Abstract
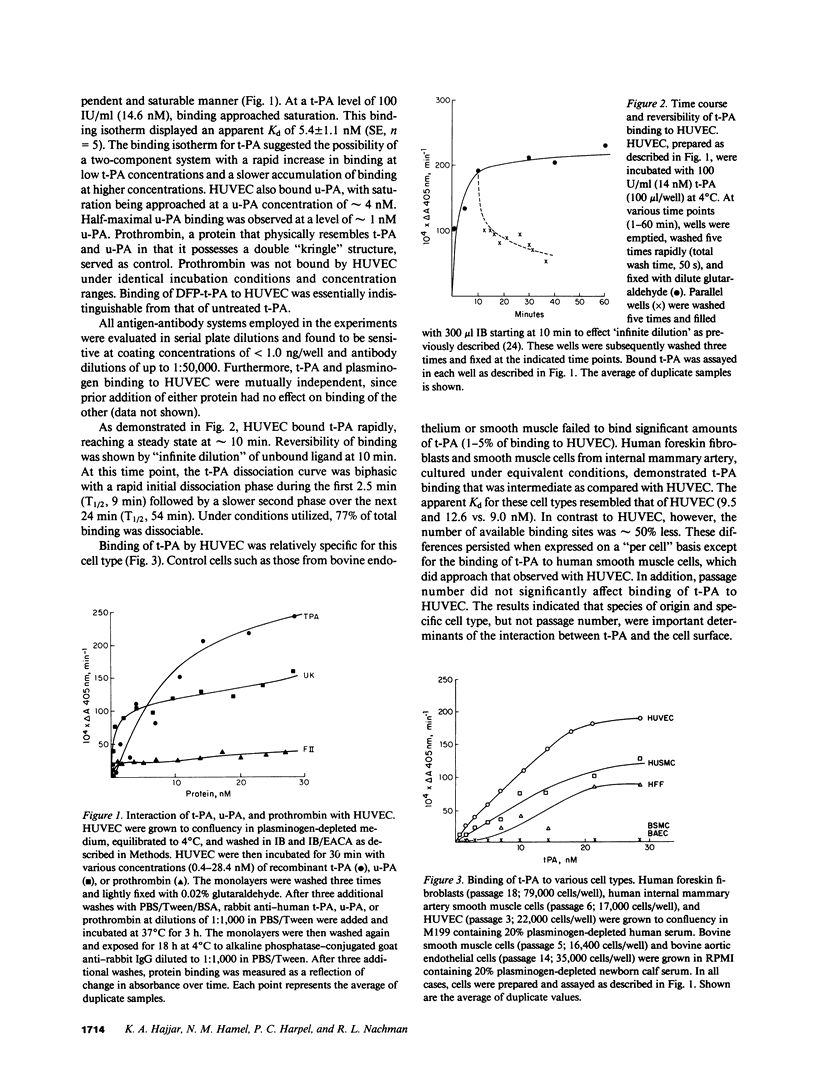
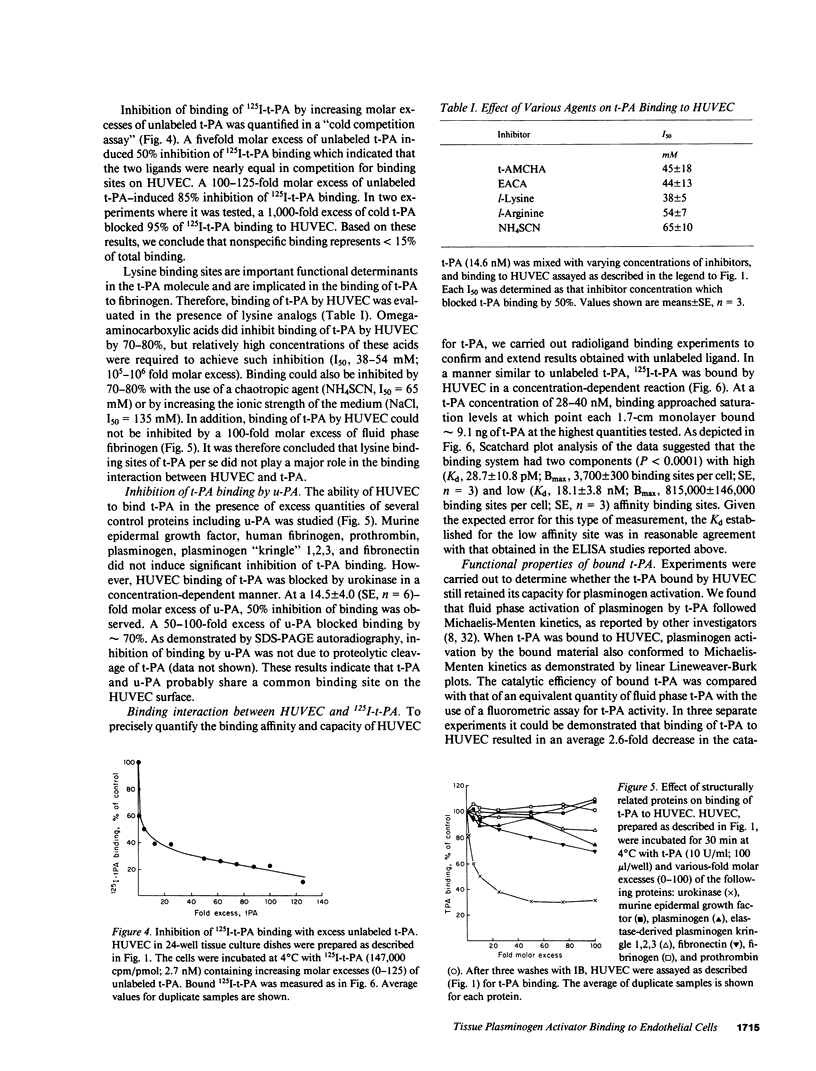
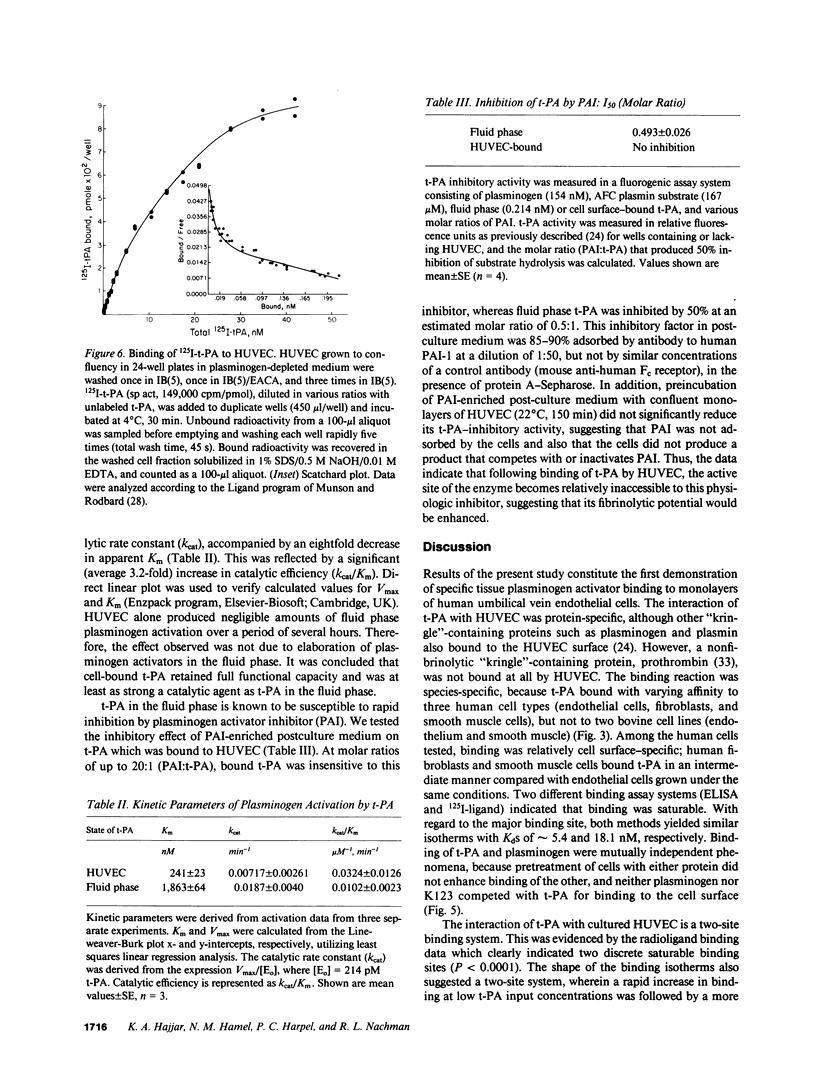
Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and urokinase (u-PA), the major activators of plasminogen, are synthesized and released from endothelial cells. We previously demonstrated specific and functional binding of plasminogen to cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). In the present study we found that t-PA could bind to HUVEC. Binding of t-PA to HUVEC was specific, saturable, plasminogen-independent, and did not require lysine binding sites. The t-PA bound in a rapid and reversible manner, involving binding sites of both high (Kd, 28.7 +/- 10.8 pM; Bmax, 3,700 +/- 300) and low (Kd, 18.1 +/- 3.8 nM; Bmax 815,000 +/- 146,000) affinity. t-PA binding was 70% inhibited by a 100-fold molar excess of u-PA. When t-PA was bound to HUVEC, its apparent catalytic efficiency increased by three- or fourfold as measured by plasminogen activation. HUVEC-bound t-PA was active site-protected from its rapidly acting inhibitor: plasminogen activator inhibitor. These results demonstrate that t-PA specifically binds to HUVEC and that such binding preserves catalytic efficiency with respect to plasminogen activation. Therefore, endothelial cells can modulate hemostatic and thrombotic events at the cell surface by providing specific binding sites for activation of plasminogen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Skriver L., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor from human fibrosarcoma cells binds urokinase-type plasminogen activator, but not its proenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7644–7651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann F., Kruithof I. E. Tissue plasminogen activator: chemical and physiological aspects. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):6–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsdorf N., Nilsson T., Wallén P. An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for determination of tissue plasminogen activator applied to patients with thromboembolic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Oct 31;50(3):740–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Osikowicz G., Feder S., Scheinbuks J. Isolation and characterization of a urokinase-type plasminogen activator (Mr = 54,000) from cultured human endothelial cells indistinguishable from urinary urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7198–7205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. R., Hartree E. F. Effects of acrosin inhibitors on the soluble and membrane-bound forms of ram acrosin, and a reappraisal of the role of the enzyme in fertilization. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jan;357(1):57–65. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bányai L., Váradi A., Patthy L. Common evolutionary origin of the fibrin-binding structures of fibronectin and tissue-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Stone O. L., Vavrin Z. Degradation of fibrin and elastin by intact human alveolar macrophages in vitro. Characterization of a plasminogen activator and its role in matrix degradation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):806–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI111275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Vavrin Z., Hibbs J. B., Jr Macrophage fibrinolytic activity: identification of two pathways of plasmin formation by intact cells and of a plasminogen activator inhibitor. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Nolli M. L., Cassani G., Blasi F. Binding of single-chain prourokinase to the urokinase receptor of human U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15819–15822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Dini G., Fibbi G. Receptors for plasminogen activator, urokinase, in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):630–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Schleef R. R., Ny T., Loskutoff D. J. The fibrinolytic system of the vascular wall. Clin Haematol. 1985 Jun;14(2):513–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibbi G., Dini G., Pasquali F., Pucci M., Del Rosso M. The Mr 17500 region of the A chain of urokinase is required for interaction with a specific receptor in A431 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 14;885(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. D., Shaw E. Thiobenzyl benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysinate, substrate for a sensitive colorimetric assay for trypsin-like enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Krupp M. N., Rifkin D. B., Lane M. D. Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor correlates with plasminogen activator activity in human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2276–2280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Harpel P. C., Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L. Binding of plasminogen to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11656–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose A., Takio K., Fujikawa K. Localization of the binding site of tissue-type plasminogen activator to fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):163–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI112546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Vaheri A. The cellular target for the plasminogen activator, urokinase, in human fibroblasts - 66 000 dalton protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;720(2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured bovine endothelial cells produce both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):631–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Edgington T. E. Synthesis of a fibrinolytic activator and inhibitor by endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. M., Wasiewski W. W., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Detwiler T. C. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to platelets. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4886–4893. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. Urokinase-type and tissue-type plasminogen activators have different distributions in cultured bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(1):19–29. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Hajjar K. A., Silverstein R. L., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Elgh F., Lund B. The structure of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene: correlation of intron and exon structures to functional and structural domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Groeneveld E. Isolation and functional characterization of the heavy and light chains of human tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3098–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Juhan-Vague I., de Cock F., Collen D. Measurement of human tissue-type plasminogen activator by a two-site immunoradiometric assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):274–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M. Studies on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 24;704(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Merkel C. H., 3rd Urokinase binding to bovine corneal endothelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1985 Sep;41(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(85)80028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L., Leung L. L., Harpel P. C. Activation of immobilized plasminogen by tissue activator. Multimolecular complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10346–10352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Tacchetti C., Cubellis M. V., Corti A., Hearing V. J., Cassani G., Appella E., Blasi F. Autocrine saturation of pro-urokinase receptors on human A431 cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassburger W., Wollmer A., Pitts J. E., Glover I. D., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Steffens G. J., Günzler W. A., Otting F., Flohé L. Adaptation of plasminogen activator sequences to known protease structures. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. Molecular mechanism of physiological fibrinolysis. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):549–550. doi: 10.1038/272549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Veerman H., Pannekoek H. Autonomous functions of structural domains on human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4670–4674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



