Abstract
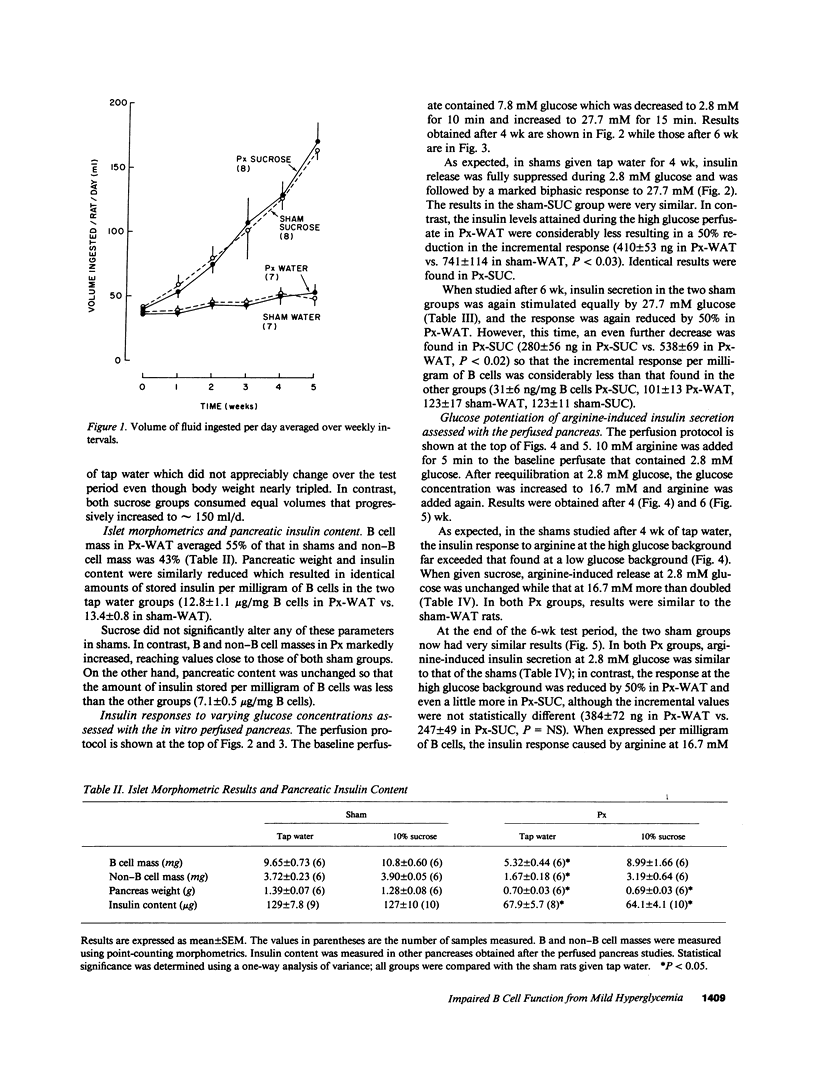
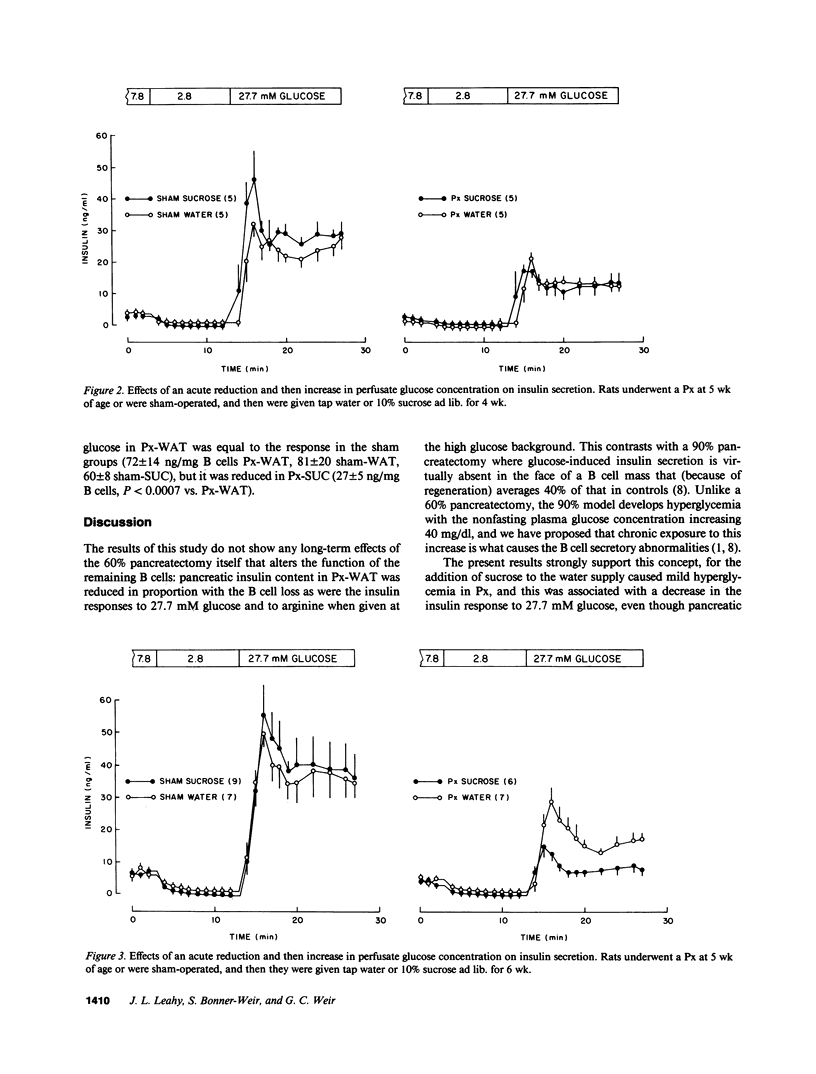
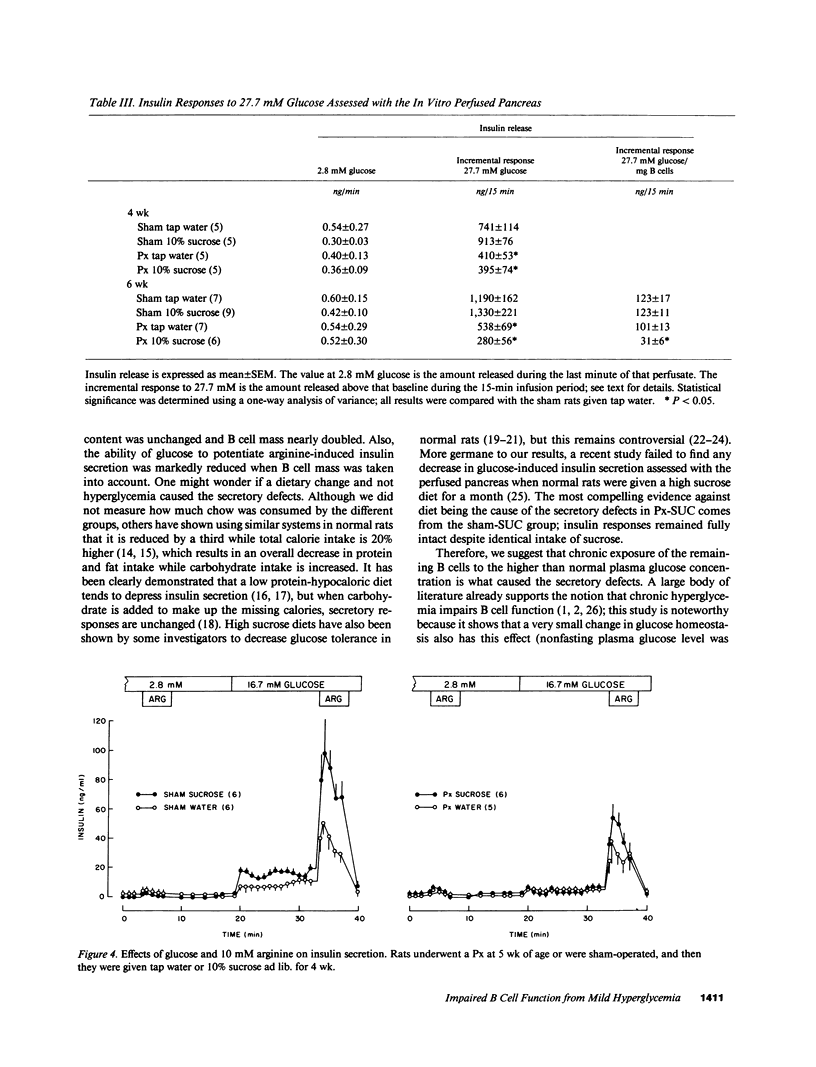
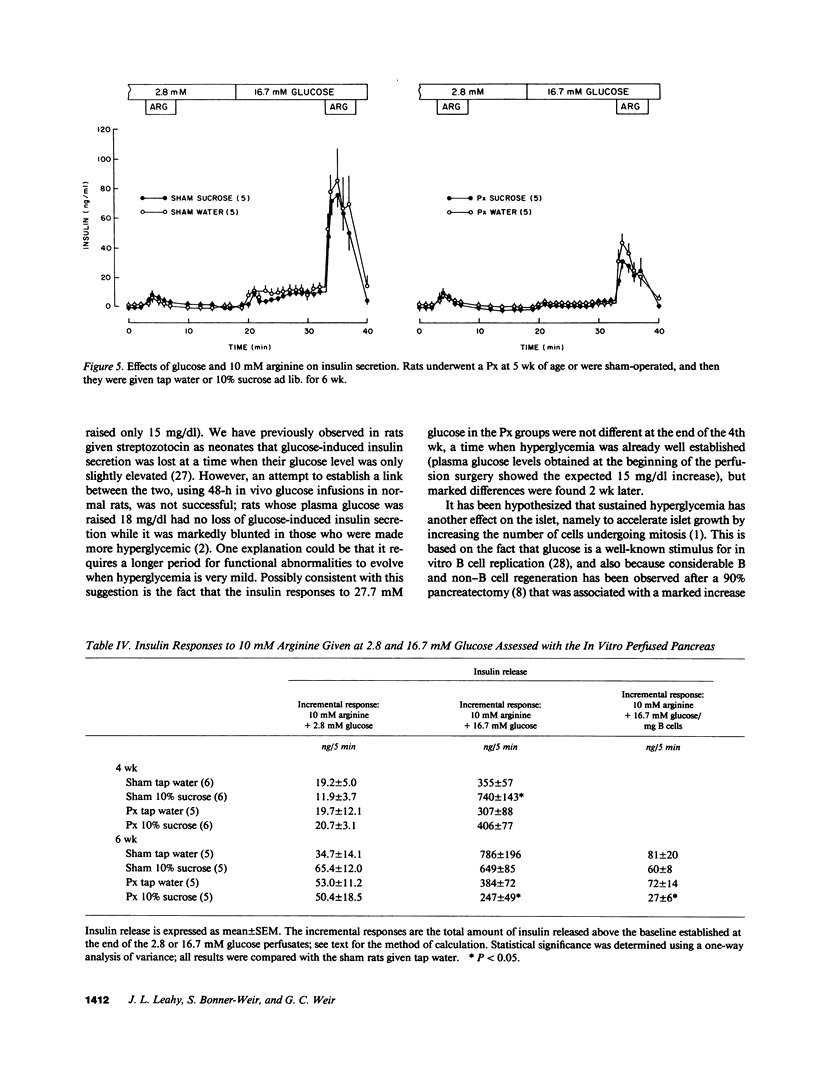
We now describe experiments that allow one to determine the consequences of B cell reduction alone vs. those that result from superimposed mild hyperglycemia. Male CD rats underwent a 60% pancreatectomy (Px); controls were sham operated. 1 wk later, either 10% sucrose (SUC) was substituted as fluid supply or tap water was continued (WAT). Plasma glucose and insulin values in Px-WAT remained equal to the sham groups; in Px-SUC the values were euglycemic for 25 d, but then nonfasting plasma glucose rose 15 mg/dl. After 6 wk, B cell mass in Px-WAT was reduced by 45% and non-B cell mass by 57%. In contrast, in Px-SUC both masses were comparable to the sham groups. The insulin response to 27.7 mM glucose was measured using the in vitro perfused pancreas. The responses were reduced in Px-WAT but in proportion to their reduced B cell mass; in contrast, it was 75% less than expected in Px-SUC. Also, the response to arginine given at 16.7 mM glucose was reduced only in Px-SUC. These results show that a lowering of B cell mass that does not result in hyperglycemia has no adverse effect on the remaining B cells. On the other hand, if even mild hyperglycemia develops, B cell function becomes impaired and results in inappropriately reduced insulin stores and insulin responses to marked stimuli.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Weir G. C. Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1544–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Discordance of exocrine and endocrine growth after 90% pancreatectomy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Robertson R. P., Lerner R. L., Hazzard W. R., Ensinck J. W., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Feb;42(2):222–229. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. M., TEITELBAUM A. EFFECT OF DIETARY SUCROSE AND STARCH ON ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE AND INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITY. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jan;206:105–108. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L. Beta cell replication in rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Effects of glucose, tolbutamide, glucocorticoid, growth hormone and glucagon. Diabetes. 1973 Sep;22(9):687–693. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.9.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier G., Bolles R. Some determinants of intake of sucrose solutions. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1968 Jun;65(3):379–383. doi: 10.1037/h0025824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganda O. P., Srikanta S., Brink S. J., Morris M. A., Gleason R. E., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Differential sensitivity to beta-cell secretagogues in "early," type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1984 Jun;33(6):516–521. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.6.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Elevated proinsulin biosynthesis in vitro from a rat model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1983 Mar;32(3):277–283. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallfrisch J., Lazar F., Jorgensen C., Reiser S. Insulin and glucose responses in rats fed sucrose or starch. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Apr;32(4):787–793. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Berry M. N., Williams M. C., Severinghaus E. M. A simple and inexpensive membrane "lung" for small organ perfusion. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanarek R. B., Hirsch E. Dietary-induced overeating in experimental animals. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):154–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kergoat M., Bailbé D., Portha B. Effect of high sucrose diet on insulin secretion and insulin action: a study in the normal rat. Diabetologia. 1987 Apr;30(4):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00270424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laube H., Schatz H., Nierle C., Fussgänger R., Pfeiffer E. F. Insulin secretion and biosynthesis in sucrose fed rats. Diabetologia. 1976 Oct;12(5):441–446. doi: 10.1007/BF01219507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Cooper H. E., Deal D. A., Weir G. C. Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo glucose infusions. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):908–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI112389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. S., Wright P. G., Marcus F. Failure to secrete immunoreactive insulin by rats fed a low protein diet. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Feb;102(2):240–245. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. J., Anderson J. W. Effects of high sucrose or starch-bran diets on glucose and lipid metabolism of normal and diabetic rats. J Nutr. 1977 Apr;107(4):584–595. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.4.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orland M. J., Chyn R., Permutt M. A. Modulation of proinsulin messenger RNA after partial pancreatectomy in rats. Relationships to glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2047–2055. doi: 10.1172/JCI111924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portha B., Giroix M. H., Picon L. Effect of diet on glucose tolerance and insulin response in chemically diabetic rats. Metabolism. 1982 Dec;31(12):1194–1199. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikanta S., Ganda O. P., Jackson R. A., Gleason R. E., Kaldany A., Garovoy M. R., Milford E. L., Carpenter C. B., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. Type I diabetes mellitus in monozygotic twins: chronic progressive beta cell dysfunction. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Sep;99(3):320–326. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-3-320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Crace C. J., Milner R. D. Persistent impairment of insulin secretory response to glucose in adult rats after limited period of protein-calorie malnutrition early in life. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):454–458. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. F., Fletcher D. J., May J. M., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Abnormal islet and adipocyte function in young B-cell-deficient rats with near-normoglycemia. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):170–175. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Grundy S. Hyperglycaemia as an inducer as well as a consequence of impaired islet cell function and insulin resistance: implications for the management of diabetes. Diabetologia. 1985 Mar;28(3):119–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00273856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand A. L., Lupien J., Bukowiecki L. J. Synergistic improvement of glucose tolerance by sucrose feeding and exercise training. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):E607–E614. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.6.E607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R. Principles and methods for the morphometric study of the lung and other organs. Lab Invest. 1963 Feb;12:131–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Knowlton S. D., Martin D. B. Glucagon secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Studies with glucose and catecholamines. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1403–1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI107887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Leahy J. L., Bonner-Weir S. Experimental reduction of B-cell mass: implications for the pathogenesis of diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(1-2):125–161. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: interplay between B-cell inadequacy and insulin resistance. Am J Med. 1982 Oct;73(4):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



