Abstract
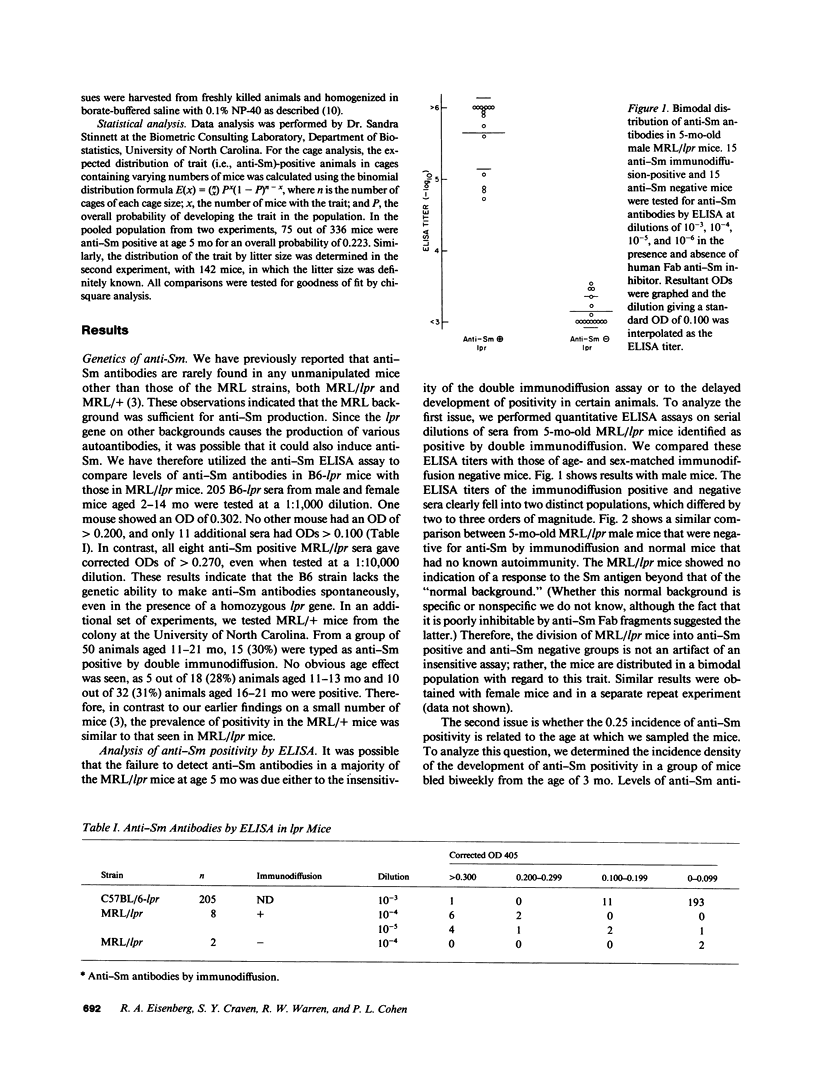
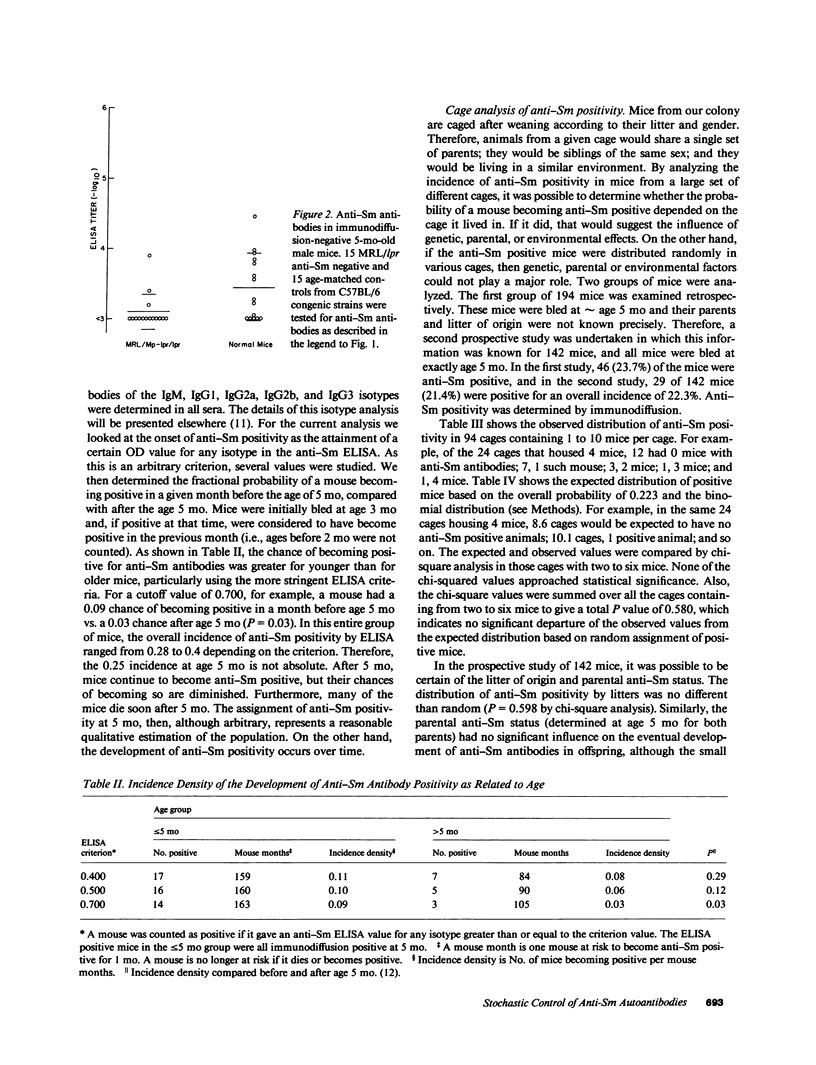
MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr autoimmune mice consistently show an approximately 25% incidence of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker autoantibody anti-Sm. In the present report, we show that the failure to find anti-Sm antibodies in three-quarters of 5-mo-old MRL/lpr mice was not an artifact of an insensitive assay, but rather that the mice fell into two populations as regards their anti-Sm positivity. Based on an extensive analysis of the incidence of anti-Sm positivity in 5-mo-old mice according to their cage of residence, we found no evidence for genetic, environmental, or parental influences on the propensity of an individual animal to become anti-Sm positive. Also, the gender of the mouse, its Sm antigen level, or its length of survival were not related to anti-Sm antibody, nor was the anti-Sm antibody status of either parent. Some animals became anti-Sm positive after 5 mo of age, but this was less likely than becoming positive before 5 mo of age. Finally, a survey of 205 autoimmune C57BL/6-lpr/lpr mice confirmed the uniqueness of the MRL background for this autoantibody response. These results together indicate that the possibility of making anti-Sm antibodies is under genetic control, but that the expression of this capability in an individual animal is governed by stochastic events. We hypothesize further that such random processes may involve the expression of particular immunoglobulin variable-region genes combined with mechanisms of extensive somatic mutation or positive feedback amplification, which would transmute an initial monoclonal response into an eventual polyclonal one.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard N. F., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L. H-2-linked Ir gene control of T cell recognition of the Sm nuclear autoantigen and the aberrant response of autoimmune MRL/Mp-+/+ mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3812–3818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. R., Lockshin M. D., Winfield J. B., Weksler M. E., Imamura M., Winchester R. J., Mellors R. C., Christian C. L. Immunologic observations on 9 sets of twins either concordant or discordant for SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19(3):545–554. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer C. M., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L. Quantitation of the Sm nuclear antigen in tissues and activated lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Mar;28(3):294–299. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Williams D. G., Bovill D., Stocks M. R., Maini R. N. Administration of monoclonal anti-Sm antibody prolongs the survival and renal function of MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):42–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. H., Huppi K., Ruezinsky D., Staudt L., Gerhard W., Weigert M. Inter- and intraclonal diversity in the antibody response to influenza hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):687–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. L., Eisenberg R. A. T cell recognition of the Sm nuclear antigen: induction of T cell proliferative responses in MRL/Mp- +/+ mice. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2142–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. L., Shores E. W., Rapoport R., Caster S., Eisenberg R. A., Pisetsky D. S. Anti-Sm autoantibodies in MRL mice: analysis of precursor frequency. Cell Immunol. 1985 Dec;96(2):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa O., Fournel C., Lotchouang E., Monier J. C., Fontaine M. Specificities of antinuclear antibodies detected in dogs with systemic lupus erythematosus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Oct;7(3-4):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Klapper D. G., Cohen P. L. The polypeptide structure of the Sm and RNP nuclear antigens. Mol Immunol. 1983 Feb;20(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Tan E. M., Dixon F. J. Presence of anti-Sm reactivity in autoimmune mouse strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):582–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Winfield J. B., Cohen P. L. Subclass restriction of anti-Sm antibodies in MRL mice. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2146–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C., Boyd R. E., Ahearn J. M., Arnett F. C., Bias W. B., Provost T. T., Stevens M. B. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of clinico-laboratory features and immunogenetic markers in 150 patients with emphasis on demographic subsets. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 Sep;64(5):285–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munves E. F., Schur P. H. Antibodies to Sm and RNP. Prognosticators of disease involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jul;26(7):848–853. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notman D. D., Kurata N., Tan E. M. Profiles of antinuclear antibodies in systemic rheumatic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Oct;83(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Crews S. T., Douglas R., Sorensen G., Johnson N., Nivera N., Gearhart P. J., Hood L. The generation of diversity in phosphorylcholine-binding antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1984;35:1–37. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60572-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Mimori T., Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The structure of mammalian small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Identification of multiple protein components reactive with anti-(U1)ribonucleoprotein and anti-Sm autoantibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5907–5914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoï D., Freitas A., Holmberg D., Bandeira A., Coutinho A. Immunocompetent autoreactive B lymphocytes are activated cycling cells in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):25–35. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shores E. W., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L. Role of the Sm antigen in the generation of anti-Sm autoantibodies in the SLE-prone MRL mouse. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3662–3667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Brunner C. M., Koffler D. Serologic studies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system dysfunction. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Apr;21(3):289–294. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn D. M., Wolfe J. F., Lindberg D. A., Fristoe F. H., Kingsland L., Sharp G. C. Identification of a clinical subset of systemic lupus erythematosus by antibodies to the SM antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1334–1337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



