Abstract
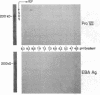
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a severe, chronic blistering disease of the skin. EBA patients have circulating and tissue-bound autoantibodies to a large (Mr = 290,000) macromolecule that is localized within the basement membrane zone between the epidermis and dermis of skin, the site of blister formation. The "EBA antigen" is known to be distinct from laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, fibronectin, the bullous pemphigoid antigen, elastin, and collagen types I, II, III, IV, and V. Sera from patients with EBA, two monoclonal antibodies to the EBA antigen, and a monoclonal antibody to the carboxyl terminus of type VII procollagen identically label human amnion and skin by immunofluorescent and immunoelectron microscopy. Western immunoblots of the EBA antigen extracted from skin and of type VII procollagen labeled with the above sera and antibodies are identical. None of the sera or antibodies labels Western blots of pepsinized type VII collagen which is missing the globular amino and carboxyl terminal domains. These data show that the EBA antigen is the carboxyl terminus of type VII procollagen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentz H., Morris N. P., Murray L. W., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E. Isolation and partial characterization of a new human collagen with an extended triple-helical structural domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3168–3172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner-Tuderman L., Schnyder U. W., Winterhalter K. H., Bruckner P. Tissue form of type VII collagen from human skin and dermal fibroblasts in culture. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):607–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Morris N. P., Murray L. W., Duncan K. G., Keene D. R., Sakai L. Y. The structure of type VII collagen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:47–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Cappelletti R., Viti M., Vannucchi S., Chiarugi V. Binding of the basement-membrane glycoprotein laminin to glycosaminoglycans. An affinity-chromatography study. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):699–704. doi: 10.1042/bj1990699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon W. R., Briggaman R. A., Inman A. O., 3rd, Queen L. L., Wheeler C. E. Differentiating anti-lamina lucida and anti-sublamina densa anti-BMZ antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on 1.0 M sodium chloride-separated skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Feb;82(2):139–144. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. B., Minus H. R. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with electron microscopical studies. Arch Dermatol. 1975 Feb;111(2):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Sakai L. Y., Hollister D. W., Burgeson R. E., Engvall E. Basement membrane diversity detected by monoclonal antibodies. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulu L., Kusumi A., Steinberg M. S., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1509–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunstrum G. P., Kuo H. J., Rosenbaum L. M., Keene D. R., Glanville R. W., Sakai L. Y., Burgeson R. E. Anchoring fibrils contain the carboxyl-terminal globular domain of type VII procollagen, but lack the amino-terminal globular domain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13706–13712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunstrum G. P., Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Large complex globular domains of type VII procollagen contribute to the structure of anchoring fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9042–9048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieboer C., Boorsma D. M., Woerdeman M. J., Kalsbeek G. L. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Immunofluorescence, electron microscopic and immunoelectron microscopic studies in four patients. Br J Dermatol. 1980 Apr;102(4):383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1980.tb06550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paller A. S., Queen L. L., Woodley D. T., Gammon W. R., O'Keefe E. J., Briggaman R. A. A mouse monoclonal antibody against a newly discovered basement membrane component, the epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Mar;84(3):215–217. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roenigk H. H., Jr, Ryan J. G., Bergfeld W. F. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Report of three cases and review of all published cases. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Jan;103(1):1–10. doi: 10.1001/archderm.103.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakashita S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane glycoprotein laminin binds to heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I., Martin G. R. Structure and function of basement membrane. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Jul;79 (Suppl 1):69s–72s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12545830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rao C. N., Kalebic T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. Laminin receptor on human breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Briggaman R. A., Gammon W. R., O'Keefe E. J. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen is synthesized by human keratinocytes cultured in serum-free medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1267–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Briggaman R. A., O'Keefe E. J., Inman A. O., Queen L. L., Gammon W. R. Identification of the skin basement-membrane autoantigen in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 19;310(16):1007–1013. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404193101602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., O'Keefe E. J., McDonald J. A., Reese M. J., Briggaman R. A., Gammon W. R. Specific affinity between fibronectin and the epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1826–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI113024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., O'Keefe E. J., Reese M. J., Mechanic G. L., Briggaman R. A., Gammon W. R. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen, a new major component of cutaneous basement membrane, is a glycoprotein with collagenous domains. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Jun;86(6):668–672. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12275978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Rao C. N., Hassell J. R., Liotta L. A., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. Interactions of basement membrane components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 27;761(3):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Scheidt V. J., Reese M. J., Paller A. S., Manning T. O., Yoshiike T., Briggaman R. A. Localization of the alpha 3 (V) chain of type V collagen in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Mar;88(3):246–252. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12465467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D., Sauder D., Talley M. J., Silver M., Grotendorst G., Qwarnstrom E. Localization of basement membrane components after dermal-epidermal junction separation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Aug;81(2):149–153. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita H., Briggaman R. A., Lawley T. J., Provost T. T., Katz S. I. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: ultrastructural and immunological studies. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Apr;76(4):288–292. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12526124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]