Abstract
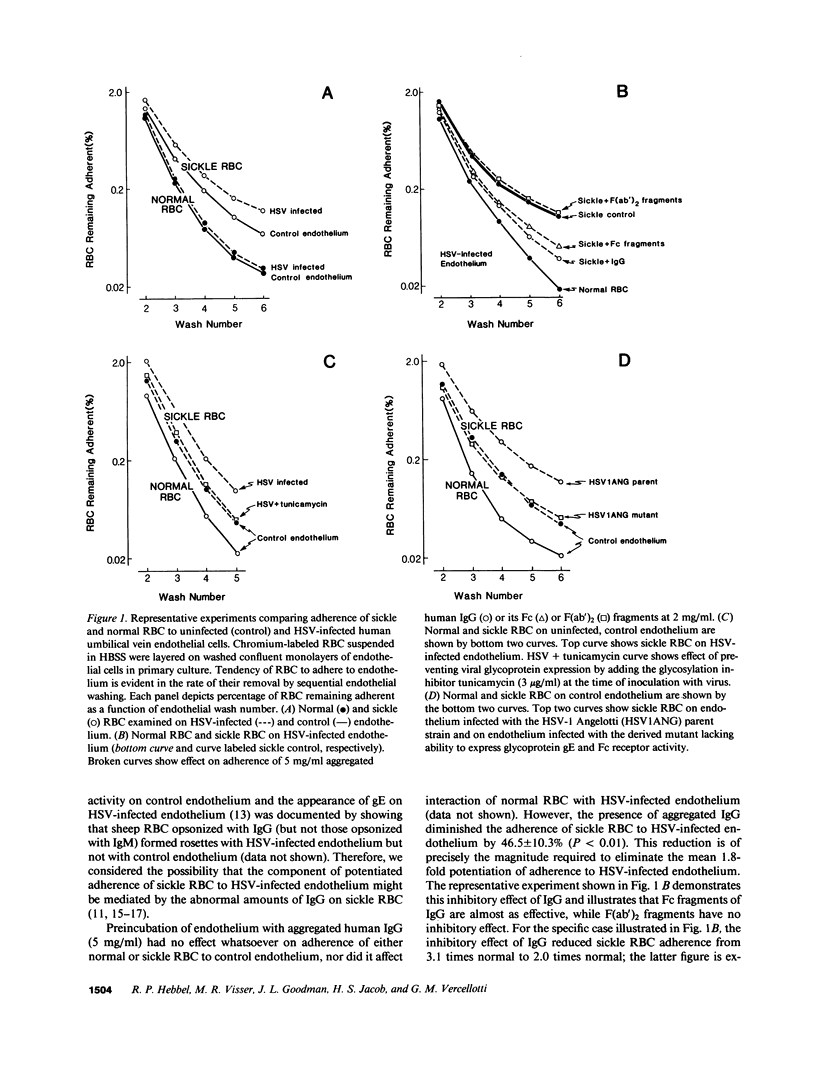
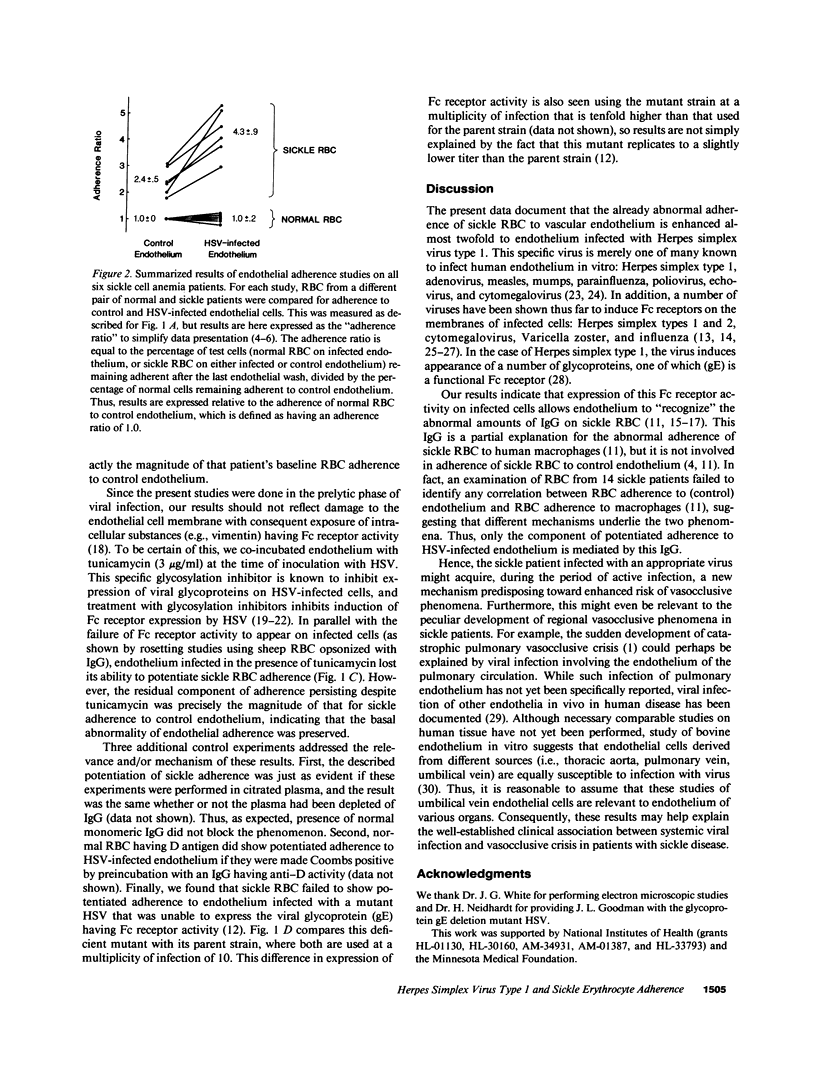
Systemic viral infection is a known precipitant of vasocclusive crisis in sickle patients, but the mechanism underlying this clinical observation is unknown. In the present studies, human umbilical vein endothelial cells were infected with Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV) to model systemic viral disease. The already abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to control endothelium is enhanced 1.8 +/- 0.4-fold to HSV-infected endothelium (P less than 0.001). This component of potentiated adherence is eliminated by maneuvers that block Fc receptors, it is prevented by tunicamycin, and it is not seen using a mutant HSV that is unable to express the Fc receptor glycoprotein. Thus, the incremental adherence seen here occurs due to expression of Fc receptor activity on HSV-infected endothelium and the consequent recognition of abnormal amounts of IgG on sickle erythrocytes. We conclude that systemic viral infection potentially can induce a novel mechanism for enhancement of erythrocyte adherence to endothelium and that this may increase the likelihood of vasocclusion during viral infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burns E. R., Wilkinson W. H., Nagel R. L. Adherence properties of sickle erythrocytes in dynamic flow systems. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jun;105(6):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cines D. B., Lyss A. P., Bina M., Corkey R., Kefalides N. A., Friedman H. M. Fc and C3 receptors induced by herpes simplex virus on cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):123–128. doi: 10.1172/JCI110422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J., Yee C., Nakamura Y., Rabson A. Characteristics of the Fc receptor induced by herpes simplex virus. Intervirology. 1978;10(1):32–39. doi: 10.1159/000148965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Macarak E. J., MacGregor R. R., Wolfe J., Kefalides N. A. Virus infection of endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):266–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Wolfe J., Kefalides N. A., Macarak E. J. Susceptibility of endothelial cells derived from different blood vessels to common viruses. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Jul;22(7):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF02623529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B. Excessive binding of natural anti-alpha-galactosyl immunoglobin G to sickle erythrocytes may contribute to extravascular cell destruction. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):27–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI112286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. A., Rehn M. M., Kalra V. K. Cell-bound autologous immunoglobulin in erythrocyte subpopulations from patients with sickle cell disease. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1127–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Starkebaum G. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Fc-mediated binding of IgG to vimentin-type intermediate filaments in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3103–3107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Boogaerts M. A., Eaton J. W., Steinberg M. H. Erythrocyte adherence to endothelium in sickle-cell anemia. A possible determinant of disease severity. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 1;302(18):992–995. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005013021803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Miller W. J. Phagocytosis of sickle erythrocytes: immunologic and oxidative determinants of hemolytic anemia. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):733–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Moldow C. F., Steinberg M. H. Modulation of erythrocyte-endothelial interactions and the vasocclusive severity of sickling disorders. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):947–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Jacob H. S., White J. G., Eaton J. W. Abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to cultured vascular endothelium: possible mechanism for microvascular occlusion in sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):154–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):956–957. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R., Rubin R., Wise G., Warren R. Adhesion of normal and sickle erythrocytes to endothelial monolayer cultures. Blood. 1979 Oct;54(4):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Peitchel R., Goldman J. N., Goldman M. An IgG-Fc receptor induced in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucukcelebi A., Barmatoski S. P., Barnhart M. I. Interactions between vessel wall and perfused sickled erythrocytes: preliminary observations. Scan Electron Microsc. 1980;(3):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTaggart S. P., Burns W. H., White D. O., Jackson D. C. Fc receptors induced by herpes simplex virus. I. Biologic and biochemical properties. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Evans E. Adherence of sickle erythrocytes to vascular endothelial cells: requirement for both cell membrane changes and plasma factors. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt H., Schröder C. H., Kaerner H. C. Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein E is not indispensable for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):600–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.600-603.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and their expression on the cell surface. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.395-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Shigeta S. Appearance of immunoglobulin G Fc receptor in cultured human cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein gE of herpes simplex virus type 1: effects of anti-gE on virion infectivity and on virus-induced fc-binding receptors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.129-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petz L. D., Yam P., Wilkinson L., Garratty G., Lubin B., Mentzer W. Increased IgG molecules bound to the surface of red blood cells of patients with sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Ruan J. W. Fc and C3b receptors on pulmonary endothelial cells: induction by injury. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):557–558. doi: 10.1126/science.6270789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe J. H., Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Timbury M. C., Macnab J. C., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Genetic and biochemical studies with herpesvirus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):717–730. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


