Abstract
The Y chromosome plays a critical role in spermatogenesis. Formerly, it had been difficult to generate knockout mice with specific Y chromosome mutations using conventional gene-targeting strategies. Recently, a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) was successfully used for editing a mouse Y chromosome-linked gene. Here, we report the generation of a mouse model with a mutation in Eif2s3y, a Y chromosome-linked gene, and analysis of its phenotype. The mouse carrying a targeted mutation of Eif2s3y was infertile and had hypoplastic testes. Histological and electron microscopic analyses showed that differentiation of spermatogonia was arrested at the stage of spermatogonial stem cells (undifferentiated spermatogonia) and that the progression of spermatogenesis was interrupted, resulting in azoospermia. Using TALEN, we verified that EIF2S3Y performs a key function in differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells.
Introduction
In humans and mice, the male-specific regions of the Y chromosome have been shown to play a critical role in fertility through regulation of spermatogenesis [1–4]. One of the most valuable findings to date was obtained by the studies of XSxrbO mice, in which the short arm of the Y chromosome is translocated to the X chromosome. In this mice, sex reversal occurs due to the translocated Y fragment containing the Sry gene, the male-determining gene; however, the mice are sterile because of a spermatogonial arrest [5–7]. Burgoyne and colleagues reported a successful rescue of the failure of early spermatogenesis by introducing a BAC clone containing Eif2s3y (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 3, and structural gene Y-linked) into the XSxrbO mice, which strongly supports the idea that EIF2S3Y performs a fundamental function in spermatogenesis [8]. Nevertheless, no mouse with targeted gene knockout in the Eif2s3y gene by conventional gene-targeting strategies has been reported.
The transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) has been successfully used for site-specific genome editing in mice to produce knockout mice [9–12]. TALENs are fusion proteins consisting of a DNA-binding domain and the FokI endonuclease at the C-terminus [13]. The recognition sequences of the DNA-binding domain can be designed to target a specific DNA sequence. Dimerization of two TALENs on targeted specific sequences in a genome causes a FokI-mediated double-strand break, resulting in stimulation of the DNA repair machinery in the cell. The breakage is repaired through nonhomologous end joining, which frequently results in small insertions or deletions. Recently, a TALEN-induced Y chromosomal gene modification in embryonic stem cells and oocytes was successfully utilized to generate knockout mice [14,15].
In this study, we report the detailed phenotype of Eif2s3y knockout mice generated using TALEN-mediated gene disruption.
Materials and Methods
Microinjection
TALEN plasmids with the CMV and T7 promoter were designed and constructed using the custom TALEN Access service (Cellectis). In vitro transcription reactions were performed using the mMessage mMachine T7 Kit (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions, using as a template 1 μg of the TALEN plasmid linearized by means of digestion with the PacI endonuclease. The RNA purification was carried out using the MEGAclear kit (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions. We determined the RNA concentration using absorbance at 260 nm, and the RNA was diluted with an injection buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.4, 0.1 mM EDTA) at a desired concentration. The RNA mixture was microinjected into the cytoplasm of an embryo at the one-cell stage using oocytes obtained from superovulated (C57BL/6×DBA2) F1 mice. The embryos injected with RNA were cultured in the M16 medium for 1 day and progressed to the two-cell stage. They were then implanted in pseudopregnant ICR female mice. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University.
Genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from tail tips of mouse pups. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed using the following primers: Eif2s3y-F (5′-GTC CAT GGC AAG TAG CTG TTG AAC-3′) and Eif2s3y-R (5′-CCC AAA ACT GCC AGG ACA ACC-3′) for Eif2s3y and Eif2s3x-F (5′-GAA GTC CGA GCA GTC AGG TC-3′) and Eif2s3x-R (5′-TCT AGG ATG GCT CCT TCA GC-3′) for Eif2s3x. PCR products were treated with ExoSTAR (GE Healthcare) and used as templates for sequencing. Either Eif2s3y-F or Eif2s3x-F was used as a sequencing primer. To confirm mutant alleles at the nucleotide level, a PCR product was cloned into a cloning vector containing M13 forward and reverse primer sequences and was sequenced using either the Eif2s3y-F or Eif2s3y-R primer. To search off-target candidate in silico, we conducted electronic PCR available at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/epcr/).
Confirmation of fertility
Mutant 1 was mated with single wild-type C57BL/six females for 3 months. Mutant 2 was mated with single wild-type C57BL/six females for the first 2 months, then mated with other two female mice for the next month, and the presence/absence of a vaginal plug was examined. When a coupling was confirmed according to a vaginal plug, the female mice were transferred to another cage. The resulting pups were genotyped as described above.
Statistical analysis
For statistical analysis, two-tailed Student's t-tests were performed using the Excel spreadsheet.
Histological and immunohistochemical analysis
Bouin's solution-fixed, paraffin-embedded testes were sliced into 7-μm-thick sections. The slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For immunohistochemical analysis of TRA98, MCA, and TRA54 staining, deparaffinized slices were mounted onto slides and incubated with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 15 min, then with 10% fetal bovine serum in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 30 min, and then with the anti-TRA98 antibody, anti-MCA antibody, or anti-TRA54 antibody overnight at 4°C. After three washes by PBS, the slides were incubated with Simple Stain Max-PO (Nichirei Bioscience) for 30 min at room temperature. After that, the slides were washed again and the staining was visualized using the NovaRED substrate kit for peroxidase (Vector Laboratories).
Immunohistochemical analysis by means of GFRα1 staining was conducted as described previously [16], using the following antibodies: a goat anti-GFRα1 antibody (Neuromics) and a rabbit anti-phospho-histone H3 antibody (Ser10; Cell Signaling). For the detection of GFRα1, we used the Can Get Signal immunostain (Toyobo). The resulting signals were detected using incubation with Alexa 488- or Alexa 594-conjugated anti-IgG antibodies (Molecular Probes).
Transmission electron microscopy
The specimens were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB) for 2 h. The samples were washed with 0.1 M PB, postfixed in 1% OsO4 buffered with 0.1 M PB for 2 h, dehydrated in a graded series of ethanol, and embedded in Epon 812. Ultrathin sections (90 nm) were placed on a copper grid, double stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and then examined under a transmission electron microscope (H-7100; Hitachi).
We determined the stages of spermatogenic cells in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images according to a previous report [17].
Results
Construction of a TALEN and preparation of Eif2s3y knockout mice
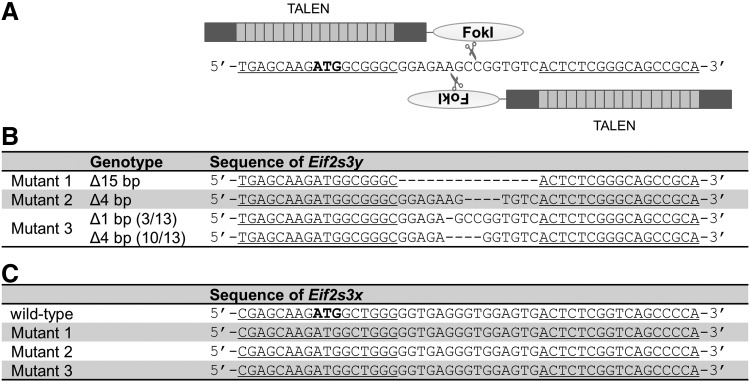
To disrupt Eif2s3y, we created TALENs that recognize exon 1 of Eif2s3y, which includes the start codon (Fig. 1A). After the TALEN produces a frameshift mutation in exon 1, the entire expression of Eif2s3y should cease. The TALEN RNAs were synthesized by in vitro transcription and injected into the cytoplasm of pronuclear-stage oocytes. Injection of RNA directly into the oocytes allowed us to generate knockout mice within a shorter period compared to gene targeting of embryonic stem cells. The resulting newborn pups were genotyped by PCR and sequenced by using DNA purified from their tail tips. PCR-directed sequencing confirmed that three pups contained the mutation in the coding sequence of Eif2s3y (Fig. 1B). Mutant 1 had an inframe deletion, and mutant 2 had a frameshift mutation. Mutant 3 was a mosaic of the two distinct mutations; single-nucleotide deletion and four-nucleotide deletion (Fig. 1B).
FIG. 1.
Generation of a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN)-mediated gene knockout in mice. (A) The Eif2s3y TALEN recognition sequence. Light gray boxes in the schematic indicate DNA-binding domains of the TALEN and deep gray boxes indicate the N- and C-terminal domains. The FokI endonuclease is fused with the C-terminal domain. The DNA sequence to which TALENs bind is underlined. The start codon is in boldface. (B) Sequences of Eif2s3y obtained in the region of the TALEN-mediated Eif2s3y knockout in mice. Deleted nucleotides are indicated by hyphens. Mutant 1 is an inframe mutant, mutant 2 is a frameshift mutant, and mutant 3 as a mosaic of two distinct frameshift mutations (single-nucleotide deletion and 4-bp deletion). The ratio of mosaicism is shown after the genotype. Δ, deletion; bp, base pairs. (C) Sequences of Eif2s3x obtained in the region of the TALEN-mediated Eif2s3y knockout in mice. No off-target mutations were found in the genomic regions of Eif2s3x surrounding the sequence homologous to the TALEN target site. The DNA sequences homologous to the Eif2s3y TALEN-binding regions are underlined. The start codon is in boldface.
Eif2s3y has an X chromosome homolog called Eif2s3x. The genomic region of Eif2s3x surrounding the sequence homologous to the TALEN-targeted site was amplified using PCR, and DNA sequencing was performed. No mutations were found surrounding Eif2s3x (Fig. 1C). We also searched for a potential off-target candidate by electronic PCR, and found that the second candidate next to Eif2s3y target site had a spacer of 686 bp. These results indicate that these mice were Eif2s3y deficient and have low possibilities of off-target mutations.
A frameshift mutation in Eif2s3y led to male infertility
For fertility check, mutants 1 and 2 were mated with wild-type C57BL/six females. Mutant 1, which carries an inframe deletion of Eif2s3y, had several pups, and the same inframe deletion was inherited. Mutant 2, which carries a frameshift mutation of Eif2s3y, was mated with nine female mice and demonstrated reproductive behavior. The five vaginal plug-positive female mice were found, but none of them produced pups (data not shown). The four plug-negative female mice did not produce pups either. All of the plug-positive female mice were subsequently mated with a wild-type C57BL/six males, and they delivered pups. Therefore, infertility of mutant 2 was not caused by female infertility.
Testes were hypoplastic in Eif2s3y knockout mice
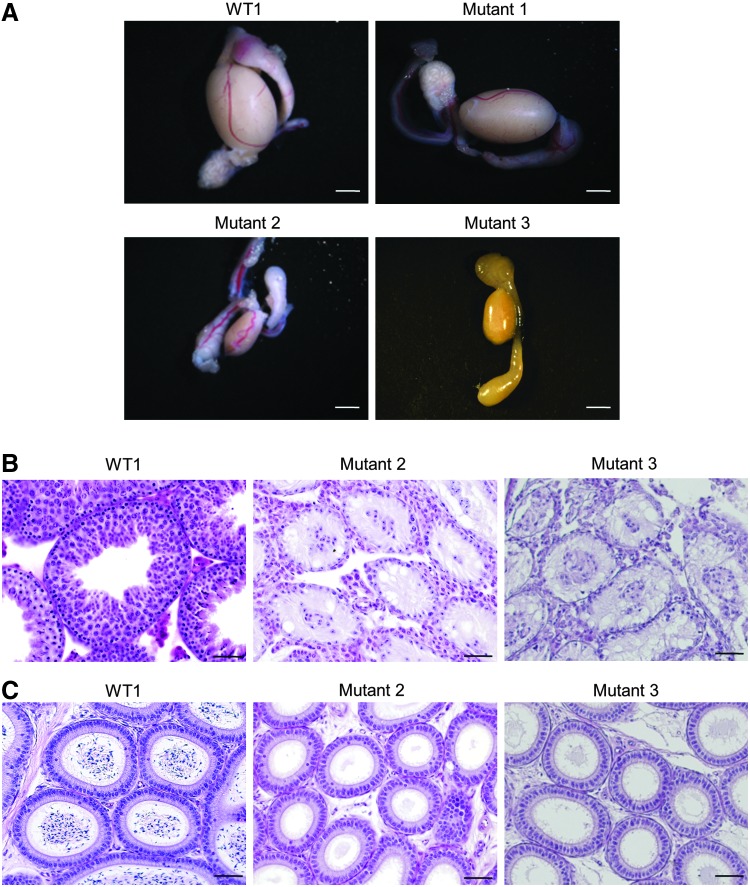
Three mutants and wild-type BDF1 male mice were dissected, body weight, body length, anogenital distance, and testis weight were analyzed (Table 1). Mutants 1 and 2 were dissected at 6 months of age and mutant 3 at 4 months of age. WT1 and WT2 were dissected at 3 months of age and WT3 at 4 months of age. WT3 is a sibling of mutant 3. The weights of the testes were found to be significantly decreased in frameshift mutants (mutants 2 and 3) when compared with the control group (WT2 and WT3) (P<0.05). As mice were dissected at different age in months, there was a limitation to compare them fully. No remarkable differences were observed in other metrics examined. Histological analysis of the testis revealed that azoospermia was shown in mutants 2 and 3 (Fig. 2B). In mutants 2 and 3, there was no sperm in the epididymis, but the structure of the epididymis was similar to that of wild-type mice (Fig. 2C).
Table 1.
Phenotypes of Eif2s3y Knockout Mice
| BW (g) | BL (mm) | AGD (mm) | TW (mg) | Dissected age (month) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT1 | 28.20 | 88.29 | 9.54 | ND | 3 |
| WT2 | 27.80 | 78.42 | 11.63 | 154.2 | 3 |
| WT3 | 31.9 | 95.45 | 10.80 | 132.9 | 4 |
| Mutant 1 | 41.15 | 99.91 | 15.85 | 123.8 | 6 |
| Mutant 2 | 41.14 | 86.13 | 13.08 | 21.5 | 6 |
| Mutant 3 | 26.6 | 86.76 | 8.65 | 16.0 | 4 |
BW, body weight; BL, body length; AGD, anogenital distance; TW, testis weight; WT, wild type; ND, no data.
FIG. 2.
Testes of the Eif2s3y knockout mice. (A) Macrostructure of a testis. The testes of mutants 2 and 3 were smaller compared to other fertile male testes. The testis weight was approximately one-sixth of the weight in the other strains. The scale bar is 2 mm. (B) Histological analysis [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining] of the testis. Testes of mutants 2 and 3 exhibited spermatogonial proliferation block. The scale bar is 50 μm. (C) Histological analysis (H&E stain) of the epididymis. Histological features of the epididymis in mutants 2 and 3 were similar to those of wild-type mice, but no sperm was observed in mutants 2 and 3. The scale bar is 50 μm.
EIF2S3Y is required for spermatogonial differentiation
Spermatogenesis consists of the spermatogonial proliferative phase, the meiotic phase, and the spermiogenesis phase. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to determine which phase of spermatogenesis is blocked in mutant 2. GFRα1, TRA98, Meichroacidin (MCA), and TRA54 were used for the staining of undifferentiated spermatogonia [18,19], testicular germ cells [20], spermatocytes [21], and spermatocytes/spermatids [22], respectively.
All the antibodies yielded a positive signal in testis slices of wild-type mice. In contrast, the number of TRA98-positive and PH3 (mitotic cell marker)-positive cells was much lower in mutant 2 compared to wild-type male mice (Fig. 3A). Rather, GFRα1-positive cells were increased in mutant 2 (Fig. 3A). These results indicated that spermatogonia were arrested at the stage of undifferentiated spermatogonia and accumulated by Eif2s3y deficiency. MCA-positive cells were observed in mutant 2, but they were topographically and morphologically abnormal (Fig. 3A). Therefore, MCA-positive cells in mutant 2 could not be considered spermatocytes. TRA54-positive cells were not observed in mutant 2 (Fig. 3A). Mutant 3, harboring two types of frameshift mutations, also showed lesser TRA98-positive cells and increased GFRα1-positive cells as mutant 2 (Supplementary Fig. S1; Supplementary materials are available online at http://www.liebertpub.com/scd). In summary, Eif2s3y deficiency leads to a fewer number of spermatogonia, which were arrested at the stage of undifferentiated spermatogonia, resulting in no spermatocytes or spermatids and male infertility.
FIG. 3.
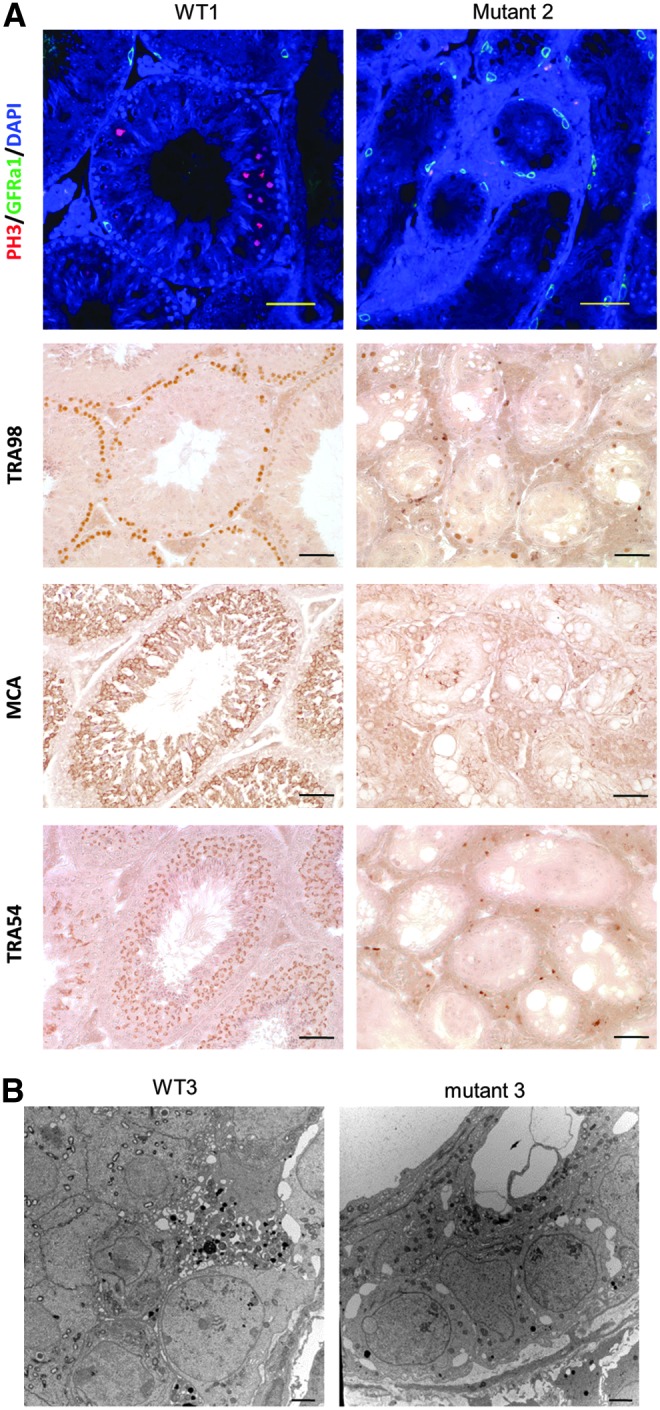
Immunohistochemistry and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of the Eif2s3y knockout mice. (A) Immunohistochemical analyses using staining for PH3 (red)/GFRα1 (green)/DAPI (blue), TRA98, MCA, or TRA54. Mutant 2 showed an increased GFRα1 signal, a lesser TRA98 signal, an abnormal MCA signal, and no TRA54 signal, suggesting that the differentiation of undifferentiated spermatogonia was arrested. GFRα1, TRA98, MCA, and TRA54 are markers of undifferentiated spermatogonia, testicular germ cells, spermatocytes, and spermatids, respectively. The scale bar is 50 μm. (B) TEM images. Mutant 3 showed the presence of undifferentiated spermatogonia and Sertoli cells. Undifferentiated spermatogonia had a nucleus with a mottled appearance of the heterochromatin. The scale bar is 2 μm.
Next, we examined the morphology of each cell type in testis by TEM. In mutant 3, only undifferentiated spermatogonia, which had a nucleus with the mottled heterochromatin, were found on the peripheral basement membrane of seminiferous tubules (Fig. 3B). Although differentiated spamatogonia and/or spermatocytes were also found in WT3, there were no cells corresponding to WT1 in mutant 3. These findings are consistent with the results of immunohistochemical analysis.
Discussion
During spermatogenesis, spermatogonial stem cells on the peripheral basement membrane of seminiferous tubules differentiate regularly and move toward the lumen [23,24]. Several factors have been shown to influence spermatogenesis, such as retinoic acid signaling [25] and Notch signaling [26]. While the molecular network regulating spermatogonial proliferation remains largely unknown [27], it was recently reported that LIN28A functions as a regulator of spermatogonial proliferation [28].
The critical role of Eif2s3y in spermatogonial proliferation has been examined by series of transgenic mice as follows: in the XSxrbO male mice, the spermatogenic block was during the differentiating A spermatogonial stage [29]. The BAC rescue approach to introduce Eif2s3y transgene into XSxrbO male mice was performed and showed that their testes were rescued from the spermatogenic block and progressed through the meiotic phase [8]. This study proved that Eif2s3y is a key gene for spermatogonial proliferation of the differentiating A spermatogonia [8].
Based on this finding, we directly investigated the function of Eif2s3y in Eif2s3y deficiency mice generated by TALEN-mediated single-gene editing. In Eif2s3y frameshift mutants (mutants 2 and 3), spermatogenesis was arrested at the stage of undifferentiated spermatogonia, suggesting that a loss of Eif2s3y causes spermatogonia to fail to differentiate into differentiating spermatogonia and to fail to undergo mitotic division to ensure germ cell reproduction (Fig. 3). Our observations using Eif2s3y deficiency mice confirmed the key role of Eif2s3y in spermatogonial proliferation. The observations made on undifferentiated spermatogonia in 4–6-month testis material may represent secondary damage/changes, since it is not seen in XSxrbO (or XO Sry) males examined during prepubertal stages. This should be clarified using younger Eif2s3y deficiency mice in the future.
Eif2s3y encodes the γ-subunit of eIF-2, which forms a ternary complex with GTP and Met-tRNA and then binds to the small (40S) ribosomal subunit, which participates in translational initiation [30]. eIF-2 is composed of three subunits: α, β, and γ. The γ-subunit contains binding domains for GTP and Met-tRNA [31–33].
Although Eif2s3y is ubiquitously expressed [34], our Eif2s3y knockout mice showed no remarkable phenotypic features except for azoospermia. In mice, Eif2s3y has an X chromosome homolog called Eif2s3x that escapes X inactivation [34]. Analyzing mice with Eif2s3x deficiency would reveal whether Eif2s3x is essential for survival in an XY mouse or whether Eif2s3y could complement Eif2s3x function. Moreover, the mechanisms of tissue-specific function of EIF2S3Y are still unclear. It would be interesting to test the idea that the total dose of Eif2s3y and Eif2s3x gene expression may be essential for spermatogenesis-related gene translation.
The Y chromosome-linked genes are thought to be involved in sex determination, spermatogenesis, growth, and regulation of male behavior. For sex determination, Sry plays a key role, and its function has been determined precisely. Until recently, gene targeting in the Y chromosome had been difficult to carry out; however, genome editing technologies allowed us to analyze the Y chromosome-linked genes. TALEN-mediated genome editing of other Y chromosome-linked genes (Zfy1, Usp9y, Ddx3y, Kdm5d, Ube1y1, and Zfy2) is expected to help decipher the biological function of the Y chromosome.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Masami Kanai-Azuma (Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Center for Experimental Animals) and Tomomi Kato (Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Department of Systems BioMedicine) for performing the microinjection. This work was supported, in part, by NIH grant no. AR050631, a grant from the National Center for Child Health and Development, grant no. 25-1, JSPS KAKENHI grant no. 24115707, JST (CREST) to H.A. and JSPS KAKENHI grant no. 25132713, MEXT KAKENHI grant no. 23570265, and the grant from the National Center for Child Health and Development, grant no. 24-3 to S.T.
Author Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
References
- 1.Lahn BT. and Page DC. (1997). Functional coherence of the human Y chromosome. Science 278:675–680 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Skaletsky H, Kuroda-Kawaguchi T, Minx PJ, Cordum HS, Hillier L, Brown LG, Repping S, Pyntikova T, Ali J, et al. (2003). The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 423:825–837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Toure A, Clemente EJ, Ellis P, Mahadevaiah SK, Ojarikre OA, Ball PA, Reynard L, Loveland KL, Burgoyne PS. and Affara NA. (2005). Identification of novel Y chromosome encoded transcripts by testis transcriptome analysis of mice with deletions of the Y chromosome long arm. Genome Biol 6:R102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burgoyne PS. and Mitchell MJ. (2007). The roles of mouse Y chromosome genes in spermatogenesis. In: The Y Chromosome and Male Germ Cell Biology in Health and Diseases. Lau YF, Chan WY, eds. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 1–25 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burgoyne PS, Levy ER. and McLaren A. (1986). Spermatogenic failure in male mice lacking H-Y antigen. Nature 320:170–172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sutcliffe MJ. and Burgoyne PS. (1989). Analysis of the testes of H-Y negative XOSxrb mice suggests that the spermatogenesis gene (Spy) acts during the differentiation of the A spermatogonia. Development 107:373–380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mazeyrat S, Saut N, Sargent CA, Grimmond S, Longepied G, Ehrmann IE, Ellis PS, Greenfield A, Affara NA. and Mitchell MJ. (1998). The mouse Y chromosome interval necessary for spermatogonial proliferation is gene dense with syntenic homology to the human AZFa region. Hum Mol Genet 7:1713–1724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mazeyrat S, Saut N, Grigoriev V, Mahadevaiah SK, Ojarikre OA, Rattigan A, Bishop C, Eicher EM, Mitchell MJ. and Burgoyne PS. (2001). A Y-encoded subunit of the translation initiation factor Eif2 is essential for mouse spermatogenesis. Nat Genet 29:49–53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sung YH, Baek IJ, Kim DH, Jeon J, Lee J, Lee K, Jeong D, Kim JS. and Lee HW. (2013). Knockout mice created by TALEN-mediated gene targeting. Nat Biotechnol 31:23–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Davies B, Davies G, Preece C, Puliyadi R, Szumska D. and Bhattacharya S. (2013). Site specific mutation of the Zic2 locus by microinjection of TALEN mRNA in mouse CD1, C3H and C57BL/6J oocytes. PLoS One 8:e60216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qiu Z, Liu M, Chen Z, Shao Y, Pan H, Wei G, Yu C, Zhang L, Li X, et al. (2013). High-efficiency and heritable gene targeting in mouse by transcription activator-like effector nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Takada S, Sato T, Ito Y, Yamashita S, Kato T, Kawasumi M, Kanai-Azuma M, Igarashi A, Kato T, Tamano M. and Asahara H. (2013). Targeted gene deletion of miRNAs in mice by TALEN system. PLoS One 8:e76004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Christian M, Cermak T, Doyle EL, Schmidt C, Zhang F, Hummel A, Bogdanove AJ. and Voytas DF. (2010). Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases. Genetics 186:757–761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang H, Hu YC, Markoulaki S, Welstead GG, Cheng AW, Shivalila CS, Pyntikova T, Dadon DB, Voytas DF, et al. (2013). TALEN-mediated editing of the mouse Y chromosome. Nat Biotechnol 31:530–532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kato T, Miyata K, Sonobe M, Yamashita S, Tamano M, Miura K, Kanai Y, Miyamoto S, Sakuma T, et al. (2013). Production of Sry knockout mouse using TALEN via oocyte injection. Sci Rep 3:3136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hasegawa K. and Saga Y. (2012). Retinoic acid signaling in Sertoli cells regulates organization of the blood-testis barrier through cyclical changes in gene expression. Development 139:4347–4355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chiarini-Garcia H. and Russell LD. (2002). Characterization of mouse spermatogonia by transmission electron microscopy. Reproduction 123:567–577 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buageaw A, Sukhwani M, Ben-Yehudah A, Ehmcke J, Rawe VY, Pholpramool C, Orwig KE. and Schlatt S. (2005). GDNF family receptor alpha1 phenotype of spermatogonial stem cells in immature mouse testes. Biol Reprod 73:1011–1016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Suzuki H, Sada A, Yoshida S. and Saga Y. (2009). The heterogeneity of spermatogonia is revealed by their topology and expression of marker proteins including the germ cell-specific proteins Nanos2 and Nanos3. Dev Biol 336:222–231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tanaka H, Pereira LA, Nozaki M, Tsuchida J, Sawada K, Mori H. and Nishimune Y. (1997). A germ cell-specific nuclear antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody raised against mouse testicular germ cells. Int J Androl 20:361–366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tokuhiro K, Hirose M, Miyagawa Y, Tsujimura A, Irie S, Isotani A, Okabe M, Toyama Y, Ito C, et al. (2008). Meichroacidin containing the membrane occupation and recognition nexus motif is essential for spermatozoa morphogenesis. J Biol Chem 283:19039–19048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pereira LA, Tanaka H, Nagata Y, Sawada K, Mori H, Chimelli LM. and Nishimune Y. (1998). Characterization and expression of a stage specific antigen by monoclonal antibody TRA 54 in testicular germ cells. Int J Androl 21:34–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.de Rooij DG. (1998). Stem cells in the testis. Int J Exp Pathol 79:67–80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.de Rooij DG. and Russell LD. (2000). All you wanted to know about spermatogonia but were afraid to ask. J Androl 21:776–798 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Raverdeau M, Gely-Pernot A, Feret B, Dennefeld C, Benoit G, Davidson I, Chambon P, Mark M. and Ghyselinck NB. (2012). Retinoic acid induces Sertoli cell paracrine signals for spermatogonia differentiation but cell autonomously drives spermatocyte meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:16582–16587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Huang Z, Rivas B. and Agoulnik AI. (2013). NOTCH1 gain of function in germ cells causes failure of spermatogenesis in male mice. PLoS One 8:e71213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sugimoto R, Nabeshima Y. and Yoshida S. (2012). Retinoic acid metabolism links the periodical differentiation of germ cells with the cycle of Sertoli cells in mouse seminiferous epithelium. Mech Dev 128:610–624 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chakraborty P, Buaas FW, Sharma M, Snyder E, de Rooij DG. and Braun RE. (2014). LIN28A marks the spermatogonial progenitor population and regulates its cyclic expansion. Stem Cells 32:860–873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sutcliffe MJ. and Burgoyne PS. (1989). Analysis of the testes of H-Y negative XOSxrb mice suggests that the spermatogenesis gene (Spy) acts during the differentiation of the A spermatogonia. Development 107:373–380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gebauer F. and Hentze MW. (2004). Molecular mechanisms of translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:827–835 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gaspar NJ, Kinzy TG, Scherer BJ, Humbelin M, Hershey JW. and Merrick WC. (1994). Translation initiation factor eIF-2. Cloning and expression of the human cDNA encoding the gamma-subunit. J Biol Chem 269:3415–3422 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Naranda T, Sirangelo I, Fabbri BJ. and Hershey JW. (1995). Mutations in the NKXD consensus element indicate that GTP binds to the gamma-subunit of translation initiation factor eIF2. FEBS Lett 372:249–252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Erickson FL. and Hannig EM. (1996). Ligand interactions with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2: role of the gamma-subunit. EMBO J 15:6311–6320 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ehrmann IE, Ellis PS, Mazeyrat S, Duthie S, Brockdorff N, Mattei MG, Gavin MA, Affara NA, Brown GM, et al. (1998). Characterization of genes encoding translation initiation factor eIF-2gamma in mouse and human: sex chromosome localization, escape from X-inactivation and evolution. Hum Mol Genet 7:1725–1737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.