Abstract
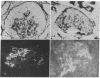
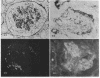
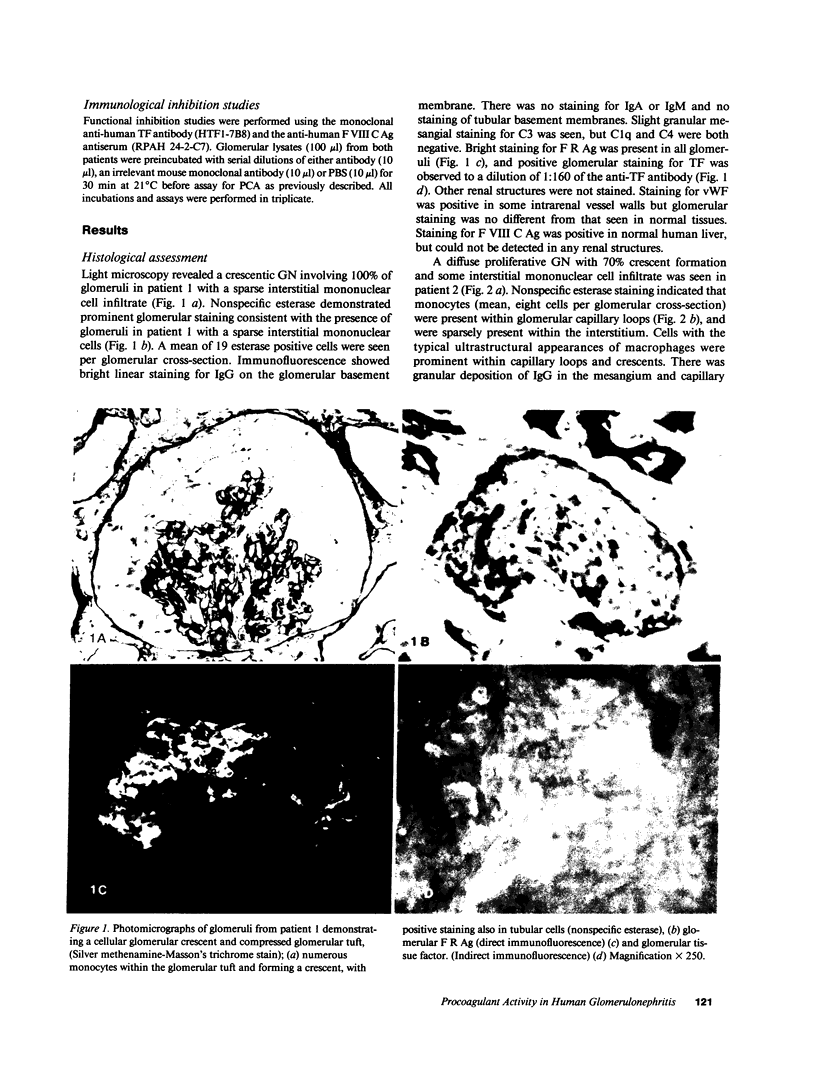
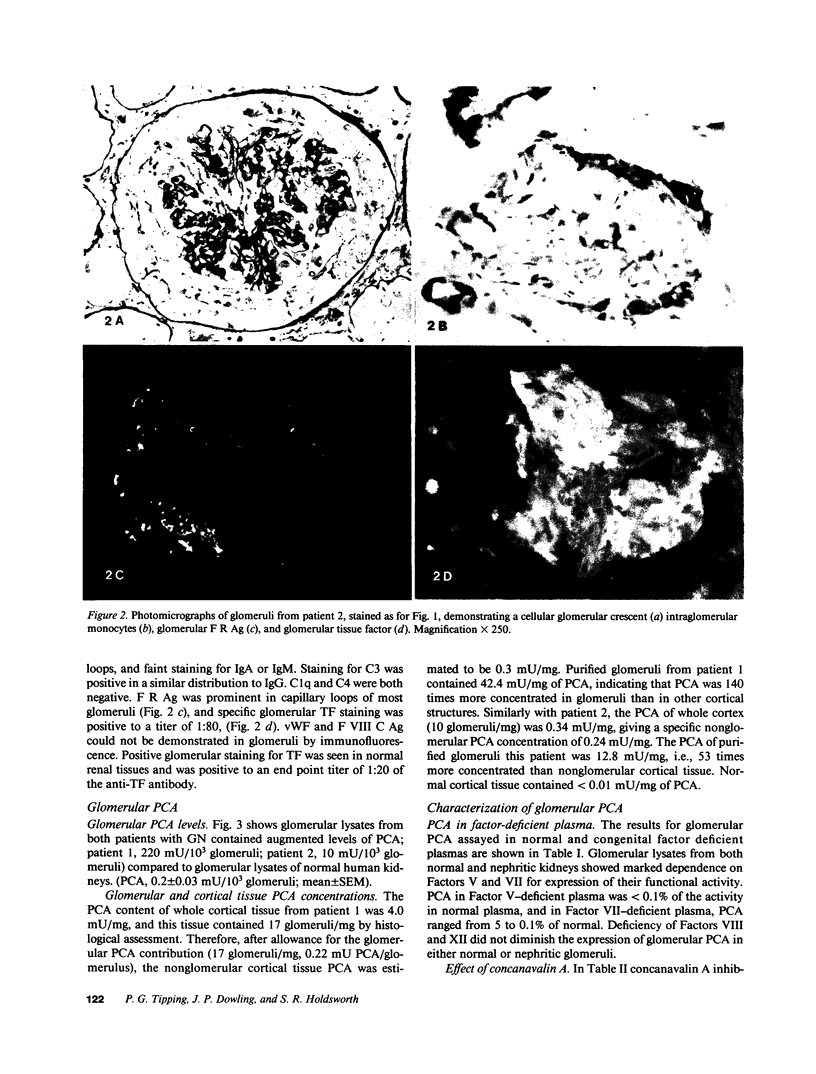
Mechanisms for initiation of glomerular fibrin deposition were studied using renal tissue obtained from two patients with rapidly progressive, crescentic glomerulonephritis. Histological examination showed extensive glomerular monocyte infiltration and fibrin deposition in both patients. Sonicated cell suspensions of isolated glomeruli from these patients contained markedly augmented levels of procoagulant activity (PCA) compared with the levels found in normal glomeruli. This PCA was characterized as tissue factor by its functional dependence on Factors VII and V, independence of Factors VIII and XII, inhibition by concanavalin A and phospholipase C, and association with cell membranes. Its coagulant activity was also inhibited by a specific monoclonal anti-human tissue factor antibody. Tissue factor could be identified in glomeruli from these two patients by indirect immunofluorescence using this antibody. These studies implicate extrinsic pathway activation via tissue factor in intraglomerular deposition of fibrin in these patients. Activated monocytes, known to be a potent source of procoagulant activity and seen in large numbers within glomeruli from these patients, are a likely source of this tissue factor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins R. C., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Matthews F. E. The macrophagen in human rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1976 Apr 17;1(7964):830–832. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D., Ross S. E., Bach R., Guha A. An inhibitory monoclonal antibody against human tissue factor. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole E. H., Schulman J., Urowitz M., Keystone E., Williams C., Levy G. A. Monocyte procoagulant activity in glomerulonephritis associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):861–868. doi: 10.1172/JCI111784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Balconi G., Lorenzet R., Pietra A., Locati D., Donati M. B., Semeraro N. Cultured human endothelial cells generate tissue factor in response to endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1893–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI110945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Rickles F. R., Bobrove A. M. Mononuclear cell tissue factor: cell of origin and requirements for activation. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):359–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario F., Castiglione A., Colasanti G., Barbiano di Belgioioso G., Bertoli S., D'Amico G. The detection of monocytes in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):513–519. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. E., Joshua D. E., Exner T., Kronenberg H. Monoclonal antibodies to human FVIIIR:Ag and FVIIIC. Pathology. 1985 Oct;17(4):579–585. doi: 10.3109/00313028509084756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geczy C. L., Hopper K. E. A mechanism of migration inhibition in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. II. Lymphokines promote procoagulant activity of macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. R., Clark W. F., Cameron J. S. The role of platelets in glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1975;5:19–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glas P., Astrup T. Thromboplastin and plasminogen activator in tissues of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1970 Oct;219(4):1140–1146. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.4.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory S. A., Edgington T. S. Tissue factor induction in human monocytes. Two distinct mechanisms displayed by different alloantigen-responsive T cell clones. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2440–2445. doi: 10.1172/JCI112260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin H., Edgington T. S. Allogeneic induction of the human T cell-instructed monocyte procoagulant response is rapid and is elicited by HLA-DR. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):962–975. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Tipping P. G. Macrophage-induced glomerular fibrin deposition in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1367–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper K. E., Geczy C. L., Davies W. A. A mechanism of migration inhibition in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. I. Fibrin deposition on the surface of elicited peritoneal macrophages on vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1052–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Michael A. F., Hoyer L. W. Immunofluorescent localization of antihemophilic factor antigen and fibrinogen in human renal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1375–1384. doi: 10.1172/JCI107686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. Coagulation and renal disease. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):183–190. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magil A. B., Wadsworth L. D. Monocytes in human glomerulonephritis. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1981 Jul;45(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T., Vassalli P., Gallo G., Baldwin D. S. An immunofluorescent study of pathogenic mechanisms in glomerular diseases. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 31;274(13):695–701. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603312741301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga G., Mazzucco G., di Belgiojoso G. B., Busnach G. The presence and possible role of monocyte infiltration in human chronic proliferative glomerulonephritides. Light microscopic, immunofluorescence, and histochemical correlations. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):271–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlfelder T. W., Niemetz J., Kreutzer D., Beebe D., Ward P. A., Rosenfeld S. I. C5 chemotactic fragment induces leukocyte production of tissue factor activity: a link between complement and coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):147–150. doi: 10.1172/JCI109269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The phospholipid requirement of tissue factor in blood coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):72–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI105716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Prydz H., Bjorklid E., Berre A. Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus and its use in studies of tissue thromboplastin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May 23;27(2):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak V. E., Glueck H. I., Weiss M. A., Lebron-Berges A., Miller M. A. Defibrination with ancrod in glomerulonephritis: effects on clinical and histologic findings and on blood coagulation. Am J Nephrol. 1982;2(4):195–207. doi: 10.1159/000166646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers R. P., Hathaway W. E., Weston W. L. The endotoxin-induced coagulant activity of human monocytes. Br J Haematol. 1975 Jul;30(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Dove F. B., Lee T. K., McGee M. P., Kardon B. Procoagulant activity of lymphocyte-macrophage populations in rabbits: selective increases in marrow, blood, and spleen cells during Shwartzman reactions. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., McGee M. P., Lee T. K. Tissue factor activity. A marker of alveolar macrophage maturation in rabbits. Effects of granulomatous pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1524–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI111358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Zimmerman T. S., Spiegelberg H. L., Vaughan J. H. Leukocyte procoagulant activity: enhancement of production in vitro by IgG and antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):549–557. doi: 10.1172/JCI108670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Edgington T. S. Immune complex-induced human monocyte procoagulant activity. I. a rapid unidirectional lymphocyte-instructed pathway. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):892–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Moran J., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. Defibrination with ancrod in nephrotoxic nephritis in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1976 Nov;10(5):343–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Holdsworth S. R. The participation of macrophages, glomerular procoagulant activity, and factor VIII in glomerular fibrin deposition. Studies on anti-GBM antibody-induced glomerulonephritis in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):10–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Glatfelter A., Brukman J. Procoagulant activity in glomeruli and urine of rabbits with nephrotoxic nephritis. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):156–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C. Hageman factor in experimental nephrotoxic nephritis in the rabbit. Lab Invest. 1985 Sep;53(3):335–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzleben C. L., Boyer J. L., Ng O. C. Manganese-bilirubin cholestasis. Further studies in pathogenesis. Lab Invest. 1987 Feb;56(2):151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharski L. R., Rosenstein R., Phillips P. G. Concanavalin A inhibition of tissue factor (thromboplastin) activity. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):783–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Prost D., Kanfer A. Quantitative assessment of procoagulant activity in isolated rat glomeruli. Kidney Int. 1985 Sep;28(3):566–568. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]