110282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Konnen K. S., Tucker B. J. Angiotensin II effects upon the glomerular microcirculation and ultrafiltration coefficient of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):419–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI108293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II-binding sites in rat and primate isolated renal tubular basolateral membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2007–2014. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Navar L. G., Ploth D. W. Evidence for angiotensin-stimulated proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in normotensive and hypertensive rats: effect of acute administration of captopril. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 May;66(5):541–544. doi: 10.1042/cs0660541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Navar L. G. Tubular transport responses to angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F621–F630. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Young J. A. Dose-dependent stimulation and inhibition of proximal tubular sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jan 17;367(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00581370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Axial heterogeneity of bicarbonate, chloride, and water transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Effects of change in luminal flow rate and of alkalemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1547–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI112747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Observations on the segmentation of the proximal tubule in the rat kidney. Comparison of results from phase contrast, fluorescence and electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Oct;16(3):239–258. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K., Kauffman S., Katz A. I. Angiotensin II binding sites in individual segments of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):315–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI112293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelayo J. C., Blantz R. C. Analysis of renal denervation in the hydropenic rat: interactions with angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 2):F87–F95. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.1.F87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Angiotensin II directly stimulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. U., Goodfriend T. L. Angiotensin and prostaglandin interactions in cultured kidney tubules. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Feb;103(2):255–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Brock T. A. Analysis of angiotensin-stimulated sodium transport in cultured smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Mar;114(3):284–290. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. W., Tucker B. J., Blantz R. C. Glomerular hemodynamics in rats with chronic sodium depletion. Effect of saralasin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):503–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI109488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirthensohn G., Guder W. G. Stimulation of phospholipid turnover by angiotensin II and phenylephrine in proximal convoluted tubules microdissected from mouse nephron. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(1):94–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00581500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. G. Actions of angiotensin on adrenergic nerve endings. Fed Proc. 1978 Feb;37(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



