Abstract
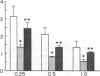
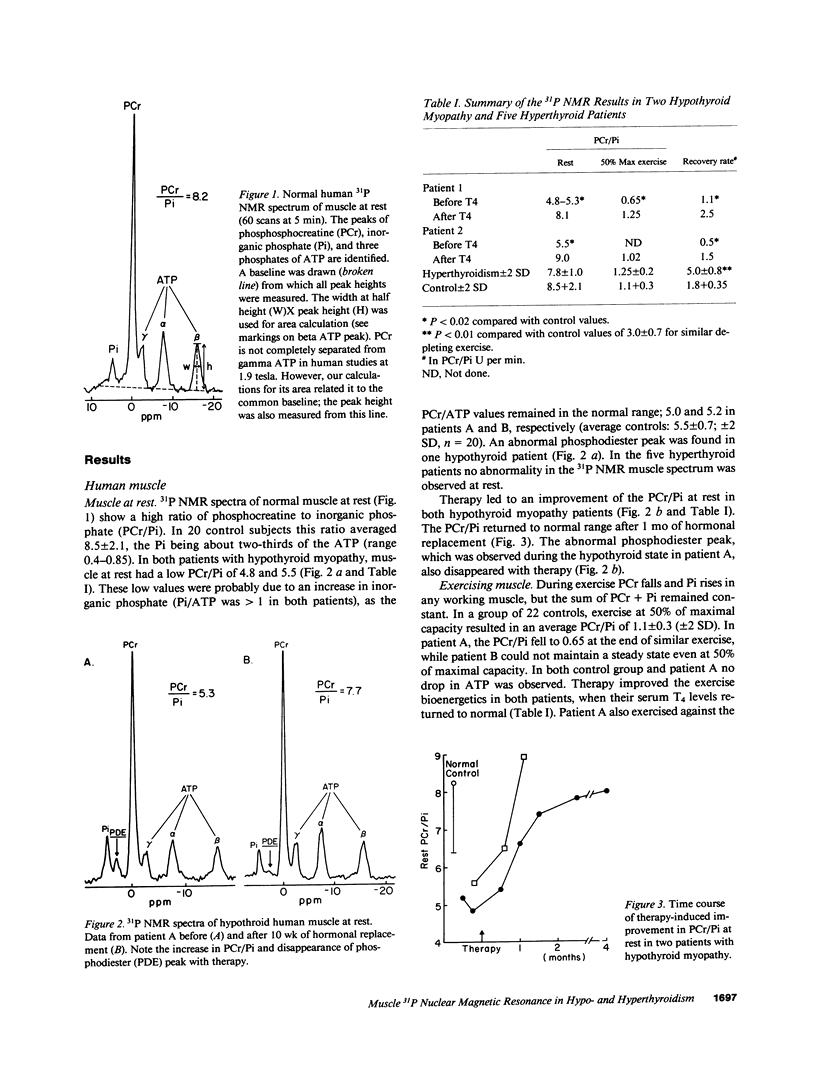
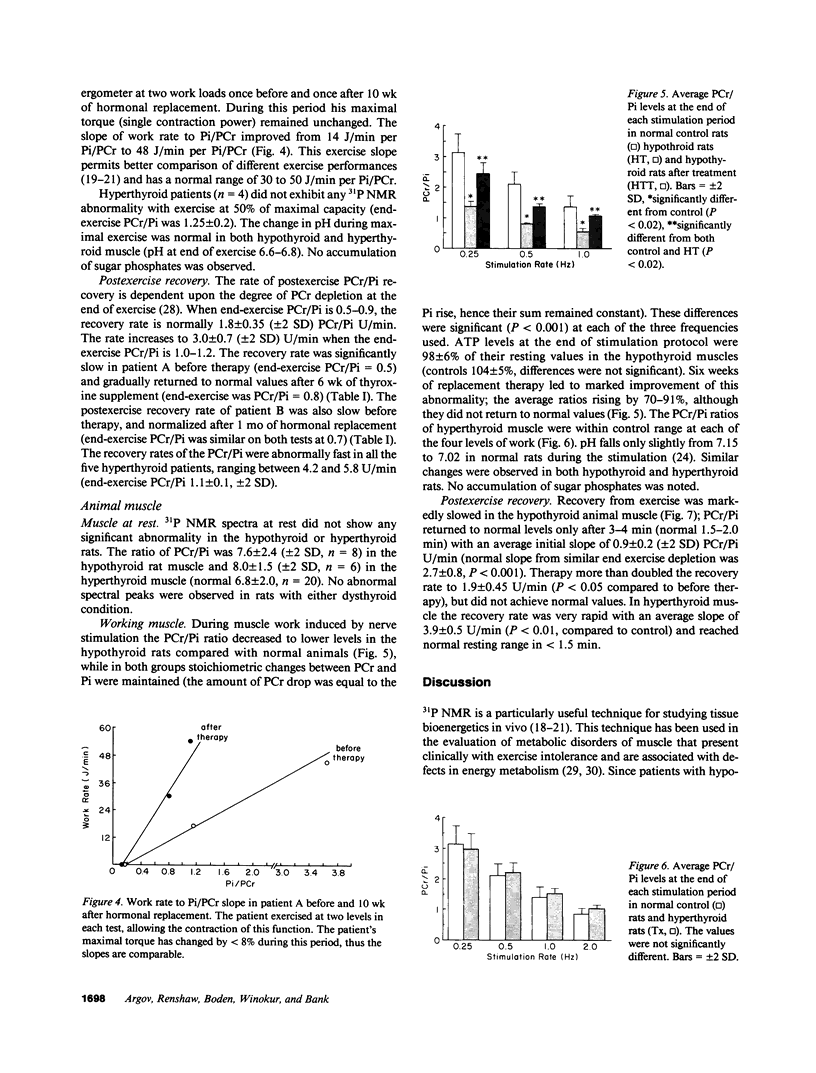
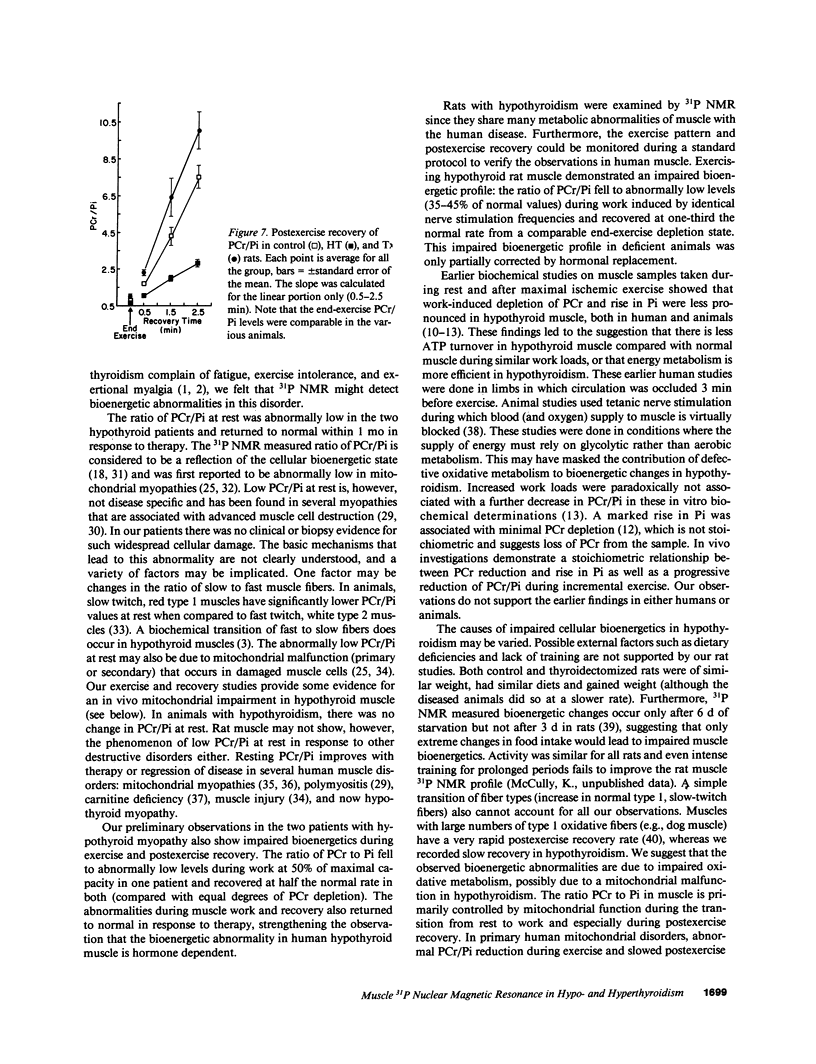
The pathophysiology of the myopathy in dysthyroid states is poorly understood. We therefore tested the effects of thyroid hormones on muscle bioenergetics in humans and rats, using in vivo 31P NMR. Two hypothyroid patients had: low phosphocreatine to inorganic phosphate ratio (PCr/Pi) at rest, increased PCr depletion during exercise and delayed postexercise recovery of PCr/Pi. Eight thyroidectomized rats did not show abnormalities at rest, but muscle work induced by nerve stimulation resulted in a significantly (P less than 0.0001) lower PCr/Pi (35-45% of control) at each of the three stimulation frequencies tested (0.25, 0.5, and 1.0 Hz). Recovery rate was markedly slowed to one-third of normal values. Thyroxine therapy reversed these abnormalities in both human and rat muscle. Five patients and six rats with hyperthyroidism did not differ from normal controls during rest and exercise but had an unusually rapid recovery after exercise. The bioenergetic abnormalities in hypothyroid muscle suggest the existence of a hormone-dependent, reversible mitochondrial impairment in this disorder. The exercise intolerance and fatigue experienced in hypothyroid muscle may be due to such a bioenergetic impairment. The changes in energy metabolism in hyperthyroid muscle probably do not cause the muscular disease in this disorder.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argov Z., Bank W. J., Maris J., Eleff S., Kennaway N. G., Olson R. E., Chance B. Treatment of mitochondrial myopathy due to complex III deficiency with vitamins K3 and C: A 31P-NMR follow-up study. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):598–602. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argov Z., Bank W. J., Maris J., Leigh J. S., Jr, Chance B. Muscle energy metabolism in human phosphofructokinase deficiency as recorded by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jul;22(1):46–51. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argov Z., Bank W. J., Maris J., Peterson P., Chance B. Bioenergetic heterogeneity of human mitochondrial myopathies: phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):257–262. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argov Z., Maris J., Damico L., Koruda M., Roth Z., Leigh J. S., Jr, Chance B. Continuous, graded steady-state muscle work in rats studied by in vivo 31P-NMR. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1428–1433. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold D. L., Matthews P. M., Radda G. K. Metabolic recovery after exercise and the assessment of mitochondrial function in vivo in human skeletal muscle by means of 31P NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1984 Sep;1(3):307–315. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold D. L., Taylor D. J., Radda G. K. Investigation of human mitochondrial myopathies by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Aug;18(2):189–196. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin K. M., Ernst S. B., Herrick R. E., Hooker A. M., Mullin W. J. Exercise capacity and cardiac function in trained and untrained thyroid-deficient rats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Dec;49(6):1022–1026. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.6.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin K. M., Hooker A. M., Herrick R. E., Schrader L. F. Respiratory capacity and glycogen depletion in thyroid-deficient muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Jul;49(1):102–106. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B. Applications of 31P NMR to clinical biochemistry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;428:318–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb12307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Eleff S., Leigh J. S., Jr, Sokolow D., Sapega A. Mitochondrial regulation of phosphocreatine/inorganic phosphate ratios in exercising human muscle: a gated 31P NMR study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6714–6718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Leigh J. S., Jr, Clark B. J., Maris J., Kent J., Nioka S., Smith D. Control of oxidative metabolism and oxygen delivery in human skeletal muscle: a steady-state analysis of the work/energy cost transfer function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8384–8388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Dawson M. J., Wilkie D. R., Gordon R. E., Shaw D. Clinical use of nuclear magnetic resonance in the investigation of myopathy. Lancet. 1982 Mar 27;1(8274):725–731. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92635-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleff S., Kennaway N. G., Buist N. R., Darley-Usmar V. M., Capaldi R. A., Bank W. J., Chance B. 31P NMR study of improvement in oxidative phosphorylation by vitamins K3 and C in a patient with a defect in electron transport at complex III in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3529–3533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts M. E., van Hardeveld C., Ter Keurs H. E., Kassenaar A. A. Force development and metabolism in skeletal muscle of euthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Jun;97(2):221–225. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0970221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fundarò A., Molinengo L., Cassone M. C. The transition from a fixed ratio to a fixed interval schedule of reinforcement in hypo and hyperthyroid rats. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1985 May;17(5):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(85)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollnick P. D., Ianuzzo C. D. Hormonal deficiencies and the metabolic adaptations of rats to training. Am J Physiol. 1972 Aug;223(2):278–282. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. D., Staub N. C. Resistance to blood flow in leg muscles of dog during tetanic isometric contraction. Am J Physiol. 1967 Sep;213(3):677–682. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.3.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson R., Tata J. R., Lindberg O., Ernster L. The relationship between the structure and activity of rat skeletal muscle mitochondria after thyroidectomy and thyroid hormone treatment. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):555–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ianuzzo C. D., Chen V., O'Brien P., Keens T. G. Effect of experimental dysthyroidism on the enzymatic character of the diaphragm. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Jan;56(1):117–121. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ianuzzo D., Patel P., Chen V., O'Brien P., Williams C. Thyroidal trophic influence on skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):74–76. doi: 10.1038/270074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., van Hardeveld C., Kassenaar A. A. Evidence for a different response of red and white skeletal muscle of the rat in different thyroid states. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Apr;87(4):768–775. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubista V., Kubistová J., Pette D. Thyroid hormone induced changes in the enzyme activity pattern of energy-supplying metabolism of fast (white), slow (red), and heart muscle of the rat. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb;18(4):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijendekker W. J., van Hardeveld C., Kassenaar A. A. Coupled diminished energy turnover and phosphorylase a formation in contracting hypothyroid rat muscle. Metabolism. 1985 May;34(5):437–441. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijendekker W. J., van Hardeveld C., Kassenaar A. A. The influence of the thyroid state on energy turnover during tetanic stimulation in the fast-twitch (mixed type) muscle of rats. Metabolism. 1983 Jun;32(6):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCully K. K., Argov Z., Boden B. P., Brown R. L., Bank W. J., Chance B. Detection of muscle injury in humans with 31-P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Muscle Nerve. 1988 Mar;11(3):212–216. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Kushmerick M. J. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of fast- and slow-twitch muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C279–C287. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Bore P. J., Styles P., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Bioenergetics of intact human muscle. A 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):77–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terjung R. L., Koerner J. E. Biochemical adaptations in skeletal muscle of trained thyroidectomized rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 May;230(5):1194–1197. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.5.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Fatigue in human metabolic myopathy. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;82:264–282. doi: 10.1002/9780470715420.ch16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Young A., Jones D. A., Edwards R. H. Muscle relaxation rate, fibre-type composition and energy turnover in hyper- and hypo-thyroid patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Oct;57(4):375–384. doi: 10.1042/cs0570375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder W. W., Baldwin K. M., Terjung R. L., Holloszy J. O. Effects of thyroid hormone administration on skeletal muscle mitochondria. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1341–1345. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder W. W., Holloszy J. O. Response of mitochondria of different types of skeletal muscle to thyrotoxicosis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C180–C184. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hardeveld C., Kassenaar A. A. Effects of experimental hypothyroidism on skeletal muscle metabolism in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Jan;87(1):114–124. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]