Abstract
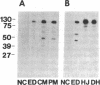
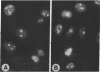
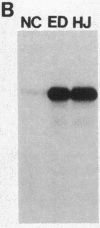
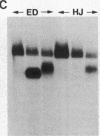
The chromatin-bound enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (ADPRP) is strongly stimulated by DNA with single- or double-stranded breaks, and transfers the ADP-ribose moiety of NAD to nuclear proteins. The activation of ADPRP is important for DNA repair and replication, and also has been postulated to play a role in the pathogenesis of lymphocyte dysfunction associated with chronic inflammatory diseases, and inborn errors of nucleoside metabolism. We have detected high titers of IgG autoantibodies to the ADPRP protein in six patients with rheumatic complaints. No other autoantibodies were detected in any of the six sera. The specificity of the anti-enzyme antibodies was established by (a) immunoprecipitation of ADPRP activity, (b) immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting of both the native 116-kD enzyme and its proteolytic digestion products. ADPRP was purified from human thymus and calf thymus. The autoantibodies reacted equivalently with both enzymes. The anti-ADPRP antibodies had a distinctive immunofluorescent pattern with HEp-2 cells, reacting intensely with nucleoli and metaphase chromosomes, and diffusely with the nucleus. Autoantibodies to ADPRP have not been described previously. The presence of a specific immune response against an enzyme that has been associated with various immunodeficiency syndromes raises intriguing possibilities concerning the relationship between DNA damage, immunodeficiency, and autoimmunity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., de Groot E. R., Feltkamp T. E. Immunology of DNA. III. Crithidia luciliae, a simple substrate for the determination of anti-dsDNA with the immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. C., Gill D. M. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10502–10508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger N. A. Poly(ADP-ribose) in the cellular response to DNA damage. Radiat Res. 1985 Jan;101(1):4–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger N. A., Sikorski G. W., Petzold S. J., Kurohara K. K. Association of poly(adenosine diphosphoribose) synthesis with DNA damage and repair in normal human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1164–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Seto S., Wasson D. B., Carrera C. J. DNA strand breaks, NAD metabolism, and programmed cell death. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jun;164(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Seto S., Wasson D. B. Lymphocyte dysfunction after DNA damage by toxic oxygen species. A model of immunodeficiency. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):746–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. G., Berger N. A. Purification and characterization of human lymphoid poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) polymerase. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5475–5481. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Celis A. Individual nuclei in polykaryons can control cyclin distribution and DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creissen D., Shall S. Regulation of DNA ligase activity by poly(ADP-ribose). Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):271–272. doi: 10.1038/296271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Gilbertson T. A., Chen P. P., Karras J. G., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. The common occurrence of internal image type anti-idiotypic antibodies in rabbits immunized with monoclonal and polyclonal human IgM rheumatoid factors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):570–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Peebles C. L., Gompper P. T., Tan E. M. Identification of Ki (Ku, p70/p80) autoantigens and analysis of anti-Ki autoantibody reactivity. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1648–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A. The lupus autoantigens and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):457–460. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Ueda K. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Smulson M. Purification and characterization of the major nonhistone protein acceptor for poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) in HeLa cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1024–1030. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda Z., Taniguchi T., Shizuta Y. Poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase. Separation and identification of three proteolytic fragments as the substrate-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, and the automodification domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4770–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Kawaminami Y., Miwa M., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. Naturally-occurring antibodies to poly(ADP-ribose) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):175–177. doi: 10.1038/265175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Miwa M., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. Studies on anti-poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):300–306. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Ueda K., Honjo T., Hayaishi O. Enzymic adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of histone and poly adenosine diphosphate ribose synthesis in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3765–3767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Mamrack P. M., Kunkle H. M., Olson M. O., Busch H. Fractionation of nucleoli. Enzymatic and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4716–4721. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Joslin F. G., Tan E. M. Specificity of anti-histone antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):779–782. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scovassi A. I., Izzo R., Franchi E., Bertazzoni U. Structural analysis of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in higher and lower eukaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;159(1):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto S., Carrera C. J., Kubota M., Wasson D. B., Carson D. A. Mechanism of deoxyadenosine and 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine toxicity to nondividing human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):377–383. doi: 10.1172/JCI111710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore C. J., Davies M. I., Goodwin P. M., Halldorsson H., Lewis P. J., Shall S., Zia'ee A. A. The involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in the degradation of NAD caused by gamma-radiation and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., Berger N. A. Unique acceptors for poly(ADP-ribose) in resting, proliferating and DNA-damaged human lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 20;740(1):8–18. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara K., Hashida T., Yoshihara H., Tanaka Y., Ohgushi H. Enzyme-bound early product of purified poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 24;78(4):1281–1288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91431-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara K., Itaya A., Tanaka Y., Ohashi Y., Ito K., Teraoka H., Tsukada K., Matsukage A., Kamiya T. Inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha, DNA polymerase beta, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, and DNA ligase II by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]