Abstract
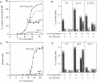
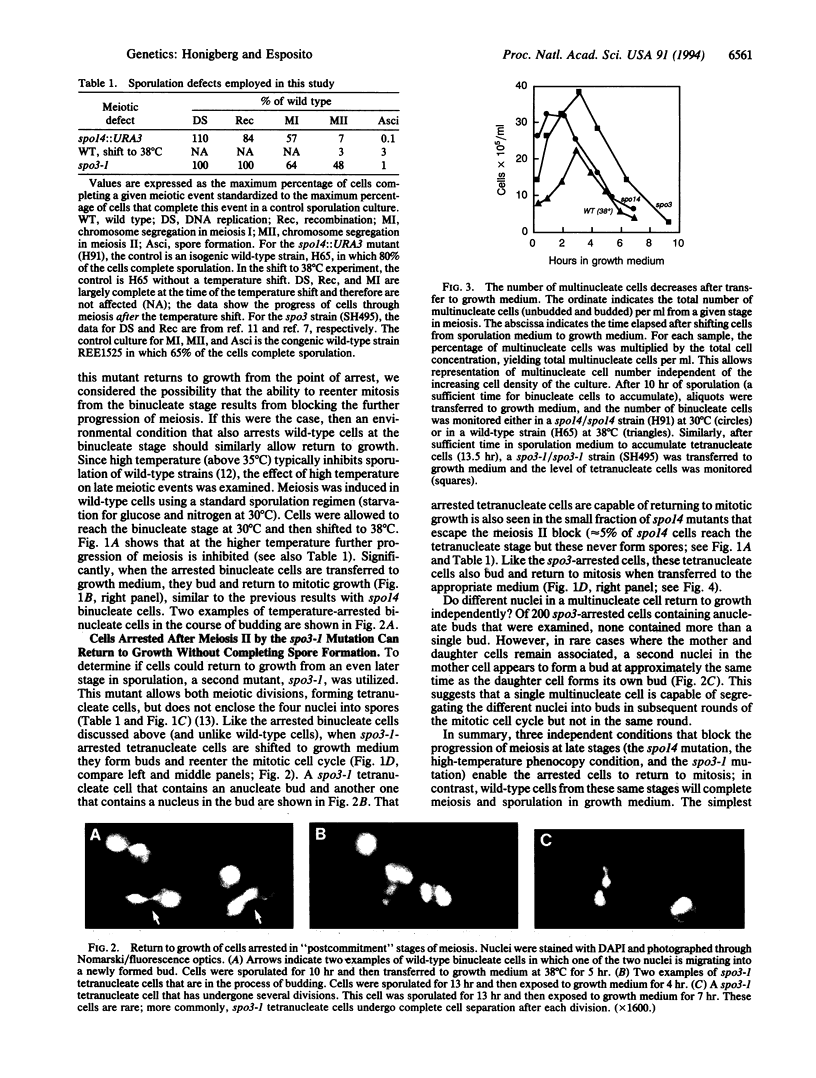
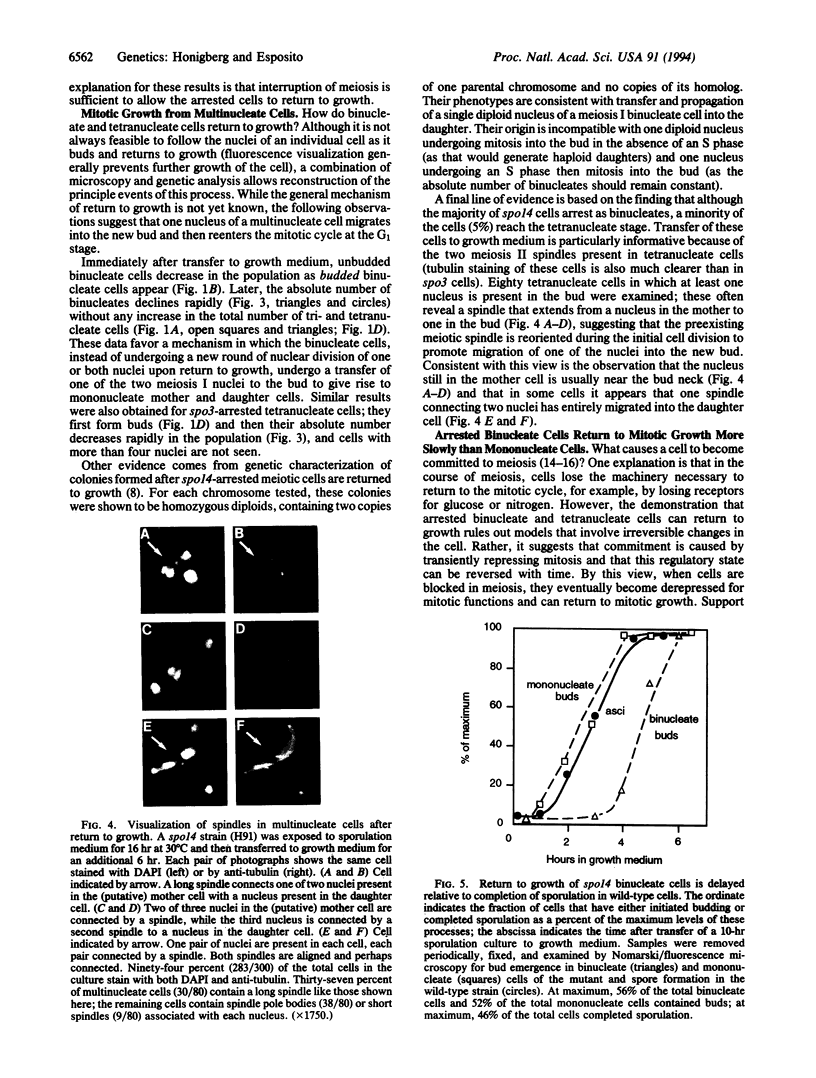
When yeast from the early stages of meiosis are transferred from sporulation to growth medium, they can reenter the mitotic cell cycle directly. In contrast, cells from later stages of meiosis (after the initiation of the first nuclear division) will complete meiosis and sporulation despite the shift to growth medium, a phenomenon known as "commitment to meiosis." This study reports the surprising finding that when the normal progression of meiosis is arrested, cells from later stages of meiosis can return to growth. Cells were arrested after the first or second meiotic division by three independent means: the spo14 mutation, the spo3-1 mutation, and a high-temperature arrest of wild-type cells. In every case, the arrested cells were able to form buds after transfer to growth medium. These cells, however, experienced a delay upon return to growth relative to uncommitted cells. We propose that the commitment phenomenon results from a transient delay of mitotic growth, which occurs specifically during meiosis, and that commitment does not involve an irreversible inhibition of mitosis as previously thought.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Reversible pachytene arrest of Saccharomyces cerevisiae at elevated temperature. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00384382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. Genes controlling meiosis and spore formation in yeast. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):215–225. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Genetic recombination and commitment to meiosis in Saccharomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3172–3176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANESAN A. T., HOLTER H., ROBERTS C. Some observations on sporulation in Saccharomyces. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg Chim. 1958;31(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. The generation of diversity and pattern in animal development. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90465-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg S. M., Conicella C., Espositio R. E. Commitment to meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: involvement of the SPO14 gene. Genetics. 1992 Apr;130(4):703–716. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter K. J., Eipel H. E. Microbial determinations by flow cytometry. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Aug;113(2):369–375. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormanec J., Schaaff-Gerstenschläger I., Zimmermann F. K., Perecko D., Küntzel H. Nuclear migration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is controlled by the highly repetitive 313 kDa NUM1 protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):277–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00290678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Y., Yeh E., Hays T., Bloom K. Disruption of mitotic spindle orientation in a yeast dynein mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10096–10100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Aberrant nuclear behavior at meiosis and anucleate spore formation by sporulation-deficient (SPO) mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jan;83(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90700-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., ROMAN H. Evidence for two types of allelic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Feb;48:255–261. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Piñon R., Salts Y. Sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: premeiotic DNA synthesis, readiness and commitment. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]