Abstract
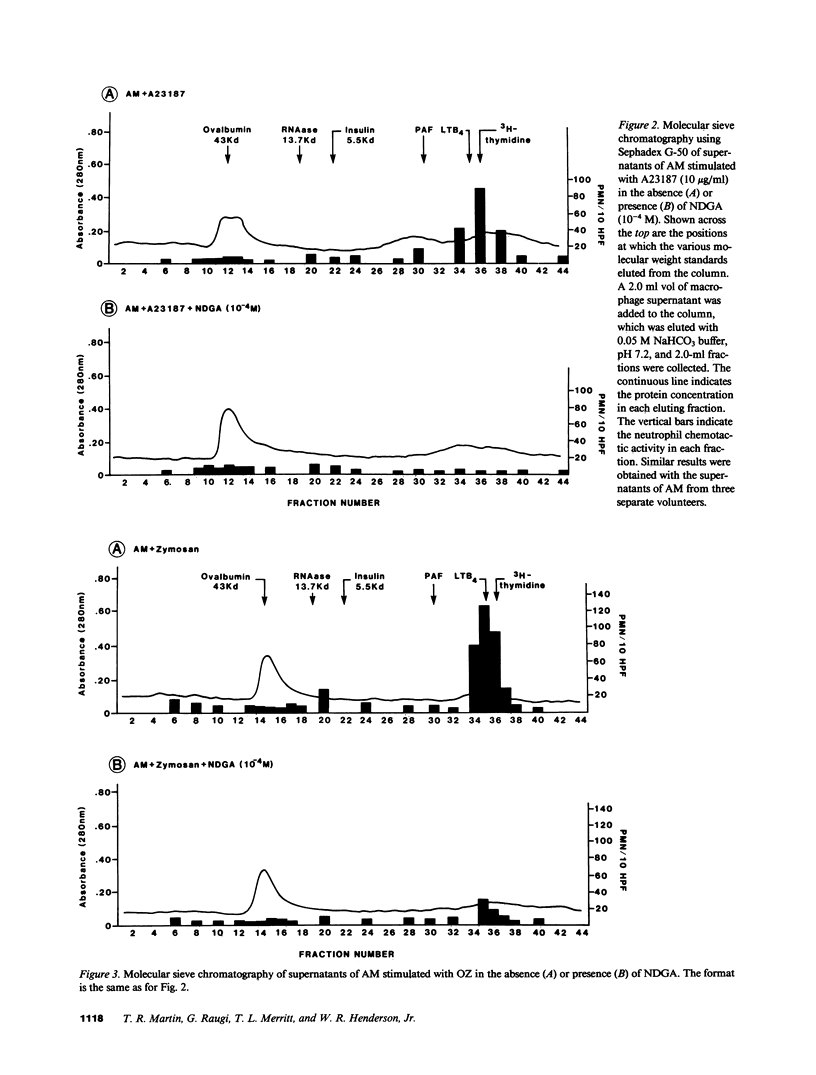
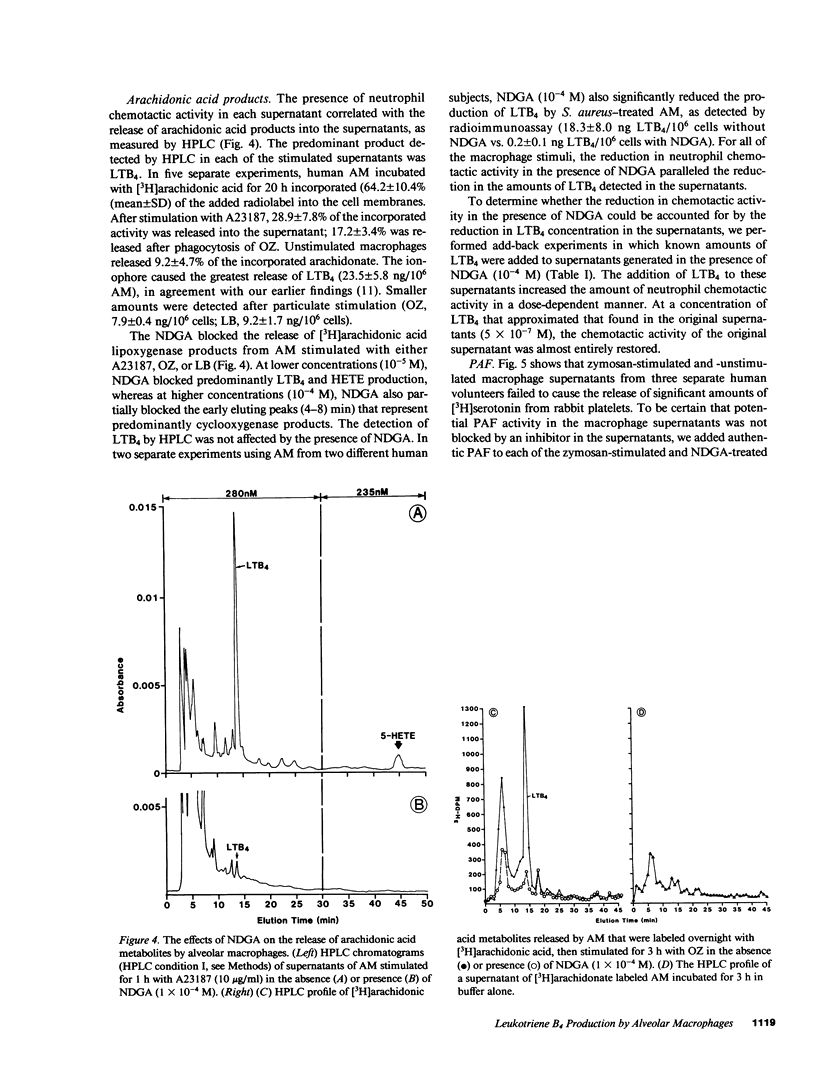
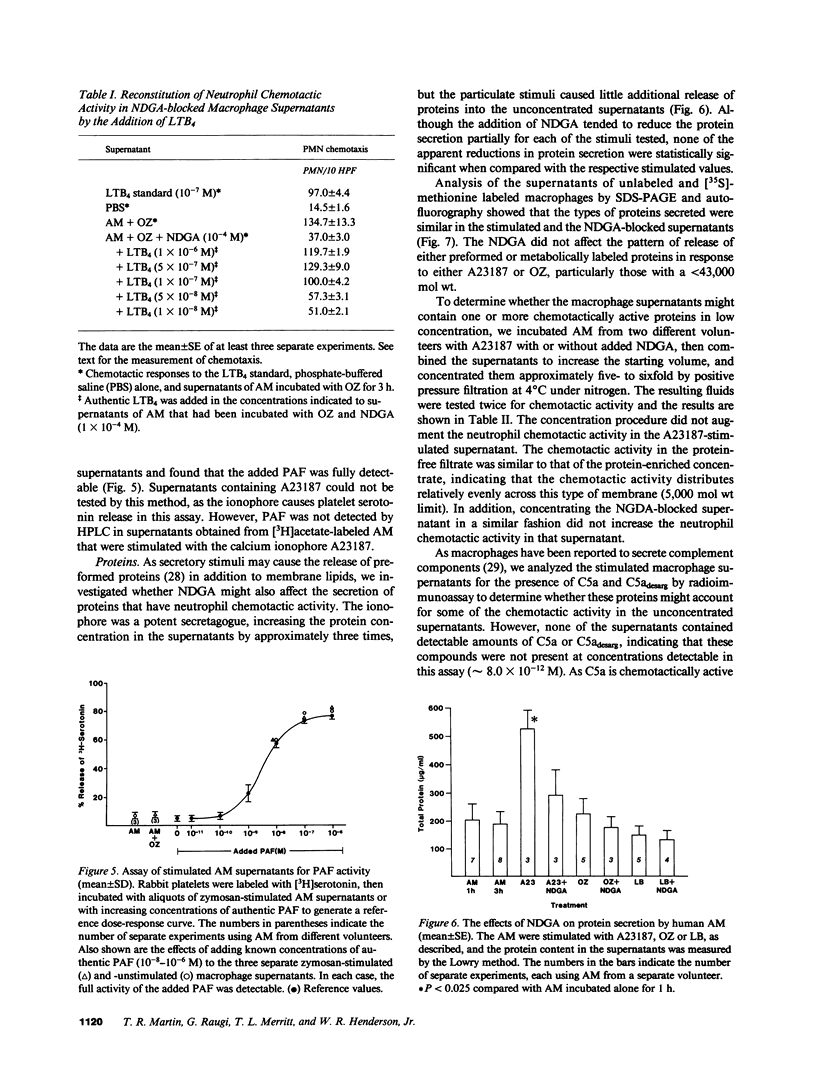
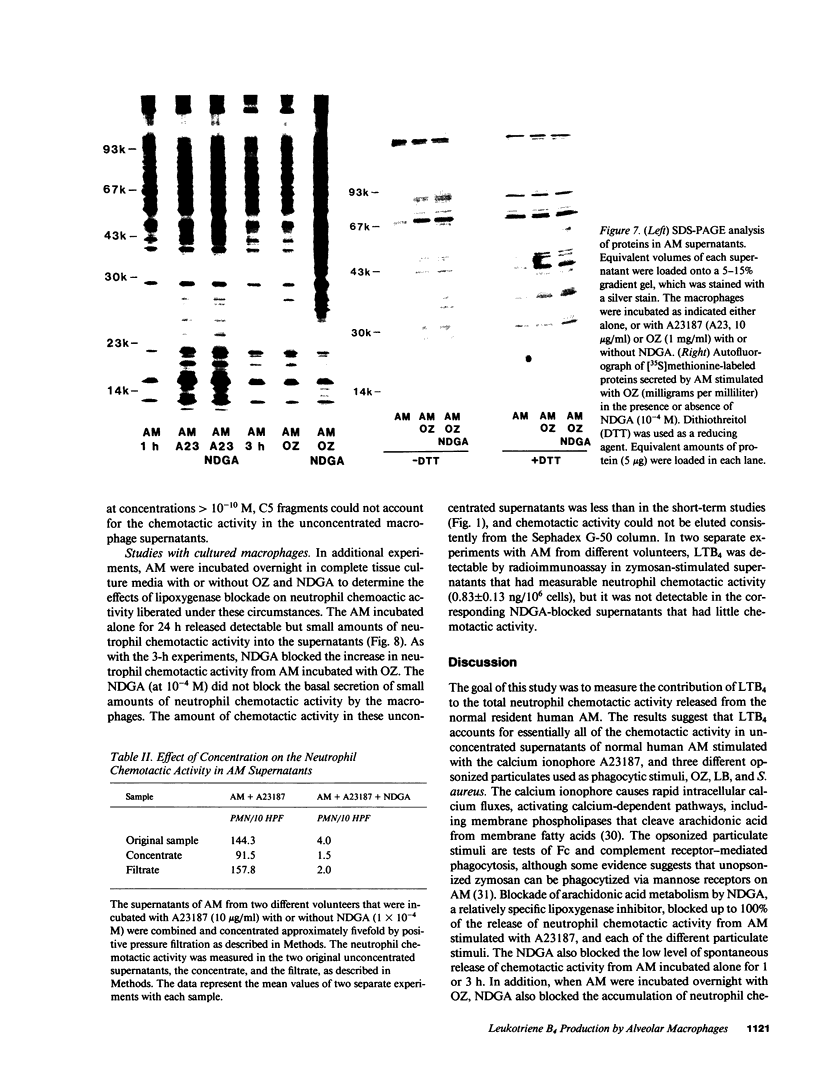
Human alveolar macrophages release chemotactic activity for neutrophils, providing a role for alveolar macrophages in regulating inflammation in the lung. As alveolar macrophages produce large amounts of leukotriene B4 (LTB4), a chemotactically active lipoxygenase product of arachidonic acid, we investigated the contribution of LTB4 to the total neutrophil chemotactic activity produced by these cells. Normal human alveolar macrophages were recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage from healthy volunteers and incubated either with the calcium ionophore A23187 for 1 h, or with opsonized zymosan particles or latex beads for 3 h. Nordihydroguaretic acid (NDGA), a relatively specific lipoxygenase inhibitor, blocked the release of neutrophil chemotactic activity after all three stimuli in a dose-dependent manner. This correlated with blockade of LTB4 production as measured by high performance liquid chromatography using freshly isolated alveolar macrophages, as well as blockade of [3H]LTB4 production by macrophages prelabeled with [3H]arachidonate. Molecular sieve chromatography using Sephadex G-50 confirmed that essentially all of the chemotactic activity in the stimulated macrophage supernatants co-eluted with authentic [3H]LTB4, and that NDGA completely blocked the chemotactic activity in the eluting fractions. Readdition of authentic LTB4 (1 X 10(-7) M) to the NDGA-blocked macrophage supernatants restored the chemotactic activity in the supernatants. The macrophage supernatants did not contain platelet-activating factor-like activity, as measured by the stimulation of [3H]serotonin release from rabbit platelets, and by high performance liquid chromatography. NDGA did not change the protein-secretion profiles of fresh alveolar macrophages, or of macrophages prelabeled with [35S]methionine. The complement (C) components C5adesarg were not detected in any of the supernatants by radioimmunoassay. Concentration of the supernatants by positive pressure filtration (5,000-D membrane) did not augment chemotactic activity in the stimulated supernatants or uncover chemotactic activity in the NDGA-blocked supernatants. As with the 3-h studies, when alveolar macrophages were incubated overnight with opsonized zymosan, all of the increase in chemotactic activity could also be blocked by NDGA. These data indicate that LTB4 is the predominant neutrophil chemotactic factor secreted by the normal resident human alveolar macrophage in response to two major types of stimuli, calcium fluxes across the cell membrane and the phagocytosis of opsonized particulates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert D. H., Snyder F. Biosynthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet-activating factor) from 1-alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine by rat alveolar macrophages. Phospholipase A2 and acetyltransferase activities during phagocytosis and ionophore stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert D. H., Snyder F. Release of arachidonic acid from 1-alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, a precursor of platelet-activating factor, in rat alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 24;796(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoux B., Duval D., Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) from alveolar macrophages by the calcium ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;10(6):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Snyder F. Improved high-performance liquid chromatographic method for isolation of platelet-activating factor from other phospholipids. J Chromatogr. 1983 Apr 8;273(2):415–420. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80963-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark P. O., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Physical and chemical properties of platelet-activating factor obtained from human neutrophils and monocytes and rabbit neutrophils and basophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 21;628(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Goodwin R. H., Jr, Leonard E. J. A 48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fels A. O., Pawlowski N. A., Cramer E. B., King T. K., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Human alveolar macrophages produce leukotriene B4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7866–7870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hunninghake G. W., Zimmerman R. L., Crystal R. G. Regulation of the release of alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Apr;121(4):723–733. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.4.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Derian C. K., Tauber A. I., Valone F. H. Novel effects of 1-O-hexadecyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorycholine mediators on human leukocyte function: delineation of the specific roles of the acyl substituents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 16;94(3):881–888. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Jr Eicosanoids and lung inflammation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1176–1185. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Klebanoff S. J. Leukotriene production and inactivation by normal, chronic granulomatous disease and myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13522–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Activation and desensitization of platelets by platelet-activating factor (PAF) derived from IgE-sensitized basophils. I. Characteristics of the secretory response. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):937–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Release of vasoactive amines from rabbit platelets induced by sensitized mononuclear leukocytes and antigen. J Exp Med. 1970 Feb;131(2):287–306. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Microfilaments and microtubules in calcium ionophore-induced secretion of lysosomal enzymes from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):769–781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Fales H. M., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Stimuli and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI109878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Immunologic reactivity of the lung: the in vivo and in vitro generation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):15–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. M., Mott G. E., Hoppens C., McManus L. M., Weintraub S. T., Ludwig J. C., Pinckard R. N. High performance liquid chromatography of platelet-activating factors. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jul;25(7):753–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmierowski J. A., Gallin J. I., Reynolds H. Y. Mechanism for the inflammatory response in primate lungs. Demonstration and partial characterization of an alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor with preferential activity for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. The biologically active leukotrienes. Biosynthesis, metabolism, receptors, functions, and pharmacology. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):889–897. doi: 10.1172/JCI111312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis T. C., Stahl W. L. A rapid, flexible method for biochemical assays using a microtiter plate reader and a microcomputer. Application for assays of protein, Na,K-ATPase and K-p-nitrophenylphosphatase. Int J Biomed Comput. 1986 May;18(3-4):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(86)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotner G. Z., Lynch J. M., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. Human neutrophil-derived platelet activating factor. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):676–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Altman L. C., Albert R. K., Henderson W. R. Leukotriene B4 production by the human alveolar macrophage: a potential mechanism for amplifying inflammation in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):106–111. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Stossel T. P., Vaughan M. Lipids of alveolar macrophages, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and their phagocytic vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2399–2407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensing H., Czarnetzki B. M. Leukotriene B4 induces in vitro fibroblast chemotaxis. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):9–12. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12258678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., Sha'afi R. I. Mechanism of action of leukotriene B4: intracellular calcium redistribution in rabbit neutrophils. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jan;118(1):13–18. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Arachidonic acid induced degranulation of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91678-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Rossing T. H., Boerth L. W., Lee T. H. Isolation and partial characterization of a human alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1230–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI111820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokach J., Hayes E. C., Girard Y., Lombardo D. L., Maycock A. L., Rosenthal A. S., Young R. N., Zamboni R., Zweerink H. J. The development of sensitive and specific radioimmunoassays for leukotrienes. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1984 Jan;13(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(84)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson W. F., Parker C. W. Monohydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) induce degranulation of human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2100–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Mason R. J., Smith A. L. Lipid peroxidation by human blood phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):638–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI107801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Franklin M., Sun F. F., Goetzl E. J. Alveolar macrophage lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid: isolation and recognition as the predominant constituents of the neutrophil chemotactic activity elaborated by alveolar macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. A. A macrophage receptor for (mannose/glucosamine)-glycoproteins of potential importance in phagocytic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):737–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]