Abstract
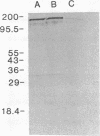
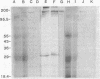
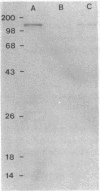
Entamoeba histolytica adheres to human colonic mucus, colonic epithelial cells, and other target cells via a galactose (Gal) or N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc) inhibitable surface lectin. Blockade of this adherence lectin with Gal or GalNAc in vitro prevents amebic killing of target cells. We have identified and purified the adherence lectin by two methods: affinity columns derivatized with galactose monomers or galactose terminal glycoproteins, and affinity columns and immunoblots prepared with monoclonal antibodies that inhibit amebic adherence. By both methods the adherence lectin was identified as a 170-kD secreted and membrane-bound amebic protein. The surface location of the lectin was confirmed by indirect immunofluorescence. Purified lectin competitively inhibited amebic adherence to target cells by binding to receptors on the target Chinese hamster ovary cells in a Gal-inhibitable manner.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo R., Orozco E. Localization and identification of an Entamoeba histolytica adhesin. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Mar;23(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Harford J. Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:531–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structure of the complex oligosaccharides of fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):789–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H. Soluble lectins: a new class of extracellular proteins. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1259–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.6367039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha R., Mirelman D. Adherence and ingestion of Escherichia coli serotype 055 by trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):882–887. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.882-887.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Meerovitch E. Entamoeba histolytica: early progressive pathology in the cecum of the gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):283–291. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournet B., Montreuil J., Strecker G., Dorland L., Haverkamp J., Vliegenthart F. G., Binette J. P., Schmid K. Determination of the primary structures of 16 asialo-carbohydrate units derived from human plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein by 360-MHZ 1H NMR spectroscopy and permethylation analysis. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5206–5214. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Effect of immunosuppression on the size and metastasis of amoebic liver abscesses in hamsters. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. E., Tite J. P., Janeway C. A., Jr The immunobiology of T cell responses to Mls-locus-disparate stimulator cells. III. Helper and cytolytic functions of cloned, Mls-reactive T cell lines. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Antibody response in intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Jan;19(1):57–62. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P., Lark D., Normark S., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. Mannose-sensitive and Gal-Gal binding Escherichia coli pili from recombinant strains. Chemical, functional, and serological properties. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1713–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hanley P., Low D., Romero I., Lark D., Vosti K., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. Gal-Gal binding and hemolysin phenotypes and genotypes associated with uropathogenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 15;313(7):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508153130704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Zamacona G., Sepúlveda B., Capín N. R. Cell-mediated immunity in patients with amebic abscess of the liver. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Joyce M. P., Broman J., Smith R. D., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Recognition of the galactose- or N-acetylgalactosamine-binding lectin of Entamoeba histolytica by human immune sera. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2327–2331. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2327-2331.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K. Oligosaccharide structures of isolated human colonic mucin species. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15510–15515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Murphy C. F., Salata R. A., Guerrant R. L., Hewlett E. L. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. I. Partial purification and relation to amoebic virulence in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):804–815. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I. Pathogenesis of disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica: studies of adherence, secreted toxins, and contact-dependent cytolysis. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):247–260. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Petri W. A., Murphy C. F., Smith R. D. Production of mouse monoclonal antibodies which inhibit in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. II. Mitogenic activity for human lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):816–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. Review of the human immune mechanisms directed against Entamoeba histolytica. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):261–272. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Ravdin J. I. The interaction of human neutrophils and Entamoeba histolytica increases cytopathogenicity for liver cell monolayers. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):19–26. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney S., Chakravarti R. N., Jain P., Vinayak V. K. Immunogenicity of axenic Entamoeba histolytica antigen and its fractions. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Haq A., Ahmad S., Lederer E. Vaccination of rabbits against Entamoeba histolytica with aqueous suspensions of trehalose-dimycolate as the adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):634–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.634-637.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Haywood P. L., Barondes S. H. Endogenous cell surface lectin in Dictyostelium: quantitation, elution by sugar, and elicitation by divalent immunoglobulin. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):682–690. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinayak V. K., Sawhney S., Jain P., Chakravarti R. N. Protective effects of crude and chromatographic fractions of axenic Entamoeba histolytica in guinea-pigs. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):483–487. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]