Abstract
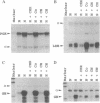
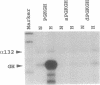
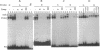
Production of the glycoprotein hormone erythropoietin (Epo) in response to hypoxic stimuli is almost entirely restricted to particular cells within liver and kidney, yet the transcriptional enhancer lying 3' to the Epo gene shows activity inducible by hypoxia after transfection into a wide variety of cultured cells. The implication of this finding is that many cells which do not produce Epo contain a similar, if not identical, oxygen-regulated control system, suggesting that the same system is involved in the regulation of other genes. We report that the human phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and mouse lactate dehydrogenase A genes are induced by hypoxia with characteristics which resemble induction of the Epo gene. In each case expression is induced by cobalt, but not by cyanide, and hypoxic induction is blocked by the protein-synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. We show that the relevant cis-acting control sequences are located in the 5' flanking regions of the two genes, and we define an 18-bp element in the 5' flanking sequence of the phosphoglycerate kinase 1 gene which is both necessary and sufficient for the hypoxic response, and which has sequence and protein-binding similarities to the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 binding site within the Epo 3' enhancer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck I., Ramirez S., Weinmann R., Caro J. Enhancer element at the 3'-flanking region controls transcriptional response to hypoxia in the human erythropoietin gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15563–15566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck I., Weinmann R., Caro J. Characterization of hypoxia-responsive enhancer in the human erythropoietin gene shows presence of hypoxia-inducible 120-Kd nuclear DNA-binding protein in erythropoietin-producing and nonproducing cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 1;82(3):704–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard K. L., Acquaviva A. M., Galson D. L., Bunn H. F. Hypoxic induction of the human erythropoietin gene: cooperation between the promoter and enhancer, each of which contains steroid receptor response elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5373–5385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Li S. S. Nucleotide sequence of the putative regulatory region of mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A gene. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):435–439. doi: 10.1042/bj2350435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. A., Dunning S. P., Bunn H. F. Regulation of the erythropoietin gene: evidence that the oxygen sensor is a heme protein. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1412–1415. doi: 10.1126/science.2849206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. A., Glass G. A., Cunningham J. M., Bunn H. F. The regulated expression of erythropoietin by two human hepatoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hondred D., Hanson A. D. Hypoxically inducible barley lactate dehydrogenase: cDNA cloning and molecular analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7300–7304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kietzmann T., Schmidt H., Probst I., Jungermann K. Modulation of the glucagon-dependent activation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene by oxygen in rat hepatocyte cultures. Evidence for a heme protein as oxygen sensor. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 26;311(3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81113-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kietzmann T., Schmidt H., Unthan-Fechner K., Probst I., Jungermann K. A ferro-heme protein senses oxygen levels, which modulate the glucagon-dependent activation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene in rat hepatocyte cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):792–798. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan A., Curtin P. T. A 24-base-pair sequence 3' to the human erythropoietin gene contains a hypoxia-responsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3928–3932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Shaklee J. B., Whitt G. S. Evolution of a gene. Multiple genes for LDH isozymes provide a model of the evolution of gene structure, function and regulation. Science. 1975 Jul 11;189(4197):102–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mat-Jan F., Alam K. Y., Clark D. P. Mutants of Escherichia coli deficient in the fermentative lactate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):342–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.342-348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell P. H., Pugh C. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Inducible operation of the erythropoietin 3' enhancer in multiple cell lines: evidence for a widespread oxygen-sensing mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Sutherland L. C., Adra C. N., Leclair B., Rudnicki M. A., Jardine K. The mouse Pgk-1 gene promoter contains an upstream activator sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5755–5761. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Tanguay R. L., Steigerwald S. D., Riggs A. D. In vivo footprint and methylation analysis by PCR-aided genomic sequencing: comparison of active and inactive X chromosomal DNA at the CpG island and promoter of human PGK-1. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1277–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. W., Ebert B. L., Ebrahim O., Ratcliffe P. J. Characterisation of functional domains within the mouse erythropoietin 3' enhancer conveying oxygen-regulated responses in different cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 6;1217(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. W., Tan C. C., Jones R. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Functional analysis of an oxygen-regulated transcriptional enhancer lying 3' to the mouse erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10553–10557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe P. J. Molecular biology of erythropoietin. Kidney Int. 1993 Oct;44(4):887–904. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen P. D., Toth S., Willis A., Heath J. K., Smith A. G. Differentiation inhibiting activity is produced in matrix-associated and diffusible forms that are generated by alternate promoter usage. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1105–1114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90387-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renno D. V., Saunders G., Bull A. T., Holt G. Transcript analysis of penicillin genes from Penicillium chrysogenum. Curr Genet. 1992 Jan;21(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00318654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. J., Badiavas E. V., Costa-Giomi P., Weinmann R., Erslev A. J., Caro J. Stimulation of erythropoietin gene transcription during hypoxia and cobalt exposure. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Nejfelt M. K., Chi S. M., Antonarakis S. E. Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3' to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G. L., Wang G. L. A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5447–5454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief F. S., Wilson S. H., Li S. S. Identification of the mouse low-salt-eluting single-stranded DNA-binding protein as a mammalian lactate dehydrogenase-A isoenzyme. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2330913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. Characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and regulation of DNA binding activity by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21513–21518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Semenza G. L. General involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in transcriptional response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A., Gunning P., Hardeman E., Wallace D. C., Kedes L. Coordinate reciprocal trends in glycolytic and mitochondrial transcript accumulations during the in vitro differentiation of human myoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Mar;142(3):566–573. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A. Regulation of glycolytic enzyme RNA transcriptional rates by oxygen availability in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;77(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00230147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfle D., Jungermann K. Long-term effects of physiological oxygen concentrations on glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in hepatocyte cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]