Abstract
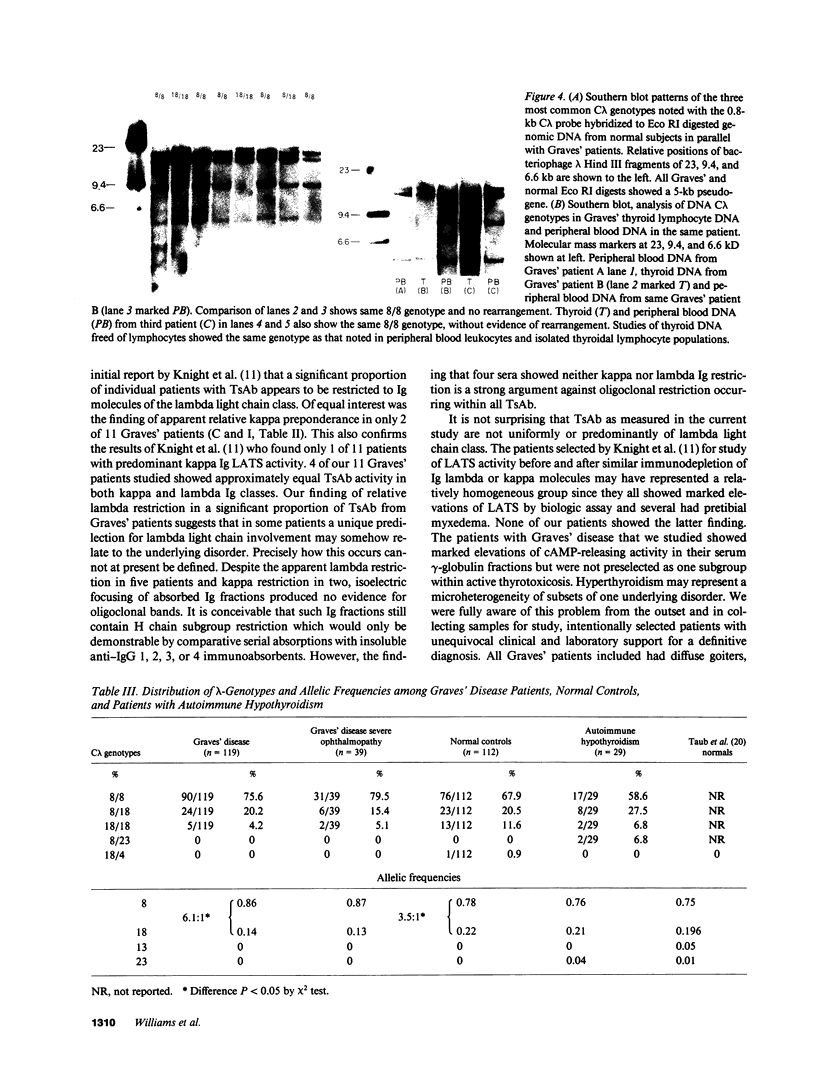
From patients with untreated Graves' disease 11 sera showing high cAMP release in the FRTL-5 cell assay were studied for relative proportions of kappa or lambda Ig molecules showing cAMP releasing activity. Immunoabsorption of gamma-globulins was performed using monoclonal murine anti-kappa or anti-lambda antibodies linked to cyanogen bromide-activated sepharose. Specific kappa- or lambda-adsorbed fractions were also eluted from immunoabsorbents using chaotrophic thiocyanate buffers and equilibrated with pH 7.4 low salt buffer by dialysis. Immunoabsorption and elution experiments showed that five Graves' sera contained predominant cAMP-releasing activity within lambda Ig fractions, whereas two Graves' sera showed predominant cAMP-releasing activity in kappa Ig fractions. Four sera showed cAMP release approximately equally divided between kappa and lambda Ig both after immunoabsorption and specific anti-kappa or anti-lambda eluates were studied. C lambda genotypes were examined by Southern blotting and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of Eco RI-digested genomic DNA from 158 patients with Graves' disease in parallel with 112 normal controls and 29 patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism. Notable shifts in proportions of 8/8 and 18/18 genotypes were present when Graves' patients were compared with normal controls. Allelic frequencies and ratios of genotype 8 to 18 were significantly different (P less than 0.05) when Graves' patients were compared either to normal controls or to patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS D. D. Bioassay of long-acting thyroid stimulator (L.A.T.S.); the dose-response relationship. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Jul;21:799–805. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-7-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. D., Adams Y. J., Knight J. G., McCall J., White P., Parkinson R., Horrocks R., van Loghem E. On the nature of the genes influencing the prevalence of Graves' disease. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 3;32(1-2):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon B., Manheimer-Lory A., Monestier M., Moran T., Dimitriu-Bona A., Alt F., Bona C. High frequency of autoantibodies bearing cross-reactive idiotopes among hybridomas using VH7183 genes prepared from normal and autoimmune murine strains. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1044–1053. doi: 10.1172/JCI112917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges M., Ingbar J. C., Endo K., Amir S., Uchimura H., Nagataki S., Ingbar S. H. A new method for assessing the thyrotropin binding inhibitory activity in the immunoglobulins and whole serum of patients with Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Mar;54(3):552–558. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-3-552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broad P. M., Schifter S., Craig R. K. The development of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid does not involve the loss of alleles on the short arm of chromosome 11. Br J Cancer. 1987 Feb;55(2):175–177. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Goñi F., Fong S., Jirik F., Vaughan J. H., Frangione B., Carson D. A. The majority of human monoclonal IgM rheumatoid factors express a "primary structure-dependent" cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3281–3285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Bear J. C. The human major histocompatibility complex and endocrine disease. Endocr Rev. 1981 Winter;2(1):50–86. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-1-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Newton R. M., Noel E. P., Marshall W. H. Gm phenotypes in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Immunogenet. 1977 Dec;4(6):429–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1977.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., de Graaf Mahoney S., Roberts J. R., Kasper C. K., Zimmerman T. S. Localization of human factor FVIII inhibitor epitopes to two polypeptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7728–7732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi F., Chen P. P., Pons-Estel B., Carson D. A., Frangione B. Sequence similarities and cross-idiotypic specificity of L chains among human monoclonal IgM kappa with anti-gamma-globulin activity. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4073–4079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Gawryl M. S., de la Fuente B. Immunochemical characterization of factor VIII inhibitors. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;150:73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISS J. P., PLESHAKOV V., CHIEN J. R. ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR AND ITS RELATION TO HYPERTHYROIDISM AND CIRCUMSCRIBED PRETIBIAL MYXEDEMA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1005–1028. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasagi K., Konishi J., Iida Y., Ikekubo K., Mori T., Kuma K., Torizuka K. A new in vitro assay for human thyroid stimulator using cultured thyroid cells: effect of sodium chloride on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate increase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jan;54(1):108–114. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-1-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight J., Laing P., Knight A., Adams D., Ling N. Thyroid-stimulating autoantibodies usually contain only lambda-light chains: evidence for the "forbidden clone" theory. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;62(2):342–347. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Noonan D. J., Levy D. E., Wilson M. C., Møller N. P., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genetic elements used for a murine lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are closely related to those for antibodies to exogenous antigens. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):805–815. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledford D. K., Goñi F., Pizzolato M., Franklin E. C., Solomon A., Frangione B. Preferential association of kappa IIIb light chains with monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1322–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manheimer-Lory A. J., Monestier M., Bellon B., Alt F. W., Bona C. A. Fine specificity, idiotypy, and nature of cloned heavy-chain variable region genes of murine monoclonal rheumatoid factor antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8293–8297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newkirk M. M., Mageed R. A., Jefferis R., Chen P. P., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequences of variable regions of two human IgM rheumatoid factors, BOR and KAS of the Wa idiotypic family, reveal restricted use of heavy and light chain variable and joining region gene segments. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):550–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Katz A. Cold agglutinins--antibodies with biological diversity. Clin Immunol Rev. 1984;3(1):131–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport B., Filetti S., Takai N., Seto P., Halverson G. Studies on the cyclic AMP response to thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) and thyrotropin (TSH) in human thyroid cell monolayers. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport B., Greenspan F. S., Filetti S., Pepitone M. Clinical experience with a human thyroid cell bioassay for thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Feb;58(2):332–338. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleusener H., Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R., Kotulla P., Bogner U., Finke R., Meinhold H., Koppenhagen K., Wenzel K. W. HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR5 associated thyrotoxicosis--two different types of toxic diffuse goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):781–785. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewring G., Smith B. R. An improved radioreceptor assay for TSH receptor antibodies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1982 Oct;17(4):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa T., Villadolid M. C., Ingbar S. H. A new serum-based assay for fat cell-binding immunoglobulins: application to the detection of the thyrotropin receptor antibodies of Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jan;62(1):10–15. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-1-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidebottom D., Grennan D. M., Sanders P. A., Read A. Immunoglobulin lambda light chain genes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Aug;46(8):587–589. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.8.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate K., Creagh F., Teece M., Kingswood C., Rees Smith B. A receptor assay for the measurement of TSH receptor antibodies in unextracted serum. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984 May;20(5):539–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1984.tb00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R. A., Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Variable amplification of immunoglobulin lambda light-chain genes in human populations. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):172–174. doi: 10.1038/304172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno H., Sasazuki T., Tamai H., Matsumoto H. Two major genes, linked to HLA and Gm, control susceptibility to Graves' disease. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):768–770. doi: 10.1038/292768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente W. A., Vitti P., Yavin Z., Yavin E., Rotella C. M., Grollman E. F., Toccafondi R. S., Kohn L. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor: stimulating and blocking antibodies derived from the lymphocytes of patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6680–6684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente W. A., Vitti P., Yavin Z., Yavin E., Rotella C. M., Grollman E. F., Toccafondi R. S., Kohn L. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor: stimulating and blocking antibodies derived from the lymphocytes of patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6680–6684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente W. A., Yavin Z., Yavin E., Grollman E. F., Schneider M., Rotella C. M., Zonefrati R., Toccafondi R. S., Kohn L. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor: the identification of blocking and stimulating antibodies. J Endocrinol Invest. 1982 Sep-Oct;5(5):293–301. doi: 10.1007/BF03350517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitti P., Rotella C. M., Valente W. A., Cohen J., Aloj S. M., Laccetti P., Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Grollman E. F., Pinchera A., Toccafondi R. Characterization of the optimal stimulatory effects of graves' monoclonal and serum immunoglobulin G on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate production in fRTL-5 thyroid cells: a potential clinical assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Oct;57(4):782–791. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-4-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitti P., Valente W. A., Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Fenzi G. F., Pinchera A., Kohn L. D. Graves' IgG stimulation of continuously cultured rat thyroid cells: a sensitive and potentially useful clinical assay. J Endocrinol Invest. 1982 May-Jun;5(3):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF03349476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. R., Solomon A., Weiss D. T., Deutsch H. F., Jefferis R. Immunogenic and antigenic epitopes of Ig. XXV. Monoclonal antibodies that differentiate the Mcg+/Mcg- and Oz+/Oz- C region isotypes of human lambda L chains. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1600–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr Cold agglutinins: studies of primary structure, serologic activity and antigenic uniqueness. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:330–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willims R. C., Jr, Kunkel H. G., Capra J. D. Antigenic specificities related to the cold agglutinin activity of gamma M globulins. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):379–381. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M. Immunochemical characterization of the thyroid-stimulating antibody (TSAb) of Graves' disease: evidence for restricted heterogeneity. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Feb;10(2):77–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin T. W., van der Heide D., Querido A., Krol M. C. Direct and quantitative measurement by immunoprecipitation assay of anti-thyrotrophin receptor antibodies in sera of patients with Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984 Feb;20(2):143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1984.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]