Abstract
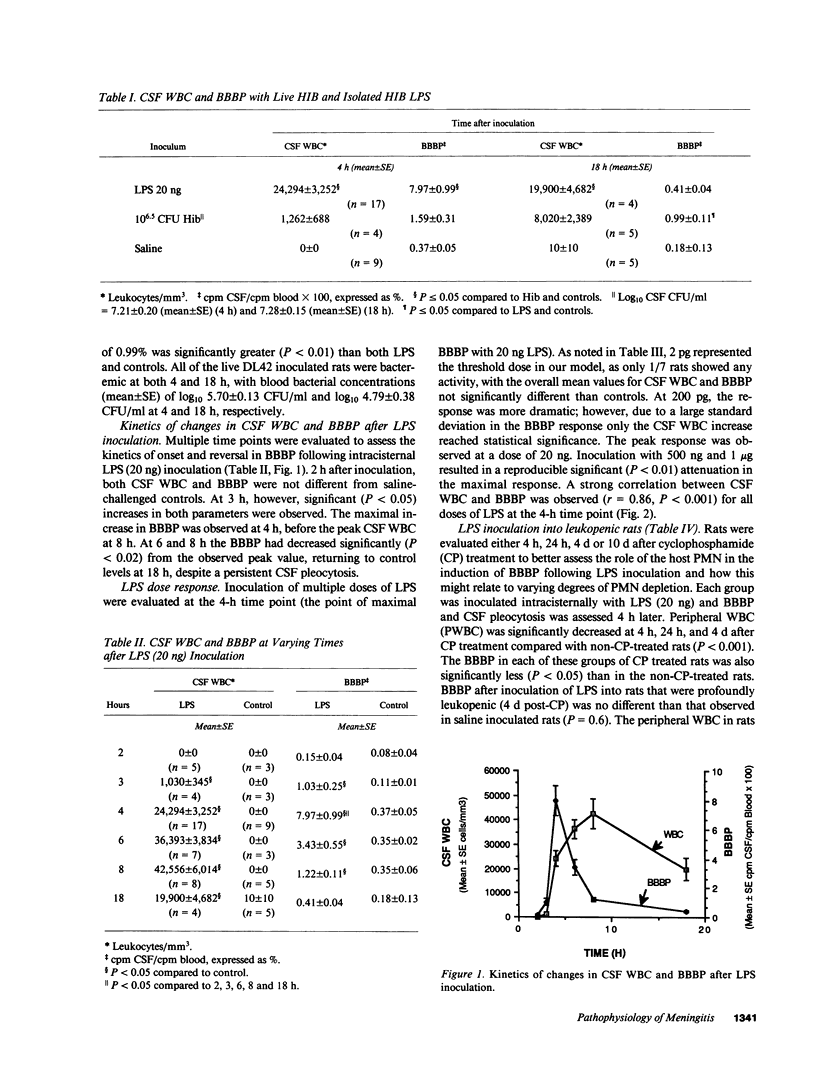
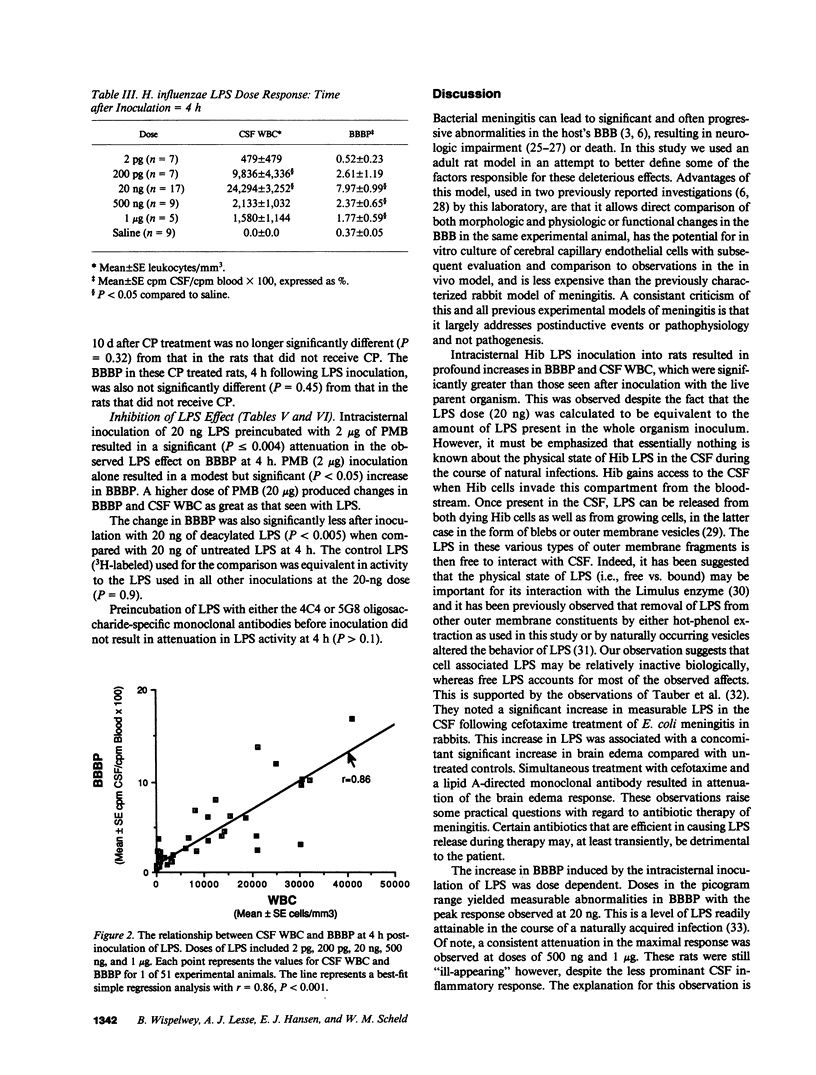
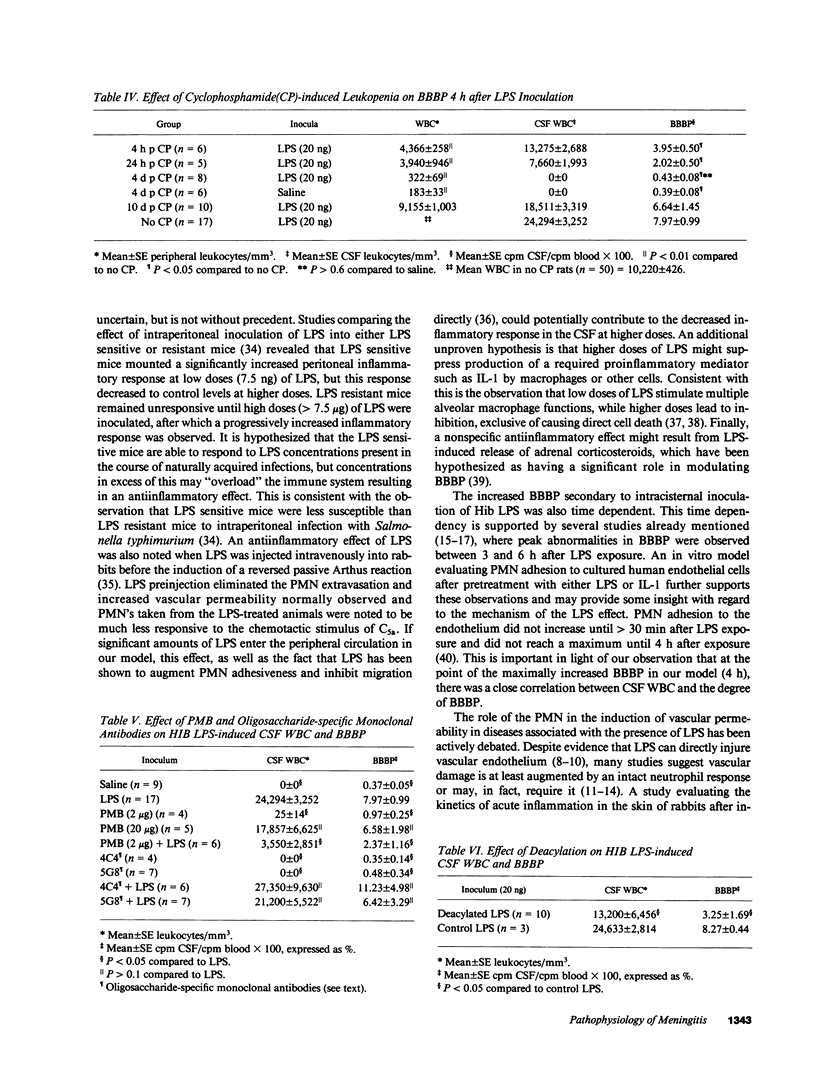
The factors responsible for blood-brain barrier (BBB) injury during bacterial meningitis are incompletely defined. We evaluated the role of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the alteration of blood-brain barrier permeability (BBBP) in an adult, normal and leukopenic, rat model of meningitis. Intracisternal inoculation of Hib LPS resulted in (a) dose-dependent increases in BBBP from 2 pg to 20 ng, with significant attenuation in the peak response after challenge with 500 ng and 1 microgram; (b) time-dependent increases in BBBP, with a delayed onset of at least 2 h, maximum alteration at 4 h, and complete reversal at 18 h; (c) greater BBBP than after challenge with the live parent strain; (d) and a close correlation (r = 0.86) between CSF pleocytosis and BBBP at 4 h. The LPS effect was significantly inhibited by preincubation with Polymyxin B and neutrophil acyloxyacyl hydrolase, however two different oligosaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies did not inhibit activity. No change in BBBP after inoculation with Hib LPS occurred in leukopenic rats. Hib LPS, in the setting of an intact leukocyte response, exerts profound effects on BBBP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alon U., Naveh Y., Gardos M., Friedman A. Neurological sequelae of septic meningitis. A follow-up study of 65 children. Isr J Med Sci. 1979 Jun;15(6):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman N. S., Siegel S. E., Nachum R., Lipsey A., Leedom J. Cerebrospinal fluid endotoxin concentrations in gram-negative bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):553–556. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Polymyxin-B inhibition of LPS-induced interleukin-1 secretion by human monocytes is dependent upon the LPS origin. Mol Immunol. 1986 Sep;23(9):965–969. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., Hartmann J. F., Vernier R. L. Electron microscopy of the effect of gram-negative endotoxin on the blood-brain barrier. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Jun;127(2):183–198. doi: 10.1002/cne.901270204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Cybulsky I. J., Movat H. Z. Neutropenic responses to intradermal injections of Escherichia coli. Effects on the kinetics of polymorphonuclear leukocyte emigration. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C., Galanos C., Fehr J. Granulocyte activation by endotoxin. I. Correlation between adherence and other granulocyte functions, and role of endotoxin structure on biologic activity. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):857–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Barsoum I. S., Ramwell P. W., Yeager H., Jr Human alveolar macrophages: effects of endotoxin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.753-758.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deich R. A., Hoyer L. C. Generation and release of DNA-binding vesicles by Haemophilus influenzae during induction and loss of competence. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):855–864. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.855-864.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge P. R., Davis H., Feigin R. D., Holmes S. J., Kaplan S. L., Jubelirer D. P., Stechenberg B. W., Hirsh S. K. Prospective evaluation of hearing impairment as a sequela of acute bacterial meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 4;311(14):869–874. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410043111401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKMAN P. L., KING W. M., BRUNSON J. G. Studies on the blood brain barrier. I. Effects produced by a single injection of gramnegative endotoxin on the permeability of the cerebral vessels. Am J Pathol. 1958 Jul-Aug;34(4):631–643. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor E. The role of granulocytes in endotoxin-induced vascular injury. Blood. 1973 Jun;41(6):797–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Patrick C. C., Hermanstorfer L., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Conservation of epitopes in the oligosaccharide portion of the lipooligosaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):513–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.513-520.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Reidy M. A., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Striker G. E. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated bovine endothelial cell injury in vitro. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Weaver L. J. Effects of lipopolysaccharide on human endothelial cells in culture. Thromb Res. 1983 Jan 1;29(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heflin A. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. Prevention by granulocyte depletion of increased vascular permeability of sheep lung following endotoxemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1253–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI110371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Leive L., Mäkelä P. H., Rietschel E. T., Strittmatter W., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide nomenclature--past, present, and future. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.699-705.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Seifert W. E., Jr, Williams R. P. Composition and antigenic activity of the oligosaccharide moiety of Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):324–330. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.324-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Bhimji S. Role for endotoxin in the leukocyte infiltration accompanying Escherichia coli inflammation. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):558–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.558-566.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopaniak M. M., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of acute inflammation induced by Escherichia coli in rabbits. II. The effect of hyperimmunization, complement depletion, and depletion of leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jan;110(1):13–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopaniak M. M., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of acute inflammation induced by Escherichia coli in rabbits. II. The effect of hyperimmunization, complement depletion, and depletion of leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jan;110(1):13–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebbar S., Cavaillon J. M., Caroff M., Ledur A., Brade H., Sarfati R., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Molecular requirement for interleukin 1 induction by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes: involvement of the heptosyl-2-keto-3-deoxyoctulosonate region. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):87–91. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. B., Holaday J. W. Blood-brain barrier: endogenous modulation by adrenal-cortical function. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1580–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.3975627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Rietschel E. T. Endotoxins of Gram-negative bacteria. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):383–402. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O. Endotoxin-mediated pulmonary endothelial cell injury. Fed Proc. 1986 Jan;45(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Cybulsky M. I., Colditz I. G., Chan M. K., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation in gram-negative infection: endotoxin, interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and neutrophils. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Grimm L. Detection of free endotoxin in cerebrospinal fluid by the Limulus lysate test. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):531–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.531-533.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L., Lipton J. M., Dietschy J. M. Biological activity, lipoprotein-binding behavior, and in vivo disposition of extracted and native forms of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):877–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI110684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Munford R. S., Harlan J. M. Deacylated lipopolysaccharide inhibits neutrophil adherence to endothelium induced by lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1393–1402. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V. J., Long W. J., Scheld W. M. Morphologic alterations of the blood-brain barrier with experimental meningitis in the rat. Temporal sequence and role of encapsulation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1084–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI112407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Hartiala K. T., Webster R. O., Howes E. L., Jr, Goldstein I. M. Antiinflammatory effects of endotoxin. Inhibition of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte responses to complement (C5)-derived peptides in vivo and in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):291–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZ M. N., DODGE P. R. BACTERIAL MENINGITIS--A REVIEW OF SELECTED ASPECTS. 1. GENERAL CLINICAL FEATURES, SPECIAL PROBLEMS AND UNUSUAL MENINGEAL REACTIONS MIMICKING BACTERIAL MENINGITIS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Apr 8;272:725–CONTD. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196504082721406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Dacey R. G., Winn H. R., Welsh J. E., Jane J. A., Sande M. A. Cerebrospinal fluid outflow resistance in rabbits with experimental meningitis. Alterations with penicillin and methylprednisolone. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):243–253. doi: 10.1172/JCI109850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Ward J. I., Band J. D., Hightower A., Fraser D. W., Broome C. V. Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1978 through 1981. The National Bacterial Meningitis Surveillance Study. JAMA. 1985 Mar 22;253(12):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P., Rutledge B. K. Cultured human vascular endothelial cells acquire adhesiveness for neutrophils after stimulation with interleukin 1, endotoxin, and tumor-promoting phorbol diesters. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):649–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Moriguchi S., Shimizu E., Ogushi F., Tsubura E. In vitro generation of tumoricidal properties in human alveolar macrophages following interaction with endotoxin. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2227–2231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrogiannopoulos G. A., Hansen E. J., Erwin A. L., Munford R. S., Rutledge J., Reisch J. S., McCracken G. H., Jr Haemophilus influenzae type b lipooligosaccharide induces meningeal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):237–244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Liu H., Hengstler B., Zak O., Tomasz A. The induction of meningeal inflammation by components of the pneumococcal cell wall. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):859–868. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Borschberg U., Sande M. A. Influence of granulocytes on brain edema, intracranial pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of lactate and protein in experimental meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):456–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Shibl A. M., Hackbarth C. J., Larrick J. W., Sande M. A. Antibiotic therapy, endotoxin concentration in cerebrospinal fluid, and brain edema in experimental Escherichia coli meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):456–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Differential anti-inflammatory effects of LPS in susceptible and resistant mouse strains. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):288–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwahlen A., Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Surface determinants of Haemophilus influenzae pathogenicity: comparative virulence of capsular transformants in normal and complement-depleted rats. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):385–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



