Abstract
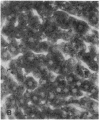
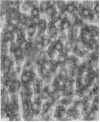
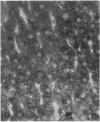
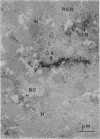
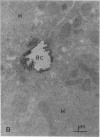
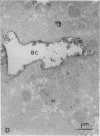
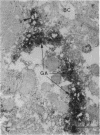
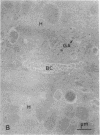
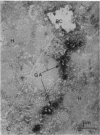
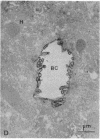
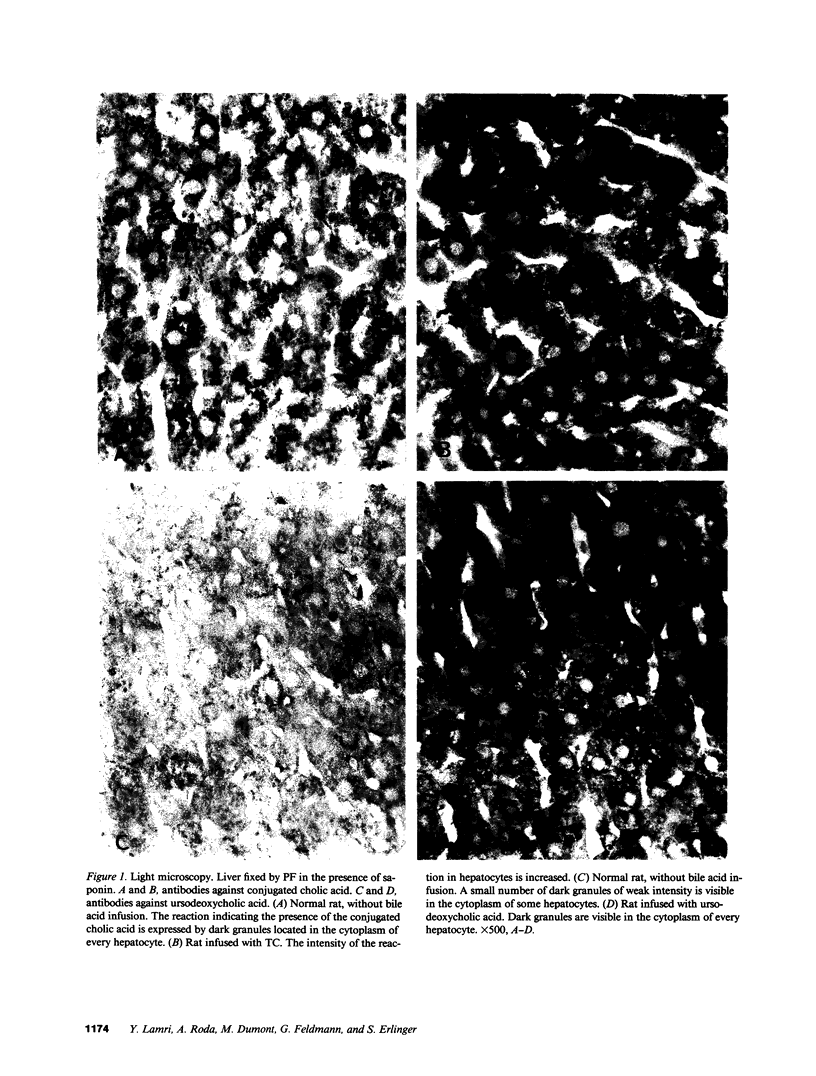
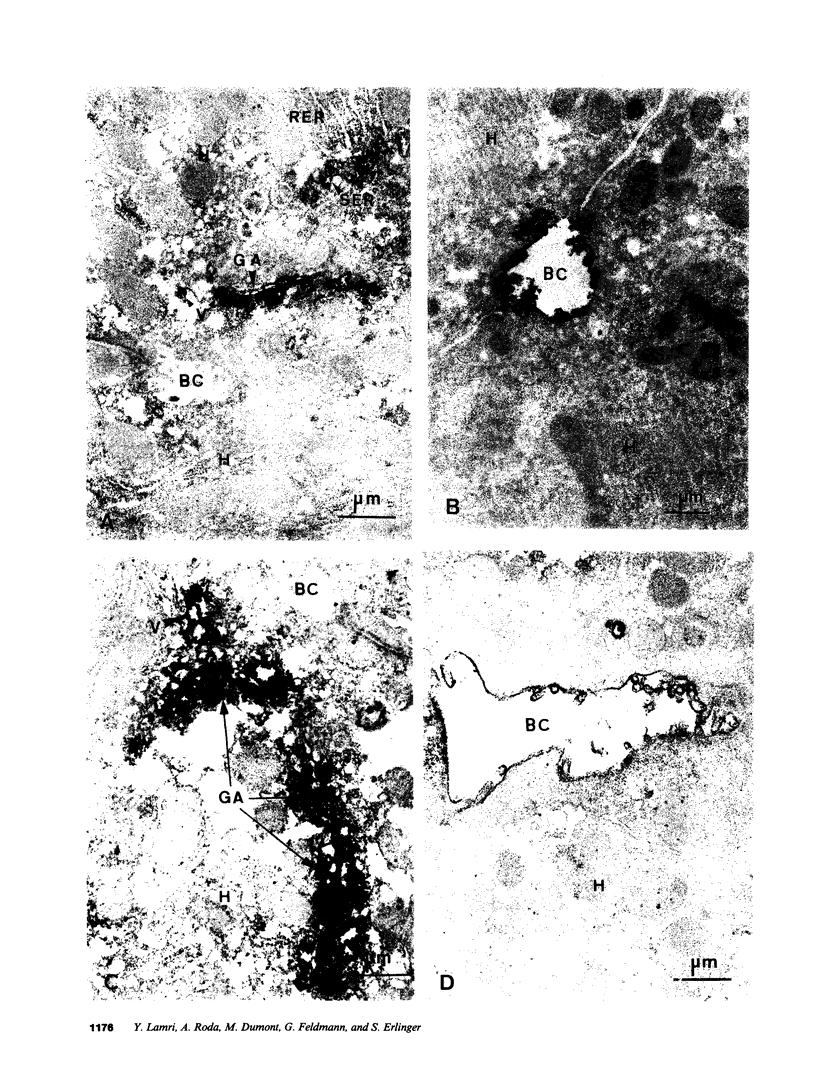
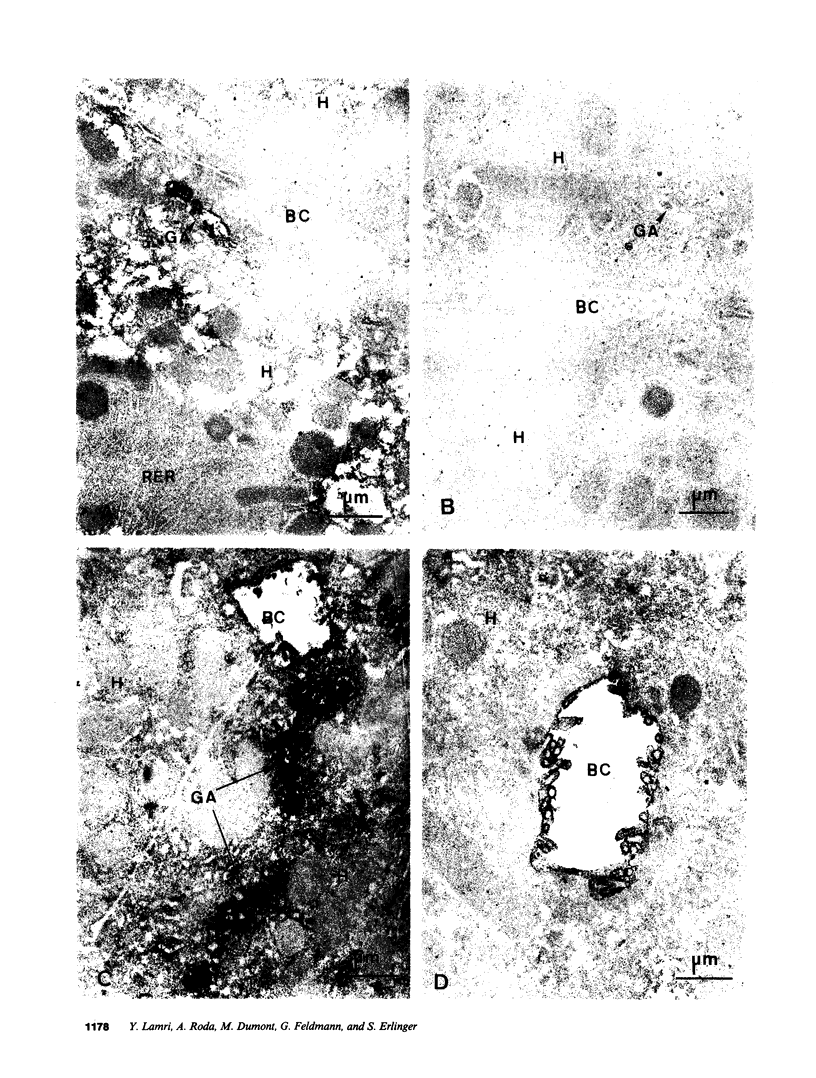
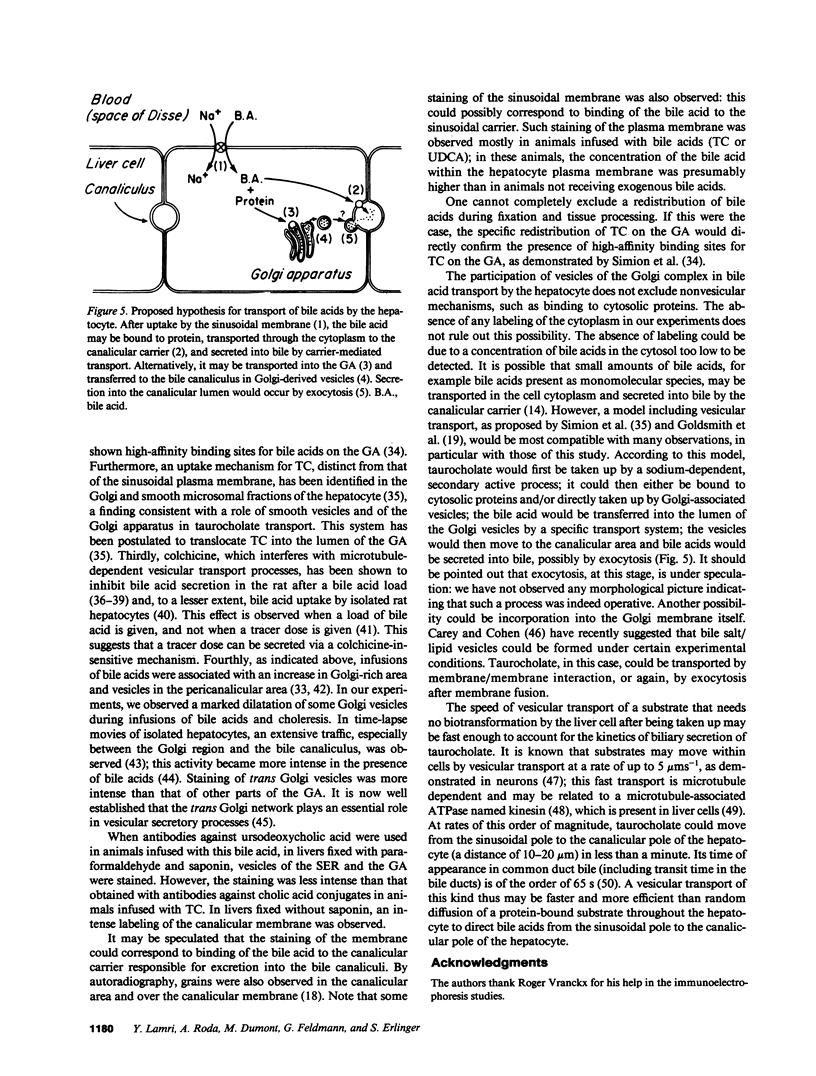
The mechanisms of intracellular transport of bile acids from the sinusoidal pole to the canalicular pole of the hepatocyte are poorly understood. There is physiological and autoradiographic evidence for a vesicular pathway. The purpose of this study was to determine the localization of natural bile acids in the liver using antibodies against cholic acid conjugates and ursodeoxycholic acid. An indirect immunoperoxidase technique was used on rat liver sections fixed either with paraformaldehyde (PF) and saponin, a membrane-permeabilizing agent that allows penetration of antibodies into the cell, or with PF alone. Retention of taurocholate in the liver after tissue processing was 26 +/- SD 15% of the bile acid initially present. When sections fixed with PF and saponin were incubated with the antibody against cholic acid conjugates, a granular cytoplasmic staining was observed by light microscopy in all hepatocytes. By electron microscopy, strong electron-dense deposits were observed mostly on vesicles of the Golgi apparatus (GA) and, sometimes, in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). After taurocholate infusion, the intensity of the reaction increased. When the liver was fixed with PF alone, almost no reaction was visible on light microscopy, but on electron microscopy the label was localized on the hepatocyte plasma membrane, mainly on the bile canalicular domain and to a lesser extent on the sinusoidal domain. With the antibody against ursodeoxycholic acid, no staining was observed in three of four livers, and a slight staining was observed in one. However, after infusion of ursodeoxycholic acid, staining of GA and SER vesicles was observed when the liver was fixed with PF and saponin. With PF alone, the reaction was intense on the canalicular membrane. These results support the view that, within the limits of the method, vesicles from the GA and possibly vesicles of the SER are involved in the intracellular transport of bile acids before canalicular secretion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Fabiato A., Leslie B. A., Putney J. W., Jr Calcium pools in saponin-permeabilized guinea pig hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15336–15345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M., Berken C. A., Gollan J. L. Role of the hepatocyte microtubular system in the excretion of bile salts and biliary lipid: implications for intracellular vesicular transport. J Lipid Res. 1988 Feb;29(2):144–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin M., Maurice M., Feldmann G., Erlinger S. Influence of colchicine and phalloidin on bile secretion and hepatic ultrastructure in the rat. Possible interaction between microtubules and microfilaments. Gastroenterology. 1980 Oct;79(4):646–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Direct determination of the driving forces for taurocholate uptake into rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1470–1481. doi: 10.1172/JCI111103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker G., Schneider S., Gerok W., Kurz G. Identification of different transport systems for bile salts in sinusoidal and canalicular membranes of hepatocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Sep;368(9):1143–1150. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. A., Huling S., Jones A. L. Hepatic handling of bile salts and protein in the rat during intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):978–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstein B., Forman D. S. Intracellular transport in neurons. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1167–1283. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. H., Vlahcevic Z. R., Prugh M. F., Swell L. Mechanism of secretion of biliary lipids: role of a microtubular system in hepatocellular transport of biliary lipids in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groothuis G. M., Hardonk M. J., Keulemans K. P., Nieuwenhuis P., Meijer D. K. Autoradiographic and kinetic demonstration of acinar heterogeneity of taurocholate transport. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):G455–G462. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.6.G455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häcki W., Paumgartner G. Determination of the biliary dead space using 14C-taurocholate as a marker. Experientia. 1973 Sep 15;29(9):1091–1093. doi: 10.1007/BF01946737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an Na+-independent transport system. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):659–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI111257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver sinusoidal membrane vesicles: evidence of sodium cotransport. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):572–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Hradek G. T., Renston R. H., Wong K. Y., Karlaganis G., Paumgartner G. Autoradiographic evidence for hepatic lobular concentration gradient of bile acid derivative. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):G233–G237. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.238.3.G233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Mooney J. S., Ockner R. K., Adler R. D. Alterations in hepatic pericanalicular cytoplasm during enhanced bile secretory activity. Lab Invest. 1979 Apr;40(4):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacich R. L., Renston R. H., Jones A. L. Effects of cytochalasin D and colchicine on the uptake, translocation, and biliary secretion of horseradish peroxidase and [14C]sodium taurocholate in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Bickel U., Buscher H. P., Gerok W., Kurz G. Bile-salt-binding polypeptides in plasma membranes of hepatocytes revealed by photoaffinity labelling. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., St Meier-Abt A., Barrett C., Boyer J. L. Mechanisms of taurocholate transport in canalicular and basolateral rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. Evidence for an electrogenic canalicular organic anion carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10614–10622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshio C., Phillips M. J. Contractility of bile canaliculi: implications for liver function. Science. 1981 May 29;212(4498):1041–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.7015506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Poucell S., Oda M. Mechanisms of cholestasis. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):593–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignal F., Maurice M., Feldmann G. Immunoperoxidase localization of albumin and fibrinogen in rat liver fixed by perfusion or immersion: effect of saponin on the intracellular penetration of labeled antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1004–1014. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6752262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Berman M. D., Berk P. D. The role of microfilaments and microtubules in taurocholate uptake by isolated rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 22;643(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Bolelli G. F. Production of a high-titer antibody to bile acids. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Apr;13(4):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Roda E., Aldini R., Festi D., Mazzella G., Sama C., Barbara L. Development, validation, and application of a single-tube radioimmunoassay for cholic and chenodeoxycholic conjugated bile acids in human serum. Clin Chem. 1977 Nov;23(11):2107–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruetz S., Fricker G., Hugentobler G., Winterhalter K., Kurz G., Meier P. J. Isolation and characterization of the putative canalicular bile salt transport system of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11324–11330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruifrok P. G., Meijer D. K. Sodium ion-coupled uptake of taurocholate by rat-liver plasma membrane vesicles. Liver. 1982 Mar;2(1):28–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1982.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Stephens J. E. Transport of sodium, chloride, and taurocholate by cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Transient holes in the erythrocyte membrane during hypotonic hemolysis and stable holes in the membrane after lysis by saponin and lysolecithin. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):55–70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simion F. A., Fleischer B., Fleischer S. Subcellular distribution of bile acids, bile salts, and taurocholate binding sites in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6459–6466. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simion F. A., Fleischer B., Fleischer S. Two distinct mechanisms for taurocholate uptake in subcellular fractions from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10814–10822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz A., Sugiyama Y., Kuhlenkamp J., Kaplowitz N. Identification and purification of a 36 kDa bile acid binder in human hepatic cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1984 Nov 5;177(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80975-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz A., Sugiyama Y., Kuhlenkamp J., Osadchey B., Yamada T., Belknap W., Balistreri W., Kaplowitz N. Cytosolic bile acid binding protein in rat liver: radioimmunoassay, molecular forms, developmental characteristics and organ distribution. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):433–439. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchy F. J., Balistreri W. F., Hung J., Miller P., Garfield S. A. Intracellular bile acid transport in rat liver as visualized by electron microscope autoradiography using a bile acid analogue. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):G681–G689. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.5.G681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchy F. J., Bucuvalas J. C., Goodrich A. L., Moyer M. S., Blitzer B. L. Taurocholate transport and Na+-K+-ATPase activity in fetal and neonatal rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):G665–G673. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.5.G665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama Y., Yamada T., Kaplowitz N. Newly identified bile acid binders in rat liver cytosol. Purification and comparison with glutathione S-transferases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3602–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Nassal M., Kramer W., Fricker G., Bickel U., Kurz G. Identity of hepatic membrane transport systems for bile salts, phalloidin, and antamanide by photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dippe P., Ananthanarayanan M., Drain P., Levy D. Purification and reconstitution of the bile acid transport system from hepatocyte sinusoidal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 17;862(2):352–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dippe P., Levy D. Characterization of the bile acid transport system in normal and transformed hepatocytes. Photoaffinity labeling of the taurocholate carrier protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8896–8901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]