Abstract
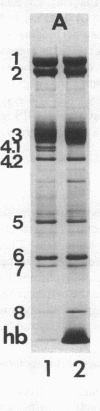
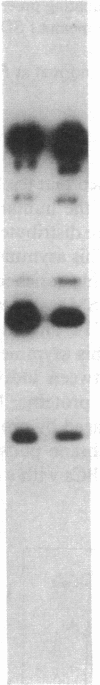
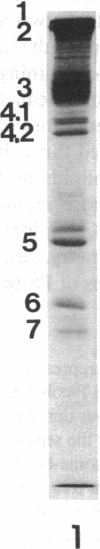
The aminophospholipids phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylserine (PS) are the major phospholipids contained in the cytoplasmic leaflet of the human erythrocyte (RBC) plasma membrane and are largely confined to that leaflet over the entire RBC lifespan. In particular, PS, which comprises approximately 13% of total RBC membrane phospholipids, is normally restricted entirely to the cytoplasmic leaflet. However, molecular mechanisms that regulate this asymmetric distribution of phospholipids are largely unknown. We examined elliptocytic RBCs that completely lacked protein 4.1 (HE [4.1 degrees]), but contained normal amounts of all other peripheral membrane proteins, and found approximately 10% of total membrane PS was accessible in the exoplasmic leaflet of these membranes. Inside out vesicles (IOVs) derived from HE [4.1 degrees] RBCs bound fewer PS liposomes than did IOVs derived from normal RBCs. Normal IOVs that were depleted of proteins 2.1 (ankyrin), 4.1, and 4.2 bound fewer PS liposomes similar to HE [4.1 degrees] IOVs, and repletion with protein 4.1 restored PS liposome binding to control levels. Addition of purified protein 4.1 to PS liposomes resulted in saturable binding with the extent of binding being proportional to the liposome PS content. Our data suggests that human RBC protein 4.1 is a PS binding protein and may be involved in the molecular mechanisms that stabilize PS in the cytoplasmic leaflet of the human RBC plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Lovrien R. E. Glycophorin is linked by band 4.1 protein to the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):655–658. doi: 10.1038/307655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Parsons S. F., Ridgwell K., Tanner M. J., Merry A. H., Thomson E. E., Judson P. A., Johnson P., Bates S., Fraser I. D. Two individuals with elliptocytic red cells apparently lack three minor erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):615–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2180615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Association between ankyrin and the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M., Foley S. F. Biochemical characterization of complex formation by human erythrocyte spectrin, protein 4.1, and actin. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6091–6098. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daleke D. L., Huestis W. H. Incorporation and translocation of aminophospholipids in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5406–5416. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck P. F., Chiu D. T., Op den Kamp J. A., Lubin B., van Deenen L. L., Roelofsen B. Accelerated transbilayer movement of phosphatidylcholine in sickled erythrocytes. A reversible process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8436–8442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., Deuticke B. Possible relationship between membrane proteins and phospholipid asymmetry in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W. Interactions between membrane skeleton proteins and the intrinsic domain of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec;694(4):331–352. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., Plasa G., Kamp D., Deuticke B. Spectrin as a stabilizer of the phospholipid asymmetry in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 4;509(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers F. A., van Linde-Sibenius Trip M., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A., Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. The phospholipid organisation in the membranes of McLeod and Leach phenotype erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80644-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. Q., Nichols M. E., Bigbee W. L., Nagel R. L., Blumenfeld O. O. Structural polymorphism of glycophorins demonstrated by immunoblotting techniques. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):618–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D., Bastacky J., Roelofsen B., Van Deenen L. L. Abnormalities in membrane phospholipid organization in sickled erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1643–1649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombers C., Verkleij A. J., de Gier J., van Deenen L. L. The interaction of spectrin-actin and synthetic phospholipids. II. The interaction with phosphatidylserine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 8;551(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombers C., de Gier J., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Spectrin-phospholipid interaction. A monolayer study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 2;603(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson F., Hunt C. A., Szoka F. C., Vail W. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack G. R., Anderson R. A., Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. Interactions between protein 4.1 and band 3. An alternative binding site for an element of the membrane skeleton. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3676–3683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S. B., Ohnishi S. Interaction of a peripheral protein of the erythrocyte membrane, band 4.1, with phosphatidylserine-containing liposomes and erythrocyte inside-out vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Chiu D. T., Lubin B. Plasma membrane phospholipid organization in human erythrocytes. Curr Top Hematol. 1985;5:63–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S., Pendlebury S. A., Green C. Lipid organization in erythrocyte membrane microvesicles. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):285–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2240285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneuret M., Devaux P. F. ATP-dependent asymmetric distribution of spin-labeled phospholipids in the erythrocyte membrane: relation to shape changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K. A., Goodman S. R. Protein 4.1: its association with the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4404–4408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sponholtz D. K., Brautigan D. L., Loach P. A., Margoliash E. Preparation of cytochrome c2 from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:255–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90528-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Olson F., Heath T., Vail W., Mayhew E., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of unilamellar liposomes of intermediate size (0.1-0.2 mumol) by a combination of reverse phase evaporation and extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 2;601(3):559–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Reinhardt B. N., Branton D. Associations of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Binding of purified bands 2.1 and 4.1 to spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):7034–7039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P., Bateman J., Kozarsky K., Mattocks K., Hermanowicz N., Choe H. R., Schlegel R. A. Involvement of spectrin in the maintenance of phase-state asymmetry in the erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut J., Düzgüneş N., Fraley R., Papahadjopoulos D. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: kinetics of calcium ion induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles followed by a new assay for mixing of aqueous vesicle contents. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6011–6021. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Op den Kamp J. A. Transbilayer movement of various phosphatidylcholine species in intact human erythrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(2):193–204. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]