Abstract
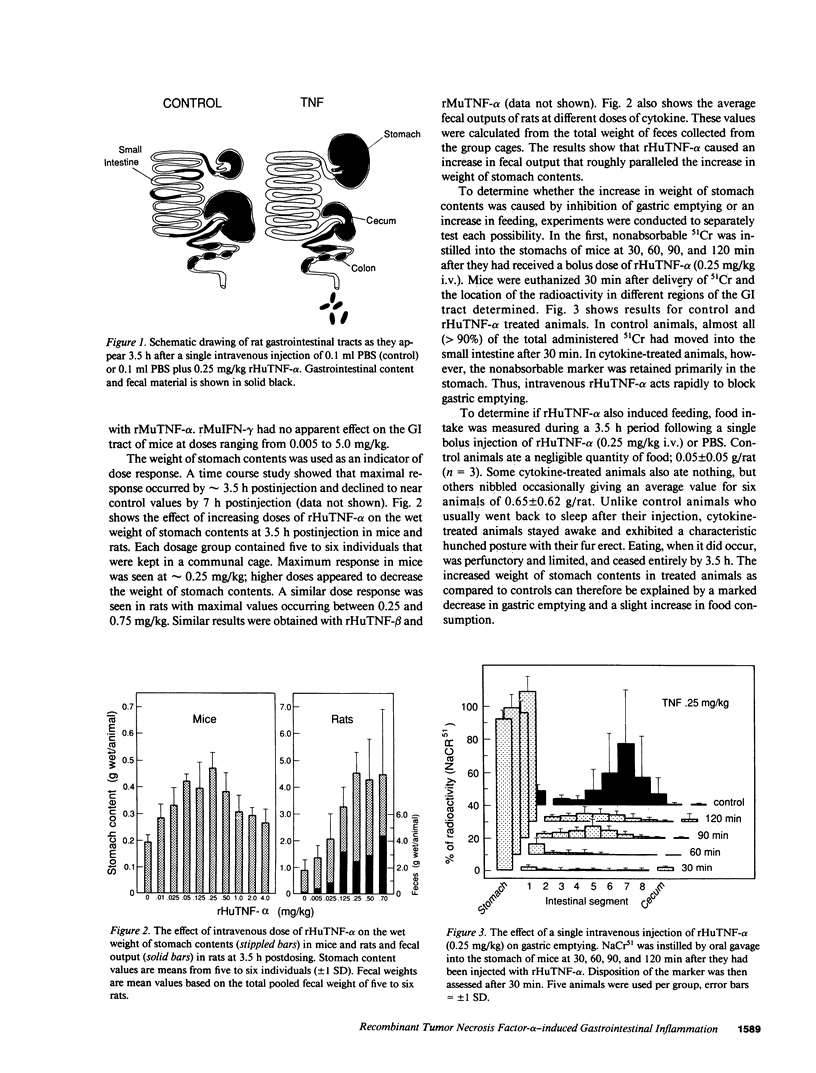
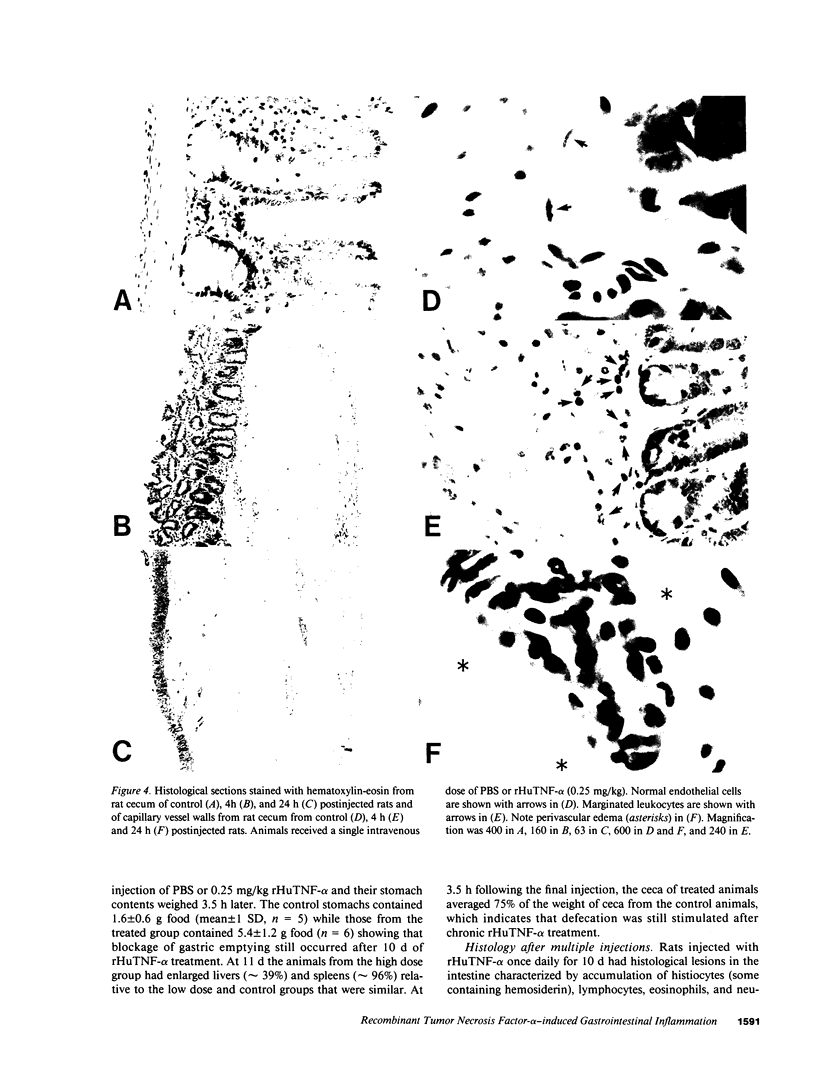
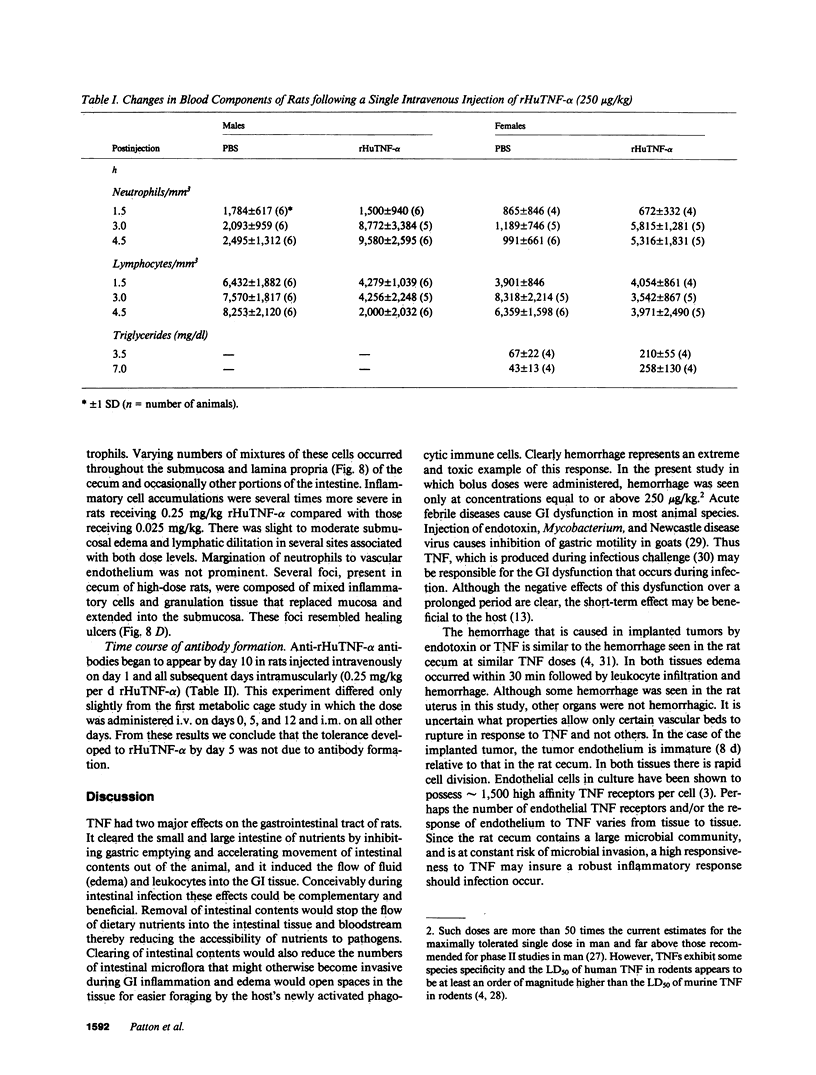
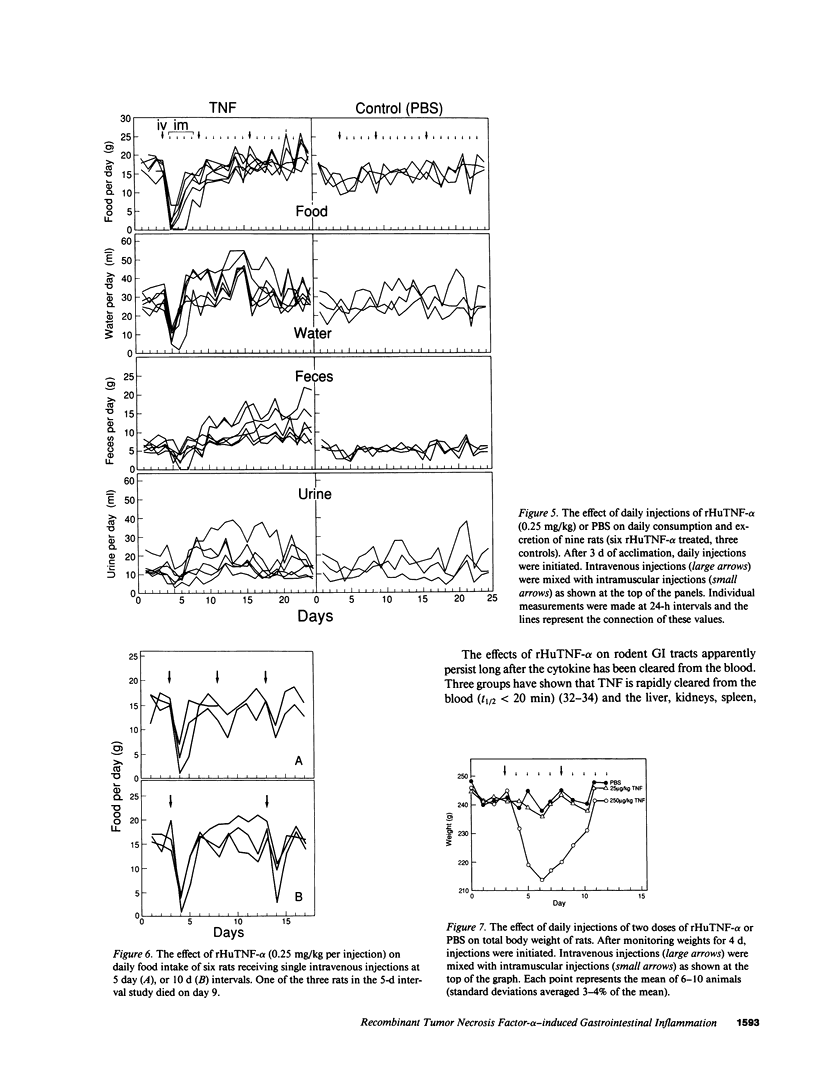
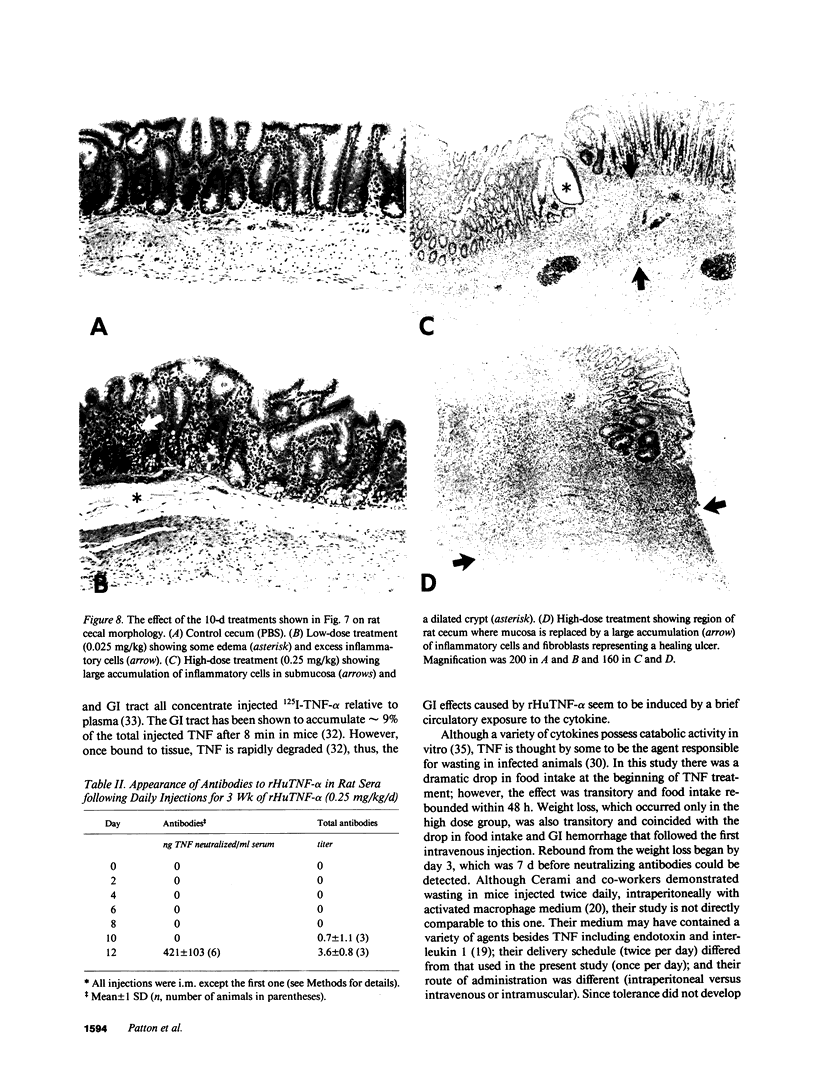
Treatment of healthy rats and mice with a single intravenous injection of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha (rHuTNF-alpha) caused a dose-dependent gastrointestinal inflammation. Within 30 min gastric emptying was blocked and tissue edema occurred in the small and large intestine. In the cecum hemorrhage occurred after 4 h at doses greater than or equal to 250 micrograms/kg. The cecum exhibited an acute inflammatory response following rHuTNF-alpha treatment similar to that seen in tumor necrosis at the same dose. The vascular endothelium became swollen, increased numbers of neutrophils and other leukocytes attached to and penetrated the endothelium, and finally hemorrhage occurred. Treatment of rats with daily injections of rHuTNF-alpha (250 micrograms/kg per d) for 3 wk failed to produce cachexia. Within 24-48 h rats became resistant to the hemorrhagic effect of rHuTNF-alpha, however, the cytokine still caused a transitory block of gastric emptying after 10 d of treatment. Treatment at 5- or 10-d intervals produced results similar to the initial injection. These results suggest that maximum hemorrhagic response will occur when rHuTNF-alpha is administered at intervals of 5-10 d rather than daily.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Ikeda Y., Le Trang N., Hotez P. J., Beutler B. Weight loss associated with an endotoxin-induced mediator from peritoneal macrophages: the role of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor). Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick D. A., Gifford G. E. Pharmacokinetics of murine tumor necrosis factor. J Immunopharmacol. 1986;8(1):89–97. doi: 10.3109/08923978609031087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg N., Joh K., Westphal O., Mittermayer C., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Haemorrhagic tumour necrosis following endotoxin administration. I. Communication: morphological investigation on endotoxin-induced necrosis of the methylcholanthrene (Meth A) tumour in the mouse. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1984;403(4):377–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00737287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung K. P., Leung S. W., Ha D. K., Ng S. W., Choy Y. M., Lee C. Y. Effect of tumour necrosis factor on growth of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 1985 Jul;27(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(85)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Aggarwal B. B., Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Nedwin G. E., Palladino M. A., Patton J. S., Pennica D., Shepard H. M., Sugarman B. J. Tumor necrosis factors: gene structure and biological activities. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):597–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):513–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. M., Carver M. E. Serum-free in vitro bioassay for the detection of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau A. S., Hannigan G. E., Freedman M. H., Williams B. R. Regulation of interferon receptor expression in human blood lymphocytes in vitro and during interferon therapy. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1632–1638. doi: 10.1172/JCI112480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. O., Kluger M. J., Vander A. J. Suppression of food intake during infection: is interleukin-1 involved? Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Dec;42(6):1179–1182. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.6.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J., Murray A. Suppression of infection by famine and its activation by refeeding--a paradox? Perspect Biol Med. 1977 Summer;20(4):471–483. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1977.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. J., Murray A. B. Anorexia of infection as a mechanism of host defense. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Mar;32(3):593–596. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. J., Murray A. B. Starvation suppression and refeeding activation of infection. An ecological necessity? Lancet. 1977 Jan 15;1(8003):123–125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91710-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino M. A., Jr, Shalaby M. R., Kramer S. M., Ferraiolo B. L., Baughman R. A., Deleo A. B., Crase D., Marafino B., Aggarwal B. B., Figari I. S. Characterization of the antitumor activities of human tumor necrosis factor-alpha and the comparison with other cytokines: induction of tumor-specific immunity. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):4023–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Shepard H. M., Wilking H., Lewis G., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Gavin L. A., Grunfeld C. Interferons and tumor necrosis factors have similar catabolic effects on 3T3 L1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8313–8317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Stanness K. A., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4548–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Knost J. A., Fein S., Abrams P. G., Foon K. A., Ochs J. J., Schoenberger C., Maluish A. E., Oldham R. K. A multiple-dose phase I trial of recombinant leukocyte A interferon in cancer patients. JAMA. 1982 Nov 19;248(19):2461–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Kirstein M., Fiers W., Baglioni C. Species specificity of human and murine tumor necrosis factor. A comparative study of tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14871–14874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Shepard H. M., Rothstein J. L., Sugarman B. J., Schreiber H. Tumor necrosis factor: a potent effector molecule for tumor cell killing by activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5233–5237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadhan-Raj S., Al-Katib A., Bhalla R., Pelus L., Nathan C. F., Sherwin S. A., Oettgen H. F., Krown S. E. Phase I trial of recombinant interferon gamma in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Feb;4(2):137–146. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., van Duin C. T. The effects of bacterial pyrogens and leucocytic pyrogen upon gastric motility and heart rate frequency in conscious goats. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1974 Aug;21(8):692–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0442.1974.tb01353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]