Abstract
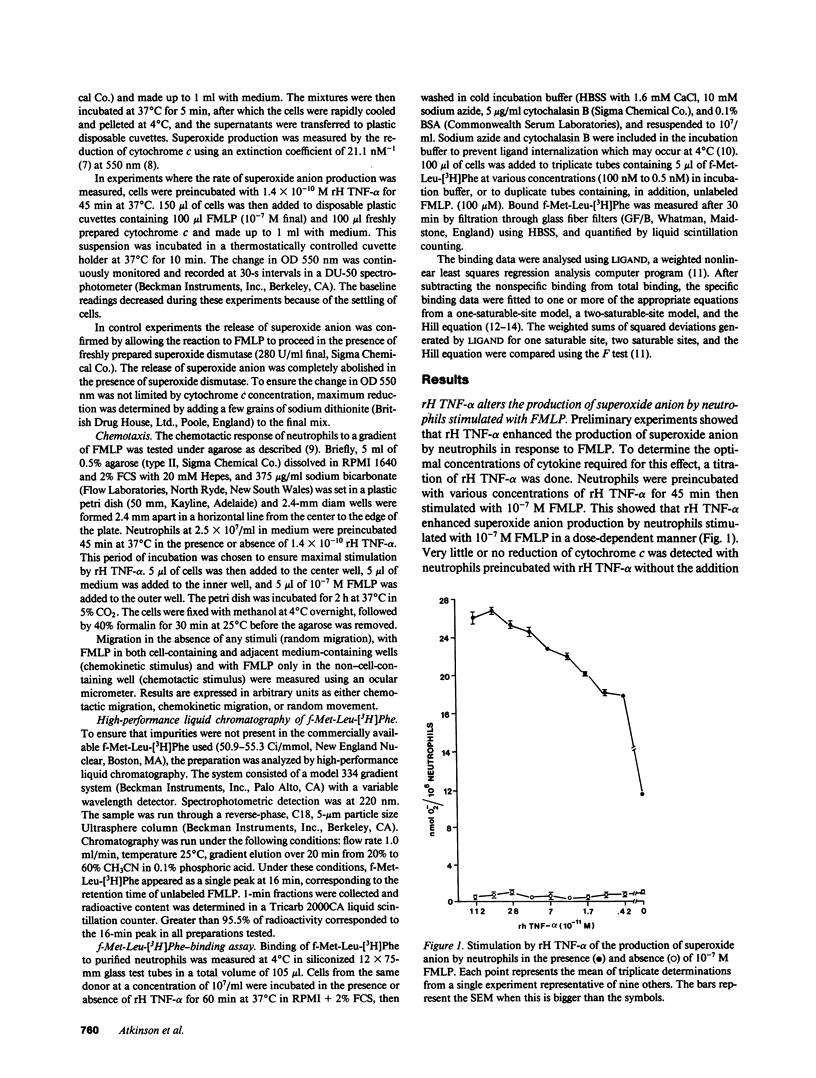
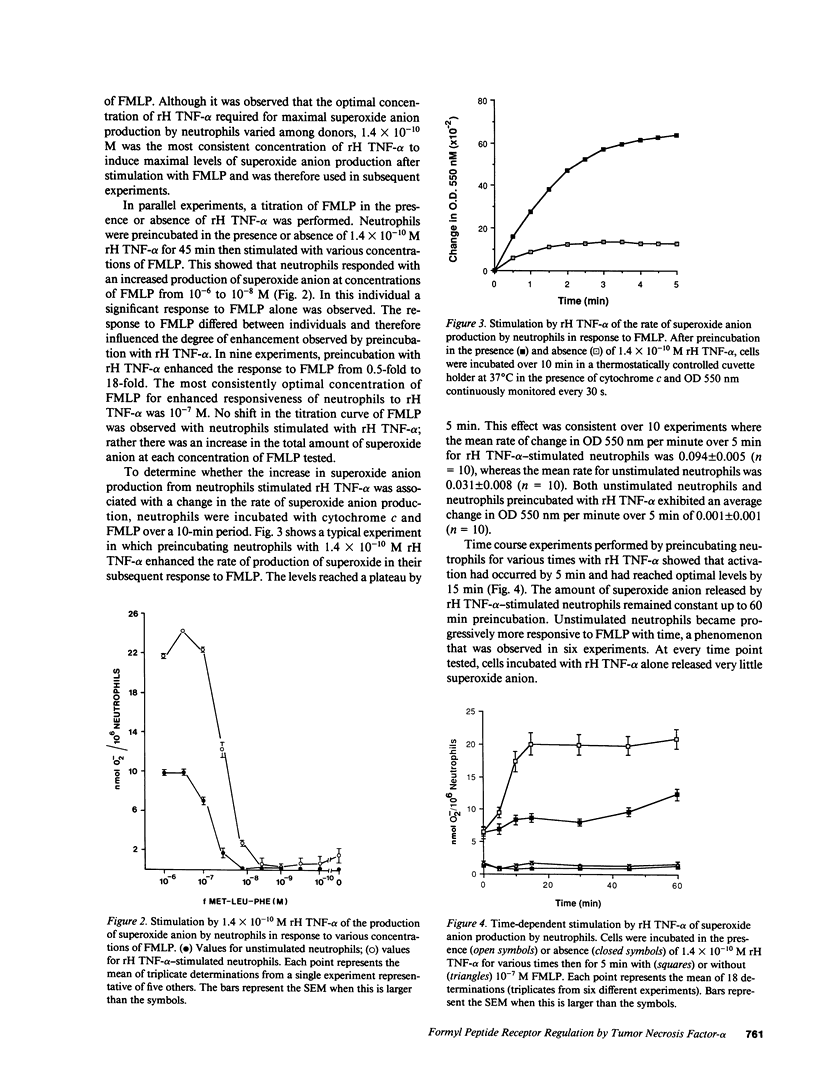
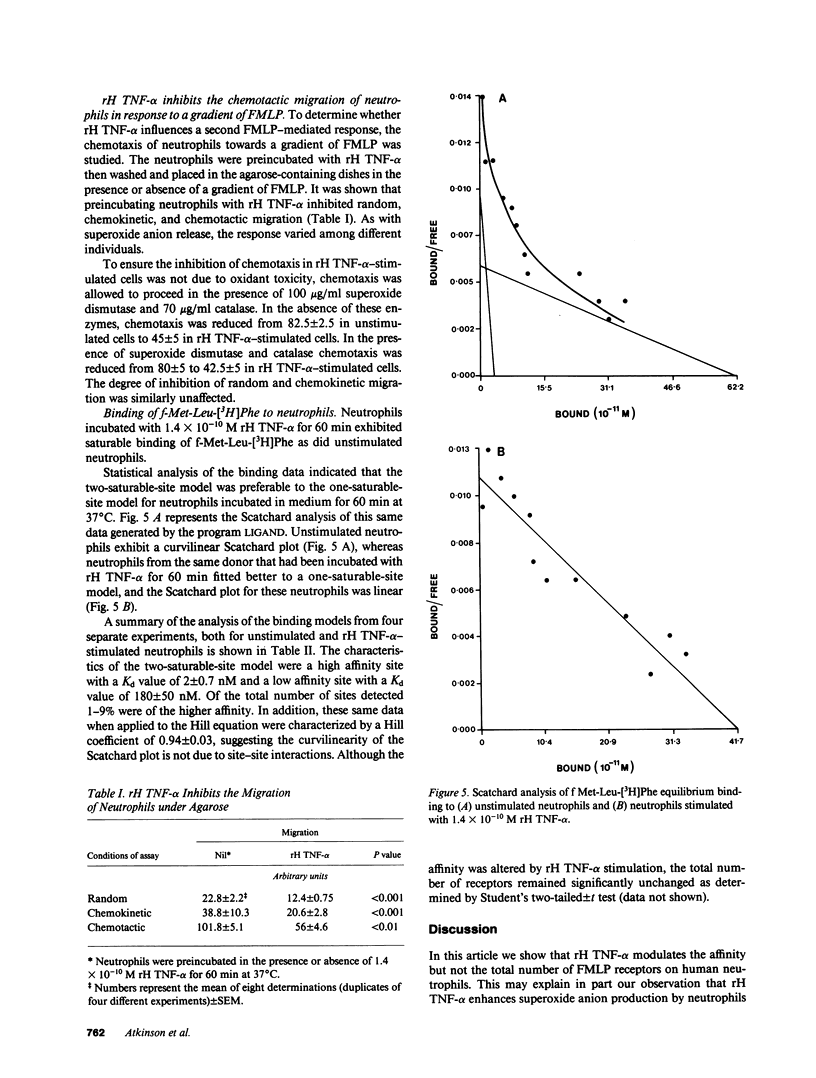
Preincubation of neutrophils with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha (rH TNF-alpha) enhanced the subsequent release of superoxide anion in response to various concentrations of N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (FMLP). Enhanced superoxide anion production was evident by 5 min and had reached a plateau by 15 min. Not only was the total amount of superoxide anion released greater, but the rate of release was also enhanced threefold by rH TNF-alpha. In contrast, rH TNF-alpha reduced or abolished neutrophil locomotion under agarose in response to a gradient of FMLP. Binding studies of f-Met-Leu-[3H]Phe to purified human neutrophils revealed a heterogeneous binding to unstimulated cells. The high affinity component consisted of approximately 2,000 sites per cell and had an average Kd of 2 +/- 0.7 nM (n = 4). The low affinity component consisted of approximately 40,000 sites per cell and had an average Kd of 180 +/- 50 nM (n = 4). rH TNF-alpha caused conversion to a linear Scatchard plot showing no significant change in total binding sites but a single Kd of 40 +/- 10 nM (n = 4). These data indicate that rH TNF-alpha may influence neutrophil responses to FMLP by regulating the affinity of FMLP receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker E. L. A multifunctional receptor on the neutrophil for synthetic chemotactic oligopeptides. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Dec;26(Suppl):701–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. W., Beckner S. K., Farrar W. L. Stimulation of specific GTP binding and hydrolysis activities in lymphocyte membrane by interleukin-2. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):166–168. doi: 10.1038/325166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Human neutrophils contain an intracellular pool of putative receptors for the chemoattractant N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):792–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Muthukumaraswamy N., Pinon D., Wu A., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Formyl peptide chemoattractants: a model of the receptor on rabbit neutrophils. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):257–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer R. J., Day A. R., Radding J. A., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Showell H. J., Becker E. L. Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2404–2410. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Chang F. H., Gifford L. A., Goetzl E. J., Bourne H. R. Pertussis toxin inhibition of chemotactic factor-induced calcium mobilization and function in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):145–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A., Harlan J. M., Sparks L. H., Gamble J. R., Agosti J. M., Waltersdorph A. M. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4220–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Lefkowitz R. J., Snyderman R. Guanine nucleotides modulate the binding affinity of the oligopeptide chemoattractant receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):748–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI111045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Lefkowitz R. J., Snyderman R. The oligopeptide chemotactic factor receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes exists in two affinity states. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., O'Flaherty J. T., Orr W., Showell H. J., Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Quantitative comparisons of various biological responses of neutrophils to different active and inactive chemotactic factors. Immunopharmacology. 1978 Dec;1(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(78)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Smiley P. A. Association of the N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe receptor in human neutrophils with a GTP-binding protein sensitive to pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):869–873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr K. M., Snyderman R. Amphotericin B alters the affinity and functional activity of the oligopeptide chemotactic factor receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1594–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin W. M., Huang C. K., Becker E. L. The formylpeptide chemotactic receptor on rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. I. Evidence for two binding sites with different affinities. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Feltner D. E., Ward P. A. Formyl peptide chemotaxis receptors on the rat neutrophil: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(4):359–375. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J., Spilberg I. Heterologous receptor population for a chemotactic factor F-Met-Leu-Phe on the human neutrophil. Effect of pH and temperature. Inflammation. 1983 Sep;7(3):301–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00917267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Marsh M. L., Kermode J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits the rise in the intracellular concentration of free calcium that is induced by chemotactic factors in rabbit neutrophils: possible role of the "G proteins" in calcium mobilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91603-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., White J. R., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol esters inhibit the fMet-Leu-Phe- and leukotriene B4-stimulated calcium mobilization and enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Quie P. G., Simmons R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1650–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J. Conversion of low-affinity interleukin 2 receptors to a high-affinity state following fusion of cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Rusk C. M. High and low affinity receptors for interleukin 2: implications of pronase, phorbol ester, and cell membrane studies upon the basis for differential ligand affinities. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):142–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Adaptation of human neutrophil responsiveness to the chemoattractant N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine. Heterogeneity and/or negative cooperative interaction of receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6280–6286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. J., Zigmond S. H. Chemotactic peptide receptor modulation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):703–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., López A. F., Williamson D. J. Selective enhancement of the expression of granulocyte functional antigens 1 and 2 on human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate potentiates the action of the calcium ionophore in stimulating arachidonic acid release and production of phosphatidic acid in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):594–600. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Wever R., Roos D. Quantitative aspects of the production of superoxide radicals by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey K. B., O'Shea J., Chused T., Brown E., Takahashi T., Frank M. M., Lawley T. J. Human C5a modulates monocyte Fc and C3 receptor expression. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuli I., Tomonaga A., Synderman R. Chemoattractant receptor functions in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes are divergently altered by membrane fluidizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5906–5910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van GELDER B., SLATER E. C. The extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


