Abstract
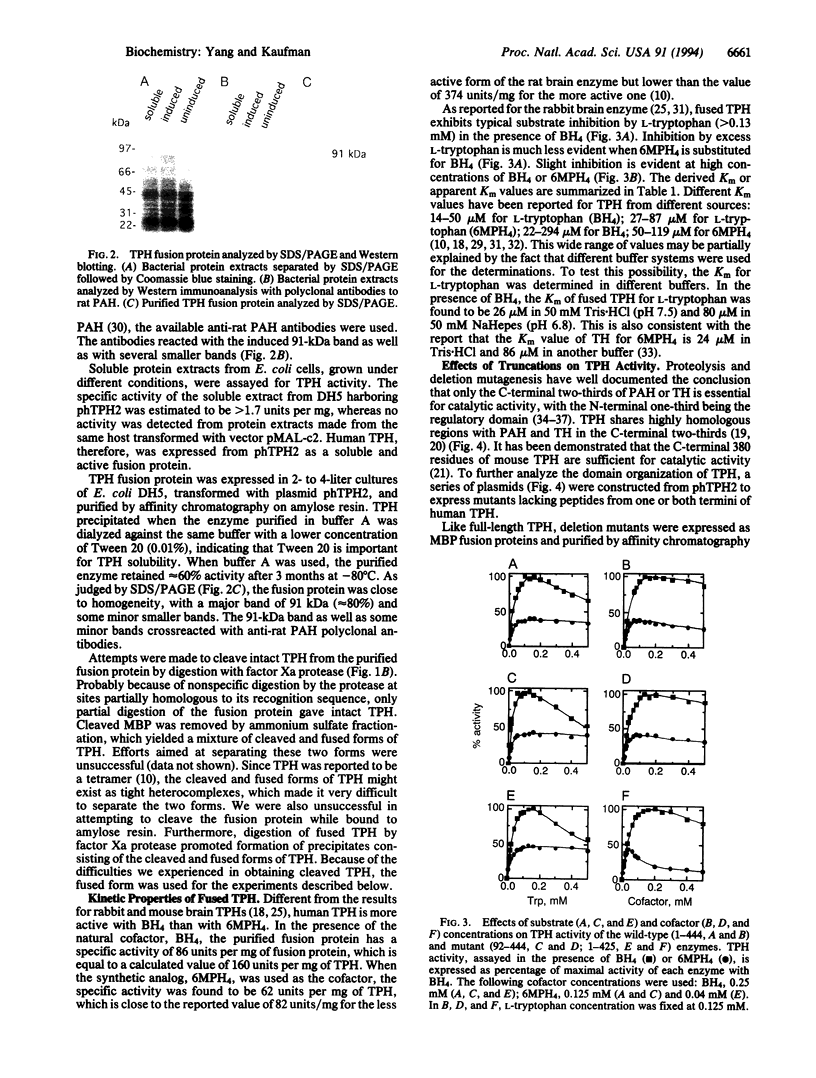
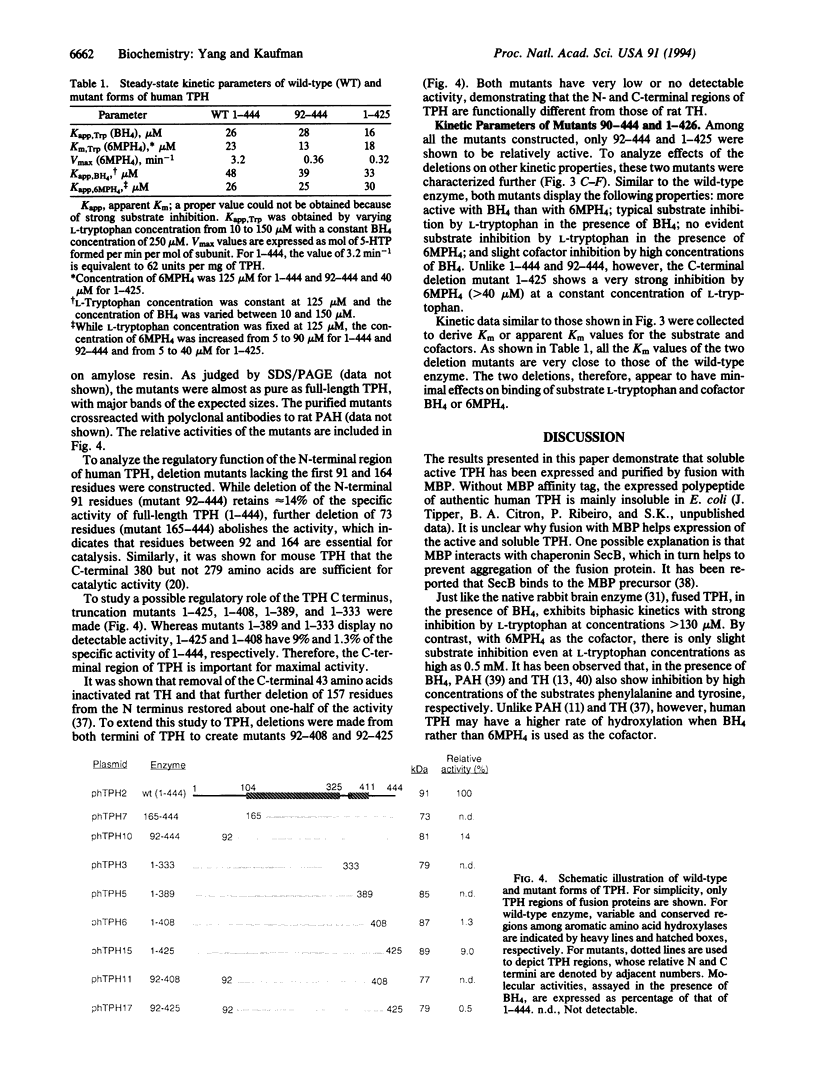
Human tryptophan hydroxylase has been expressed as a soluble and active form in Escherichia coli by fusion with an affinity tag, maltose-binding protein. The fusion protein has been purified to near homogeneity by affinity chromatography on crosslinked amylose resin. The purified fusion protein has a specific activity of 86 nmol of 5-hydroxytryptophan per min per mg of fusion protein. A series of truncation mutants have also been made to explore the domain organization of tryptophan hydroxylase. All deletion mutants were subject to affinity purification and kinetic characterization. While removal of the N-terminal 164 amino acids completely inactivates the enzyme, deletion of the first 91 residues results in a 7-fold reduction in specific activity. From the C terminus, deletion of 36, 55, or 112 amino acids abolishes the activity, whereas deletion of 19 residues decreases the specific activity by approximately 11-fold. These results are consistent with a model for tryptophan hydroxylase in which the enzyme consists of an N-terminal regulatory domain, a catalytic core, and a small C-terminal region of uncertain but important function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Joh T. H. Limited proteolysis of rat brain tyrosine hydroxylase defines an N-terminal region required for regulation of cofactor binding and directing substrate specificity. J Mol Neurosci. 1991;2(4):203–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Smith J. A., Joh T. H. Characterization of the catalytic domain of bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1446–1453. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boularand S., Darmon M. C., Ganem Y., Launay J. M., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of human tryptophan hydroxylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4257–4257. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B. A., Davis M. D., Kaufman S. Purification and biochemical characterization of recombinant rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase produced in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Apr;3(2):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M. C., Guibert B., Leviel V., Ehret M., Maitre M., Mallet J. Sequence of two mRNAs encoding active rat tryptophan hydroxylase. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):312–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubner S. C., Lauriano C., Haycock J. W., Fitzpatrick P. F. Site-directed mutagenesis of serine 40 of rat tyrosine hydroxylase. Effects of dopamine and cAMP-dependent phosphorylation on enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12639–12646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubner S. C., Lohse D. L., Fitzpatrick P. F. Expression and characterization of catalytic and regulatory domains of rat tyrosine hydroxylase. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1452–1460. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kaufman S. The stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by lysolecithin and -chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4345–4353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick P. F., Chlumsky L. J., Daubner S. C., O'Malley K. L. Expression of rat tyrosine hydroxylase in insect tissue culture cells and purification and characterization of the cloned enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2042–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kappelman A. H., Kaufman S. Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4165–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Lloyd T., Kaufman S. Production of antibodies to rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. Cross-reactivity with other pterin-dependent hydroxylases. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;8(5):501–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa H., Nakata H. Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase from rat brain stem. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:83–87. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon P. M., Kumamoto C. A. Mutations of the molecular chaperone protein SecB which alter the interaction between SecB and maltose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs B. S., Wojchowski D., Benkovic S. J. Expression of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase in insect cells and site-directed mutagenesis of putative non-heme iron-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8046–8052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G. Tryptophan hydroxylation in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Aug 11;16(6):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenett H. E., Ledley F. D., Reed L. L., Woo S. L. Full-length cDNA for rabbit tryptophan hydroxylase: functional domains and evolution of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa H., Ichiyama A. Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase from mouse mastocytoma: high-performance liquid chromatography assay. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:88–92. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., O'Shea E. K., Kim P. S., Sauer R. T. Sequence requirements for coiled-coils: analysis with lambda repressor-GCN4 leucine zipper fusions. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1400–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2147779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki M., Phillips R. S., Kaufman S. Proteolytic modification of the amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal regions of rat hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2051–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jéquier E., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Tryptophan hydroxylase inhibition: the mechanism by which p-chlorophenylalanine depletes rat brain serotonin. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 May;3(3):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. Regulation of the activity of hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1986;25:37–64. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(86)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Wessel T. C., Stone D. M., Carver C. H., Joh T. H., Park D. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding tryptophan hydroxylase from rat central serotonergic neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Mar;9(4):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn D. M., Meyer M. A., Lovenberg W. Comparisons of tryptophan hydroxylase from a malignant murine mast cell tumor and rat mesencephalic tegmentum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Feb;199(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn D. M., Ruskin B., Lovenberg W. Tryptophan hydroxylase. The role of oxygen, iron, and sulfhydryl groups as determinants of stability and catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4137–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse D. L., Fitzpatrick P. F. Identification of the intersubunit binding region in rat tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 30;197(3):1543–1548. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg W., Jequier E., Sjoerdsma A. Tryptophan hydroxylation: measurement in pineal gland, brainstem, and carcinoid tumor. Science. 1967 Jan 13;155(3759):217–219. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3759.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H., Fujisawa H. Purification and properties of tryptophan 5-monooxygenase from rat brain-stem. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):41–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro P., Wang Y., Citron B. A., Kaufman S. Deletion mutagenesis of rat PC12 tyrosine hydroxylase regulatory and catalytic domains. J Mol Neurosci. 1993 Summer;4(2):125–139. doi: 10.1007/BF02782125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll J., Kozak C. A., Goldman D. Characterization and chromosomal mapping of a cDNA encoding tryptophan hydroxylase from a mouse mastocytoma cell line. Genomics. 1990 May;7(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90522-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong J. H., Kaufman S. Tryptophan hydroxylase. Purification and some properties of the enzyme from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4152–4158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. H., Citron B. A., Ribeiro P., Kaufman S. High-level expression of rat PC12 tyrosine hydroxylase cDNA in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization of the cloned enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8779–8783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. J., Miles E. W. Threonine 183 and adjacent flexible loop residues in the tryptophan synthase alpha subunit have critical roles in modulating the enzymatic activities of the beta subunit in the alpha 2 beta 2 complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7520–7528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond R. E., Schwarzschild M. A., Rittenhouse A. R. Acute regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nerve activity and by neurotransmitters via phosphorylation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:415–461. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






