Abstract
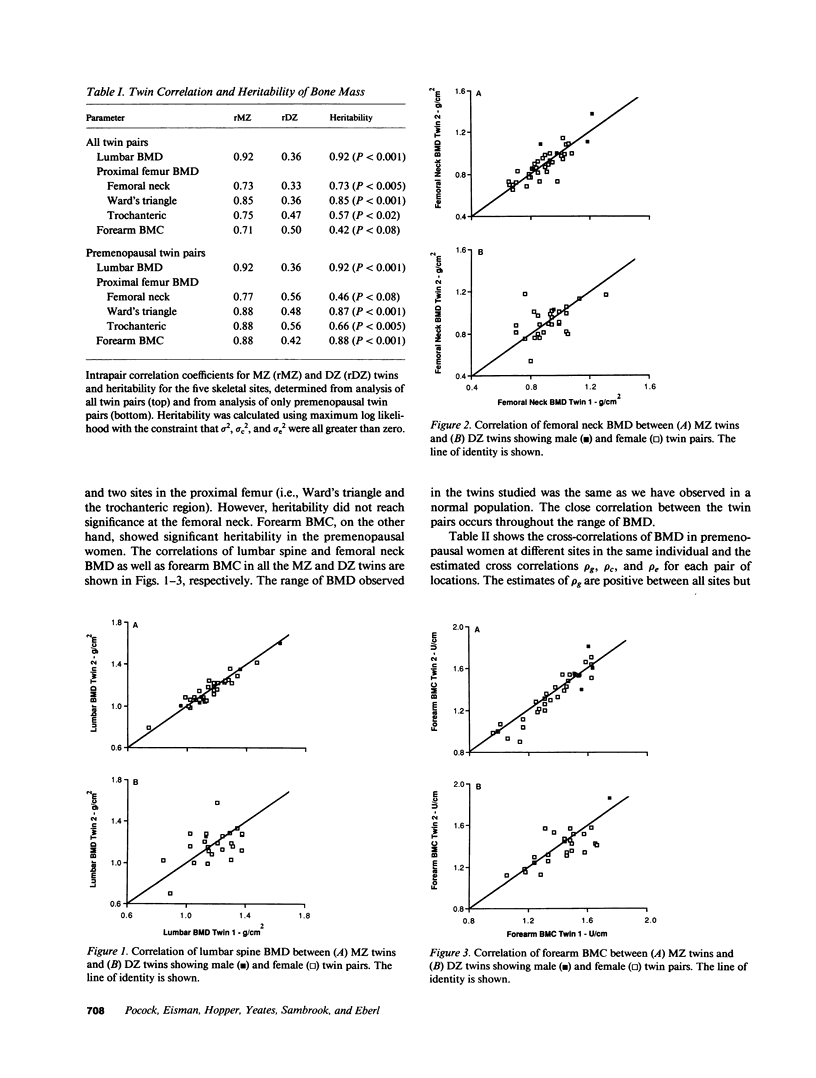
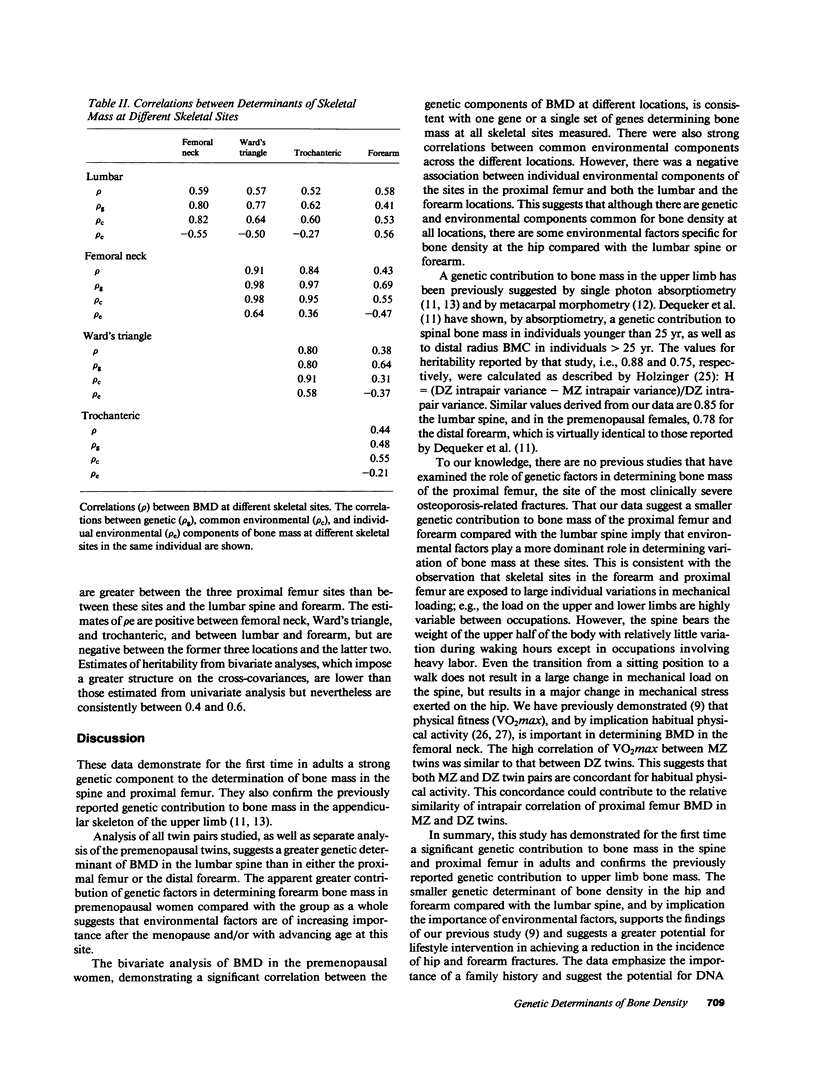
The relative importance of genetic factors in determining bone mass in different parts of the skeleton is poorly understood. Lumbar spine and proximal femur bone mineral density and forearm bone mineral content were measured by photon absorptiometry in 38 monozygotic and 27 dizygotic twin pairs. Bone mineral density was significantly more highly correlated in monozygotic than in dizygotic twins for the spine and proximal femur and in the forearm of premenopausal twin pairs, which is consistent with significant genetic contributions to bone mass at all these sites. The lesser genetic contribution to proximal femur and distal forearm bone mass compared with the spine suggests that environmental factors are of greater importance in the aetiology of osteopenia of the hip and wrist. This is the first demonstration of a genetic contribution to bone mass of the spine and proximal femur in adults and confirms similar findings of the forearm. Furthermore, bivariate analysis suggested that a single gene or set of genes determines bone mass at all sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRAND P. O., RYHMING I. A nomogram for calculation of aerobic capacity (physical fitness) from pulse rate during sub-maximal work. J Appl Physiol. 1954 Sep;7(2):218–221. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1954.7.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloia J. F., Cohn S. H., Vaswani A., Yeh J. K., Yuen K., Ellis K. Risk factors for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Am J Med. 1985 Jan;78(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90468-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer V., Meyer B. M., Keele M. S., Upton S. J., Hagan R. D. Role of exercise in prevention of involutional bone loss. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(6):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotes J. E., Davies C. T., Edholm O. G., Healy M. J., Tanner J. M. Factors relating to the aerobic capacity of 46 healthy British males and females, ages 18 to 28 years. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Oct 7;174(1034):91–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell H. W. Osteoporosis of the slender smoker. Vertebral compression fractures and loss of metacarpal cortex in relation to postmenopausal cigarette smoking and lack of obesity. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Mar;136(3):298–304. doi: 10.1001/archinte.136.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genant H. K., Cann C. E., Ettinger B., Gordan G. S. Quantitative computed tomography of vertebral spongiosa: a sensitive method for detecting early bone loss after oophorectomy. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Nov;97(5):699–705. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-5-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. L., Mathews J. D. Extensions to multivariate normal models for pedigree analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 Oct;46(Pt 4):373–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krølner B., Pors Nielsen S. Bone mineral content of the lumbar spine in normal and osteoporotic women: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Mar;62(3):329–336. doi: 10.1042/cs0620329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krølner B., Pors Nielsen S. Measurement of bone mineral content (BMC) of the lumbar spine, I. Theory and application of a new two-dimensional dual-photon attenuation method. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980;40(7):653–663. doi: 10.1080/00365518009091978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Westlake J., Spence M. A. Extensions to pedigree analysis. III. Variance components by the scoring method. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 May;39(4):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller M., Horsman A., Harvald B., Hauge M., Henningsen K., Nordin B. E. Metacarpal morphometry in monozygotic dizygotic elderly twins. Calcif Tissue Res. 1978 May 26;25(2):197–201. doi: 10.1007/BF02010768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. E., Westlin N. E. Bone density in athletes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971;77:179–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyster N., Morton M., Linnell S. Physical activity and osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1984;16(1):44–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock N. A., Eisman J. A., Yeates M. G., Sambrook P. N., Eberl S. Physical fitness is a major determinant of femoral neck and lumbar spine bone mineral density. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):618–621. doi: 10.1172/JCI112618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock N. A., Eisman J. A., Yeates M. G., Sambrook P. N., Eberl S., Wren B. G. Limitations of forearm bone densitometry as an index of vertebral or femoral neck osteopenia. J Bone Miner Res. 1986 Aug;1(4):369–375. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650010410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs B. L., Wahner H. W., Seeman E., Offord K. P., Dunn W. L., Mazess R. B., Johnson K. A., Melton L. J., 3rd Changes in bone mineral density of the proximal femur and spine with aging. Differences between the postmenopausal and senile osteoporosis syndromes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):716–723. doi: 10.1172/JCI110667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenker R. A. Proceedings: Percentages of cortical and trabecular bone mineral mass in the radius and ulna. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Jun;126(6):1309–1312. doi: 10.2214/ajr.126.6.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Nance W. E., Kang K. W., Christian J. C., Johnston C. C., Jr Genetic factors in determining bone mass. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2800–2808. doi: 10.1172/JCI107476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. C., Whitehead M. I. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. 1982 Aug 28-Sep 4Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 285(6342):585–588. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6342.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. L. Treatment of lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 2;310(5):320–321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402023100514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vernejoul M. C., Bielakoff J., Herve M., Gueris J., Hott M., Modrowski D., Kuntz D., Miravet L., Ryckewaert A. Evidence for defective osteoblastic function. A role for alcohol and tobacco consumption in osteoporosis in middle-aged men. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Oct;(179):107–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



