Abstract
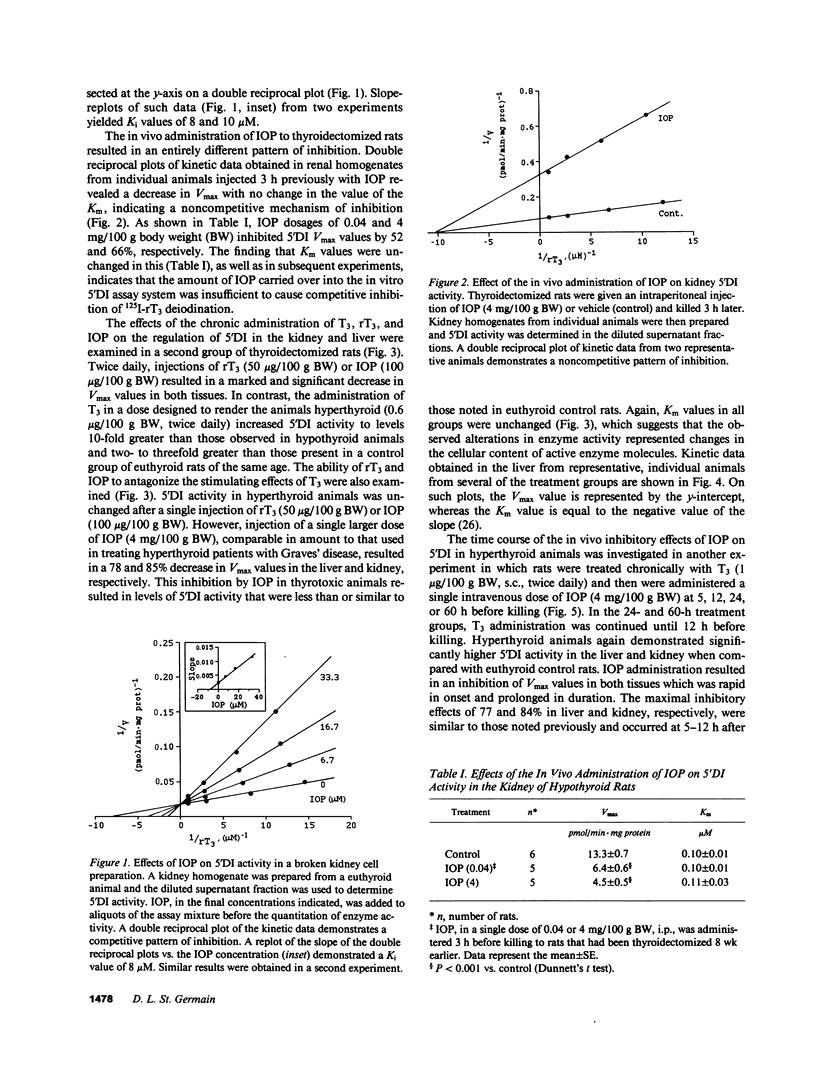
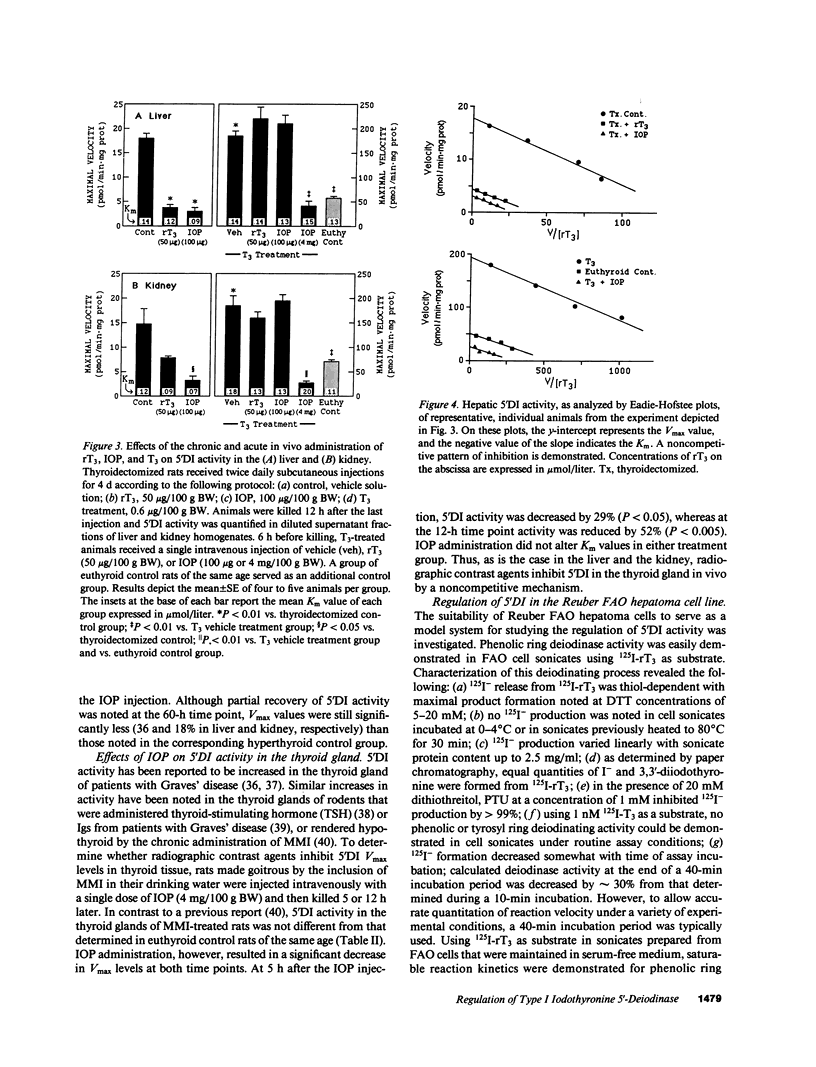
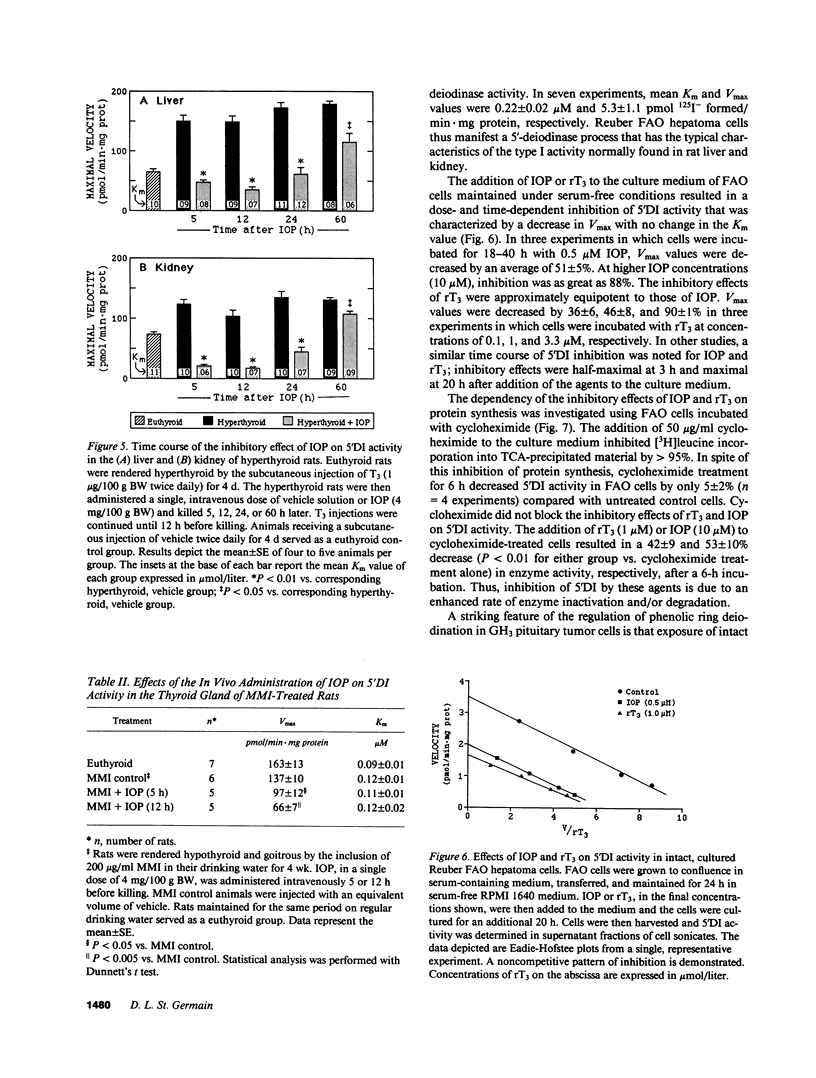
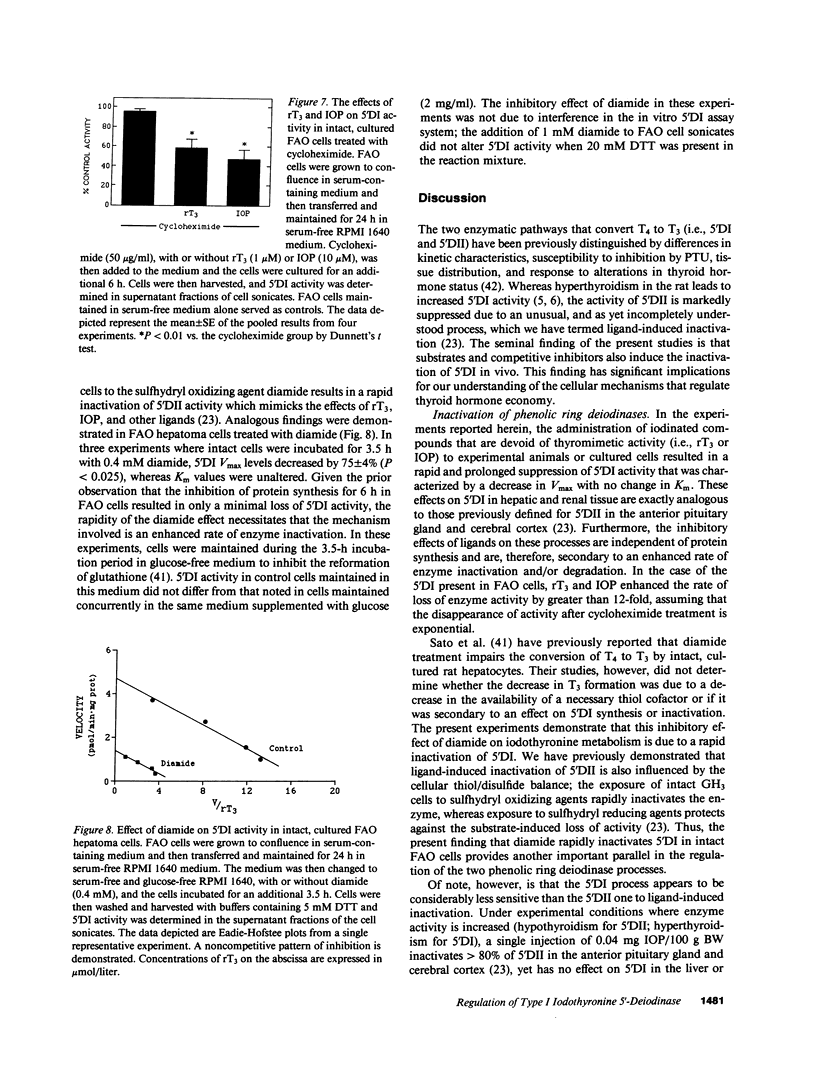
Alterations in thyroid hormone status and the administration of radiographic contrast agents can markedly influence iodothyronine metabolism and, in particular, the activity of type I 5'-deiodinase (5'DI). In the present studies, the mechanisms responsible for these effects have been reassessed. As previously reported, the addition of iopanoic acid (IOP) to broken cell preparations resulted in a competitive pattern of 5'DI inhibition. However, the in vivo administration to rats of IOP or 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (rT3) resulted in a noncompetitive pattern of inhibition of 5'DI in the liver, kidney, and thyroid gland, whereby marked decreases in maximal enzyme velocity (V max) were noted, with no change in the value of the Michaelis-Menten constant. In rats rendered hyperthyroid by the injection of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3), 5'DI activity was significantly increased in the liver and the kidney. The administration of IOP to these thyrotoxic animals resulted in a rapid loss of enzyme activity characterized by an approximate 80% decrease in 5'DI V max values in both tissues. Furthermore, this inhibitory effect persisted for longer than 60 h after a single IOP injection. IOP administration also decreased 5'DI V max levels in the thyroid gland by 52%. In other experiments, treatment of intact Reuber FAO hepatoma cells with IOP or rT3 induced a rapid decrease in 5'DI V max levels. In cells treated with cycloheximide, these agents enhanced the rate of disappearance of enzyme activity by greater than 12-fold, indicating a predominant effect on accelerating the rate of enzyme inactivation and/or degradation. These studies demonstrate that iodothyronines and other iodinated compounds have complex regulatory effects on 5'DI that entail alterations in the rates of both enzyme activation and inactivation. The previously accepted concept that rT3 and IOP impair thyroxine (T4) to T3 conversion in vivo by acting as competitive inhibitors is an oversimplification. Rather, the clinically beneficial effects of administering these agents to patients with hyperthyroidism may result primarily from the rapid and prolonged inactivation of 5'DI which occurs in the thyroid gland and peripheral tissues.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENUA R. S., KUMAOKA S., LEEPER R. D., RAWSON R. W. The effect of dl-3,3',5'-triiodothyronine in Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Oct;19:1344–1346. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-10-1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgi H., Wimpfheimer C., Burger A., Zaunbauer W., Rösler H., Lemarchand-Béraud T. Changes of circulating thyroxine, triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine after radiographic contrast agents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Dec;43(6):1203–1210. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-6-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A study of extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine (T4) to 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in vitro. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):453–463. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Chopra U., Wu S. Y., Fisher D. A., Nakamura Y. Pathways of metabolism of thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1978;34:521–567. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571134-0.50018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coiro V., Harris A., Goodman H. M., Vagenakis A., Braverman L. Effect of pharmacological quantities of infused 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine on thyroxine monodeiodination to 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):68–75. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtin F., Pelletier G., Walker P. Subcellular localization of thyroxine 5'-deiodinase activity in bovine anterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson V. J., Cavalieri R. R., Rosenberg L. L. Thyroxine-5'-deiodinase of rat thyroid, but not that of liver, is dependent on thyrotropin. Endocrinology. 1982 Aug;111(2):434–440. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-2-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekkes D., Hennemann G., Visser T. J. One enzyme for the 5'-deiodination of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine and 3',5'-diiodothyronine in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 May 1;31(9):1705–1709. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90672-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galton V. A., Hiebert A. The ontogeny of the enzyme systems for the 5'- and 5-deiodination of thyroid hormones in chick embryo liver. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2604–2610. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey K. Statistics in practice. Comparing the means of several groups. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1450–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami A., Rosenberg I. N. Iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase in brown adipose tissue: thiol activation and propylthiouracil inhibition. Endocrinology. 1986 Aug;119(2):916–923. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-2-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSTEE B. H. J. On the evaluation of the constants Vm and KM in enzyme reactions. Science. 1952 Sep 26;116(3013):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3013.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han D. C., Sato K., Fujii Y., Tsushima T., Shizume K. 3,3',5'-Triiodothyronine inhibits iodothyronine-5'-deiodinating activity induced by 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine at equimolar concentrations in cultured fetal mouse liver. Endocrinology. 1986 Sep;119(3):1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-3-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Inada M., Tanaka K., Mashio Y., Naito K., Nishikawa M., Imura H. Triiodothyronine generation from thyroxine in human thyroid: enhanced conversion in Graves' thyroid tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1211–1217. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. S., Crutchfield F. L., Dratman M. B. Effect of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism on triiodothyronine production in perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1984 Mar;114(3):992–997. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-3-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. Changes in the particulate subcellular component of hepatic thyroxine-5'-monodeiodinase in hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Aug;105(2):548–554. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-2-548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. The role of thyroid hormone deiodination in the regulation of hypothalamo-pituitary function. Neuroendocrinology. 1984 Mar;38(3):254–260. doi: 10.1159/000123900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Utiger R. D. Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Mar;7(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(78)80037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Utiger R. D. Iodothyronine metabolism in liver and kidney homogenates from hyperthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Endocrinology. 1978 Jul;103(1):156–161. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Utiger R. D. Iodothyronine metabolism in rat liver homogenates. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):459–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI108957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpman B. A., Rapoport B., Filetti S., Fisher D. A. Treatment of neonatal hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease with sodium ipodate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jan;64(1):119–123. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinmann R. E., Vagenakis A. G., Braverman L. E. The effect of iopanoic acid on the regulation of thyrotropin secretion in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Aug;51(2):399–403. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg P., Boye N. Outer and inner ring monodeiodination of thyroxine by dog thyroid and liver: a comparative study using a particulate cell fraction. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):2124–2130. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-2124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg P. Mechanisms governing the relative proportions of thyroxine and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine in thyroid secretion. Metabolism. 1984 Apr;33(4):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg P. The effect of some iodine-containing radiocontrast agents on iodothyronine secretion from the perfused canine thyroid. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1904–1908. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg P. Thyroxine entering the thyroid gland via the vascular bed may leave the gland as triiodothyronines. Studies with perfused dog thyroid lobes. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):895–900. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Wilson I. B. Enzymic parameters: measurement of V and Km. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 22;242(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Rosenberg I. N. Iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase from rat kidney: substrate specificity and the 5'-deiodination of reverse triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1376–1383. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Silva J. E., Kaplan M. M., Mellen S. A., Visser T. J., Larsen P. R. Acute posttranscriptional regulation of cerebrocortical and pituitary iodothyronine 5'-deiodinases by thyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1984 Mar;114(3):998–1004. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-3-998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann U. D., Shaw E. A., Kaplan M. M. Iodothyronine deiodination reaction types in several rat tissues: effects of age, thyroid status, and glucocorticoid treatment. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1513–1521. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obregon M. J., Pascual A., Mallol J., Morreale de Escobar G., Escobar del Rey F. Evidence against a major role of L-thyroxine at the pituitary level: studies in rats treated with iopanoic acid (telepaque). Endocrinology. 1980 Jun;106(6):1827–1836. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-6-1827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITMAN C. S., BARKER S. B. Inhibition of thyroxine action by 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1959 Mar;64(3):466–468. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-3-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN C. S., BARKER S. B. Antithyroxine effects of some thyroxine analogues. Am J Physiol. 1959 Dec;197:1271–1274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN J. A., TINGLEY J. O., NICKERSON J. F., HILL S. R., Jr Antimetabolic activity of 3,3',5'-triiodo-DL-thyronine in man. Metabolism. 1960 Mar;9:293–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roti E., Robuschi G., Manfredi A., D'Amato L., Gardini E., Salvi M., Montermini M., Barlli A. L., Gnudi A., Braverman L. E. Comparative effects of sodium ipodate and iodide on serum thyroid hormone concentrations in patients with Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Apr;22(4):489–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb00148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Mimura H., Wakai K., Tomori N., Tsushima T., Shizume K. Modulating effect of glutathione disulfide on thyroxine-5'-deiodination by rat hepatocytes in primary culture: effect of glucose. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):878–886. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik O. A., Ledbetter M. L., Malter J. S. Role of aminoacylation of histidyl-tRNA in the regulation of protein degradation in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6322–6329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen D. C., Wu S. Y., Chopra I. J., Huang H. W., Shian L. R., Bian T. Y., Jeng C. Y., Solomon D. H. Long term treatment of Graves' hyperthyroidism with sodium ipodate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):723–727. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Leonard J. L., Crantz F. R., Larsen P. R. Evidence for two tissue-specific pathways for in vivo thyroxine 5'-deiodination in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1176–1184. doi: 10.1172/JCI110554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Leonard J. L. Regulation of rat cerebrocortical and adenohypophyseal type II 5'-deiodinase by thyroxine, triiodothyronine, and reverse triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1627–1635. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallridge R. C., Wartofsky L., Burman K. D. The effect of experimental hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism on 5'-monodeiodination of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine and 3',5'-diiodothyronine by rat liver and kidney. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):2066–2069. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-2066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Germain D. L. The effects and interactions of substrates, inhibitors, and the cellular thiol-disulfide balance on the regulation of type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):1860–1868. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara M., Lau R., Wasser H. L., Nelson A. M., Kuma K., Hershman J. M. Thyroid T4 5'-deiodinase activity in normal and abnormal human thyroid glands. Metabolism. 1984 Apr;33(4):332–336. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. S., Tsou C. T., Lin W. H., Hershman J. M. Long term treatment of Graves' disease with iopanoic acid (Telepaque). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Oct;65(4):679–682. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-4-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Johnson D. E. The effect of repeated administration of ipodate (Oragrafin) in hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Dec;47(6):1358–1362. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-6-1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Reggio R., Florsheim W. H. Characterization of thyrotropin-induced increase in iodothyronine monodeiodinating activity in mice. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):901–908. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Reggio R., Florsheim W., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H. Stimulation of thyroidal iodothyronine 5'-monodeiodinase by long-acting thyroid stimulator (LATS). Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1987 Feb;114(2):193–200. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1140193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Shyh T. P., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Huang H. W., Chu P. C. Comparison sodium ipodate (oragrafin) and propylthiouracil in early treatment of hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Mar;54(3):630–634. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-3-630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn J., Roelfsema F., van der Heide D. Contribution fron local conversion of thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine to intracellular 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine in several organs in hypothyroid rats at isotope equilibrium. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Nov;101(3):386–396. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1010386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn J., van der Heide D., Roelfsema F. The contribution of local thyroxine monodeiodination to intracellular 3,5, 3'-triiodothyronine in several tissues of hyperthyroid rats at isotopic equilibrium. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):174–182. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



