Abstract
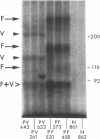
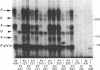
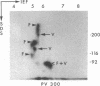
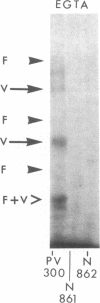
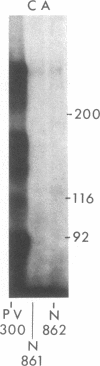
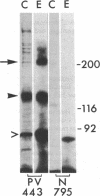
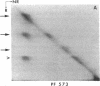
Immunoprecipitations of cultured keratinocyte extracts have shown that pemphigus vulgaris (PV) sera bind a polypeptide of 210,000 mol wt with disulfide-linked chains of 130,000 and 85,000 mol wt. To identify proteins in normal human skin recognized by PV antibodies, we performed immunoprecipitations of normal human epidermal extracts. All 22 PV sera tested immunoprecipitated a complex of polypeptides (PV complex) of 210,000, 130,000, and 85,000 mol wt, after reduction. One- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis showed that the 130,000- and 85,000-mol-wt polypeptides of the PV antigen from both cultured keratinocytes and epidermis have identical charges and sizes. In addition to precipitating the PV complex, 14 of 22 PV sera also have antibodies to a calcium-sensitive epitope on a different complex of polypeptides (PF complex) which has previously been shown to be precipitated by all pemphigus foliaceus (PF) sera. The PF complex consists of polypeptides of 260,000, 160,000, 110,000, and 85,000 mol wt. Although the majority of PV sera also precipitate the PF complex, no PF sera precipitate the PV complex. Thus, PV and PF can be absolutely distinguished on a molecular level using the patients' autoantibodies. The PV and PF complexes, although distinct, have certain similarities. The 85,000-mol-wt polypeptide of each is identical. The 160,000-mol wt-peptide of the PF complex and the 130,000-mol-wt peptide of the PV complex have the same isoelectric point and both are capable of disulfide linkage to the 85,000-mol-wt polypeptide. The PV and PF complexes are closely related and may prove important in cell adhesion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. C., Miller L. J., Schmalstieg F. C., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystryn J. C., Abel E., DeFeo C. Pemphigus foliaceus. Subcorneal intercellular antibodies of unique specificity. Arch Dermatol. 1974 Dec;110(6):857–861. doi: 10.1001/archderm.110.6.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystryn J. C., Rodriguez J. Absence of intercellular antigens in the deep layers of the epidermis in pemphigus foliaceus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):339–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI108944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Patel H., Calvanico N. J. Isolation of pemphigus antigen from human saliva. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):760–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre R. W., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal protein complex with a calcium-sensitive epitope are characteristic of pemphigus foliaceus patients. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1719–1724. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Leukocyte adherence-related glycoproteins LFA-1, Mo1, and p150,95: a new group of monoclonal antibodies, a new disease, and a possible opportunity to understand the molecular basis of leukocyte adherence. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):661–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Shafran K. M., Webber P. S., Lazarus G. S., Singer K. H. Anti-cell surface pemphigus autoantibody stimulates plasminogen activator activity of human epidermal cells. A mechanism for the loss of epidermal cohesion and blister formation. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):259–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Yokoo K. M., Goldman R. D. Further analysis of pemphigus autoantibodies and their use in studies on the heterogeneity, structure, and function of desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1109–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Geoghegan W. D., Jordon R. E. Complement fixation by pemphigus antibody. II. Complement enhanced detachment of epidermal cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):517–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiistala U. Suction blister device for separation of viable epidermis from dermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Feb;50(2):129–137. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulu L., Kusumi A., Steinberg M. S., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1509–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. Epithelial cell adhesion molecules. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Mar;163(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90554-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. L., Wuepper K. D. Isolation and purification of a pemphigus vulgaris antigen from human epidermis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1113–1120. doi: 10.1172/JCI111297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Loftus J. C., Levin E. G., Fair D. S., Dixon D., Forsyth J., Ginsberg M. H. Immunologic relationship between platelet membrane glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa and cell surface molecules expressed by a variety of cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6002–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Identification of the components of the murine T cell antigen receptor complex. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B., Papay R. Pemphigus antibody interaction with human epidermal cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):778–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI109189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu S. Y., Beutner E. H. Isolation and characterization of antigens reactive with pemphigus antibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Nov;61(5):270–276. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12676492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R. A specific antigen-antibody interaction triggers the cellular pathophysiology of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Jul;113 (Suppl 28):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb15628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S. H., Shevach E. M., Katz S. I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Klaus-Kovtun V., Sampaio S. A. Antigenic specificity of fogo selvagem autoantibodies is similar to North American pemphigus foliaceus and distinct from pemphigus vulgaris autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Aug;87(2):197–201. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12695334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Koulu L., Thivolet C. Distinction between epidermal antigens binding pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):313–320. doi: 10.1172/JCI111426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Rubinstein N., Klaus-Kovtun V. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen is synthesized by both human keratinocytes and human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Dec;85(6):542–545. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Yaar M., Hawley-Nelson P., Katz S. I. Pemphigus antibodies identify a cell surface glycoprotein synthesized by human and mouse keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):281–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI110615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]