Abstract
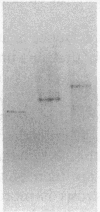
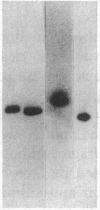
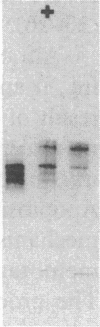
The possible role of group specific component (Gc) (vitamin D-binding protein) in the clearance of cellular actin entering the circulation was examined with 125I-labeled Gc and actin injected into a rabbit model. Although filamentous F-actin is depolymerized primarily by plasma gelsolin, greater than or equal to 90% 125I-actin injected in either monomeric G- or F-form became complexed eventually with Gc (1:1 molar ratio). Clearance of Gc complexes was much faster (greater than 90% within 5 h) than that of native Gc (t1/2 = 17.2 h). Nephrectomy did not significantly alter the clearance of either Gc or actin. Since Gc complexes are dramatically increased in situations of tissue necrosis such as in fulminant hepatic failure, the current results suggest a crucial role for Gc in sequestration and clearance of released cellular actin.
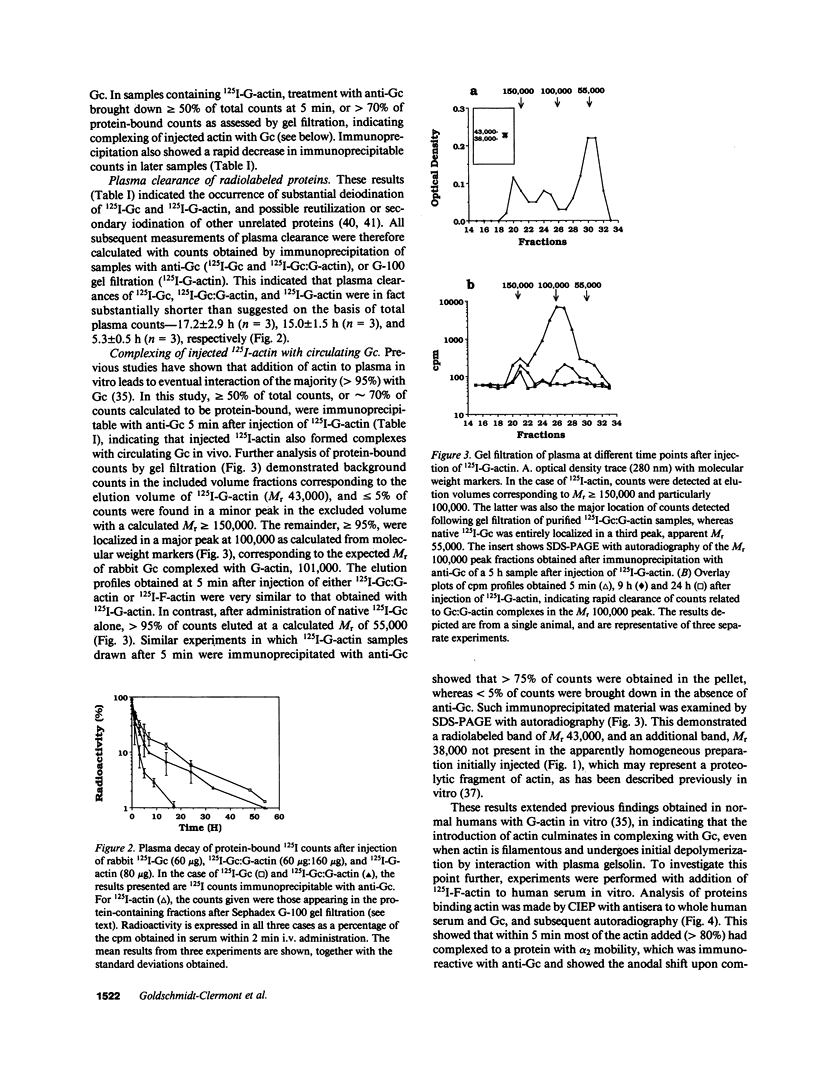
Full text
PDF


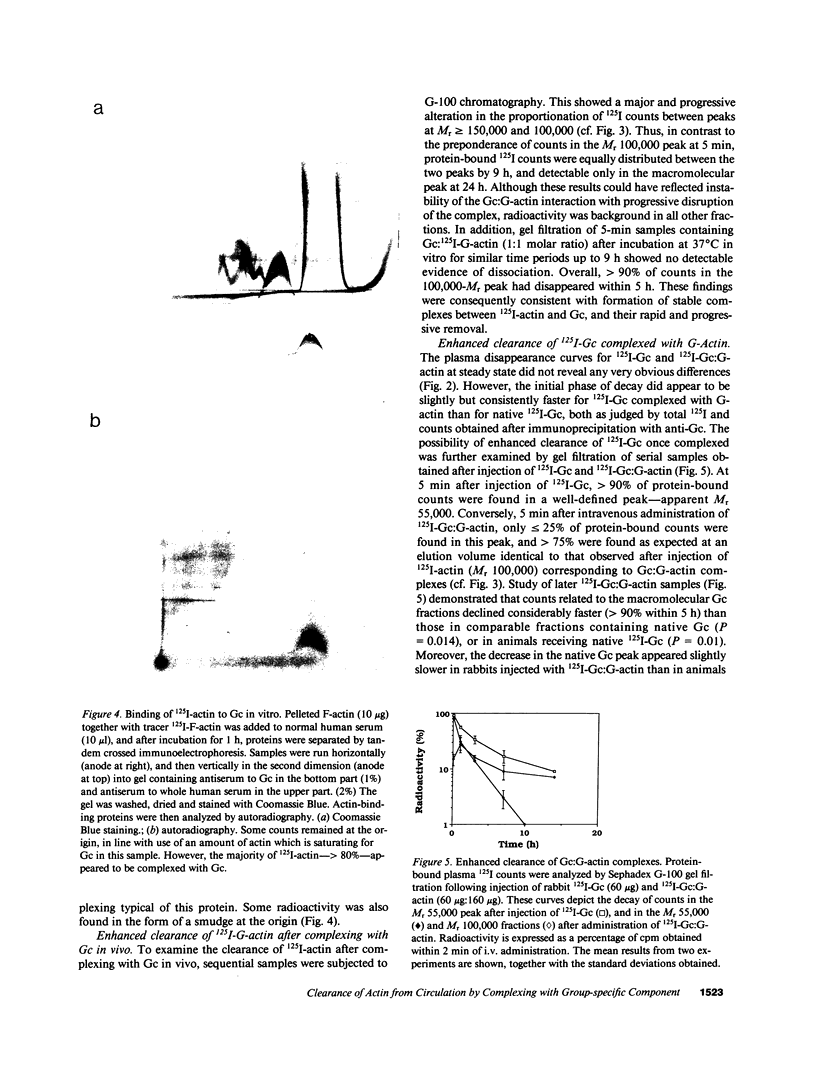



Images in this article
Selected References
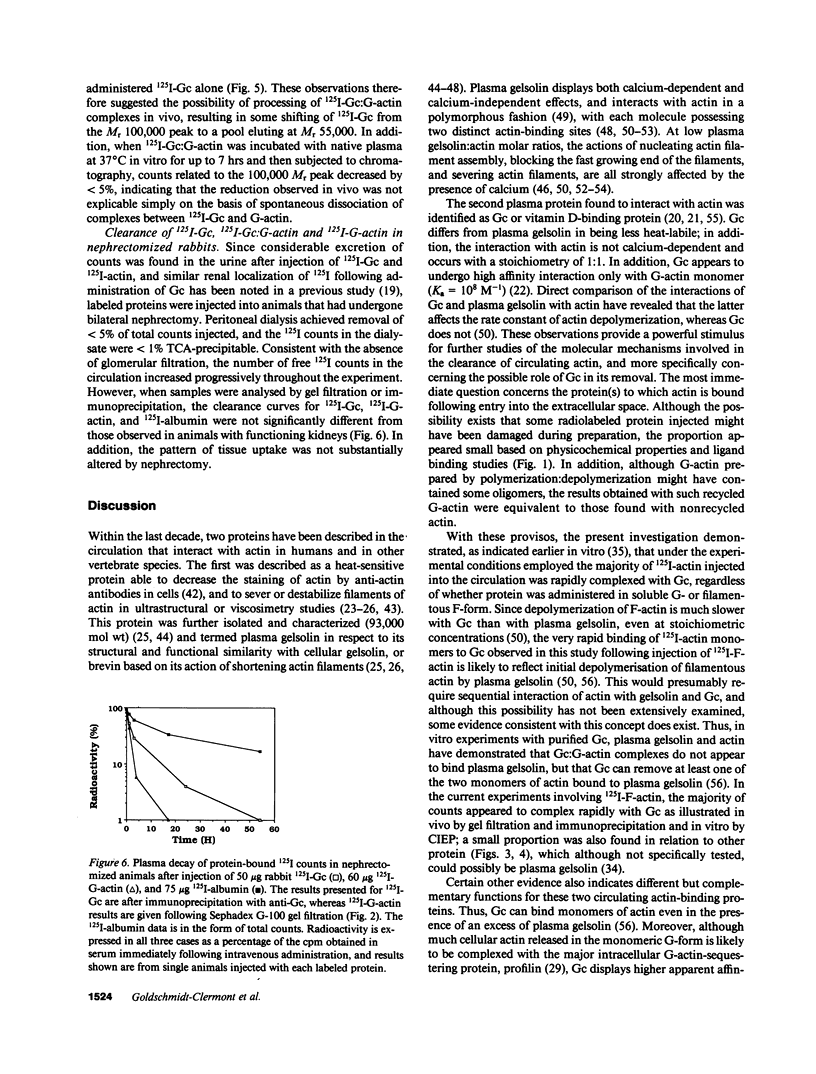
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouillon R., Van Kerkhove P., De Moor P. Characteristics of the vitamin D binding protein in different species. Calcif Tissue Res. 1976 Aug;21 (Suppl):172–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon R., Vandoren G., Van Baelen H., De Moor P. Lack of effect of the vitamin D status on the concentration of the vitamin D-binding protein in rat serum. Endocrinology. 1980 Jul;107(1):160–163. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-1-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon R., van Baelen H., de Moor P. The measurement of the vitamin D-binding protein in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Aug;45(2):225–231. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Kurth M. C. Actin-gelsolin interactions. Evidence for two actin-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7480–7487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaponnier C., Borgia R., Rungger-Brändle E., Weil R., Gabbiani G. An actin-destabilizing factor is present in human plasma. Experientia. 1979 Aug 15;35(8):1039–1041. doi: 10.1007/BF01949928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H. The variants of the group-specific component. A review of their distribution in human populations. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Sep-Oct;9(9):1133–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constans J., Oksman F., Viau M. Binding of the apo and holo forms of the serum vitamin D-binding protein to human lymphocyte cytoplasm and membrane by indirect immunofluorescence. Immunol Lett. 1981 Aug;3(3):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(81)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., David E. V. Serum vitamin D-binding protein is a third member of the albumin and alpha fetoprotein gene family. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2420–2424. doi: 10.1172/JCI112256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E. Rat vitamin D binding protein. Determination of the full-length primary structure from cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3441–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Walgate J., Haddad J. G., Jr Human serum binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites. I. Physicochemical and immunological identification in human tissues. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5958–5964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Walgate J., Haddad J. G., Jr Human serum binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites. II. Specific, high affinity association with a protein in nucleated tissue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5965–5971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coué M., Korn E. D. Interaction of plasma gelsolin with ADP-actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3628–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Schanfield M. S., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Group-specific component (Gc) proteins bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D. L., Arnaud P., Galbraith R. M. Evidence of increased Gc:actin complexes in pregnant serum: a possible result of trophoblast embolism. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1983 Dec;4(4):185–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1983.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D. L., Werner P. A., Cheng M. H., Galbraith R. M. Presence of Gc (vitamin D-binding protein) and interactions with actin in human placental tissue. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol. 1985 Jan;7(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1985.tb00257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagraeus A., Norberg R. Anti-actin antibodies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:1–13. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Allen R. C., Nel A. E., Emerson D. L., Day J. R., Galbraith R. M. Gc (vitamin D-binding protein) binds the 33.5 K tryptic fragment of actin. Life Sci. 1986 Feb 24;38(8):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90588-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Galbraith R. M., Emerson D. L., Marsot F., Nel A. E., Arnaud P. Distinct sites on the G-actin molecule bind group-specific component and deoxyribonuclease I. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 1;228(2):471–477. doi: 10.1042/bj2280471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Galbraith R. M., Emerson D. L., Werner P. A., Nel A. E., Lee W. M. Accurate quantitation of native Gc in serum and estimation of endogenous Gc: G-actin complexes by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jun 14;148(3):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Van Alstyne E. L., Day J. R., Emerson D. L., Nel A. E., Lazarchick J., Galbraith R. M. Group-specific component (vitamin D binding protein) prevents the interaction between G-actin and profilin. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6467–6472. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHFELD J. Immune-electrophoretic demonstration of qualitative differences in human sera and their relation to the haptoglobins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb04844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Fraser D. R., Lawson D. E. Vitamin D plasma binding protein. Turnover and fate in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1550–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI110186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G. Human serum binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites (DBP): evidence that actin is the DBP binding component in human skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):538–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper K. D., McLeod J. F., Kowalski M. A., Haddad J. G. Vitamin D binding protein sequesters monomeric actin in the circulation of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1365–1370. doi: 10.1172/JCI112963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., Schwartz J. H. Characterization of brevin, a serum protein that shortens actin filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6798–6802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. E., Bamburg J. R., Weeds A. G. Actin filament disassembly in blood plasma. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. E., Weeds A. G. Plasma actin depolymerizing factor has both calcium-dependent and calcium-independent effects on actin. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2728–2741. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Chaponnier C., Lind S. E., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P., Yin H. L. Interactions of gelsolin and gelsolin-actin complexes with actin. Effects of calcium on actin nucleation, filament severing, and end blocking. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3714–3723. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Lind S. E., Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Effects of semi-dilute actin solutions on the mobility of fibrin protofibrils during clot formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 16;841(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P., Lind S. E. Sequential binding of actin monomers to plasma gelsolin and its inhibition by vitamin D-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):72–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90878-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Blum C. B., Ramakrishnan R., Dell R. B., Goodman D. S. Turnover of the plasma binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Dec;53(6):1110–1116. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-6-1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Actin polymerization and its regulation by proteins from nonmuscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):672–737. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Janmey P. A., Mole J. E., Yin H. L. Isolation and properties of two actin-binding domains in gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15232–15238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laki K., Muszbek L. On the interaction of F-actin with fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Emerson D. L., Werner P. A., Arnaud P., Goldschmidt-Clermont P., Galbraith R. M. Decreased serum group-specific component protein levels and complexes with actin in fulminant hepatic necrosis. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):271–275. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees A., Haddad J. G., Lin S. Brevin and vitamin D binding protein: comparison of the effects of two serum proteins on actin assembly and disassembly. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):3038–3047. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind S. E., Smith D. B., Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Role of plasma gelsolin and the vitamin D-binding protein in clearing actin from the circulation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):736–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI112634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Carrel S., Forni M., Ritschard J., Donath A., Alberto P. Tumor localization of radiolabeled antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with carcinoma: a critical evaluation. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 3;303(1):5–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007033030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. F., Kowalski M. A., Haddad J. G. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to human serum vitamin D binding protein (Gc globulin): recognition of an epitope hidden in membranes of circulating monocytes. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):77–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg R., Thorstensson R., Utter G., Fagraeus A. F-Actin-depolymerizing activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaloni D., Carlier M. F., Coué M., Lal A. A., Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. The critical concentration of actin in the presence of ATP increases with the number concentration of filaments and approaches the critical concentration of actin.ADP. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6274–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini M., Emerson D. L., Galbraith R. M. Linkage between surface immunoglobulin and cytoskeleton of B lymphocytes may involve Gc protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):73–74. doi: 10.1038/306073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini M., Galbraith R. M., Emerson D. L., Nel A. E., Arnaud P. Structural studies of T lymphocyte Fc receptors. Association of Gc protein with IgG binding to Fc gamma. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1804–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini M., Galbraith R. M., Werner P. A., Emerson D. L., Arnaud P. Gc (vitamin D binding protein) binds to cytoplasm of all human lymphocytes and is expressed on B-cell membranes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;31(2):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte F., Harricane M. C. Interactions of plasma gelsolin with actin. Isolation and characterization of binary and ternary plasma-gelsolin-actin complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 2;154(1):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoentgen F., Metz-Boutigue M. H., Jollès J., Constans J., Jollès P. Homology between the human vitamin D-binding protein (group specific component), alpha-fetoprotein and serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80738-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorstensson R., Utter G., Norberg R. Further characterization of the Ca2+-dependent F-actin-depolymerizing protein of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):11–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Baelen H., Bouillon R., De Moor P. Vitamin D-binding protein (Gc-globulin) binds actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2270–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J. S., Sandoval I. V. Purification and characterization of a new mammalian serum protein with the ability to inhibit actin polymerization and promote depolymerization of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3983–3991. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Brune J. L., Naylor S. L., Cupples R. L., Naberhaus K. H., Bowman B. H. Human group-specific component (Gc) is a member of the albumin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7994–7998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Albrecht J. H., Fattoum A. Identification of gelsolin, a Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein of actin gel-sol transformation, and its intracellular distribution in a variety of cells and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):901–906. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Purification and structural properties of gelsolin, a Ca2+-activated regulatory protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9490–9493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P. Ca2+ control of actin gelation. Interaction of gelsolin with actin filaments and regulation of actin gelation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9494–9500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]