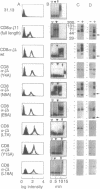
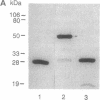
Abstract
To define the T-cell receptor signal transduction motif, we have transfected human and murine T-cell lines with a chimeric receptor consisting of the extracellular and transmembrane domains of human CD8 alpha and the membrane-proximal portion of CD3 zeta containing at its C terminus either an 18-amino acid segment (NQLYNELNLGRREEYDVL) or alanine-scanning point mutant derivatives. Crosslinking of the extracellular domain of the chimera is sufficient to initiate Ca2+ flux, interleukin 2 production, and tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins including the chimera. Subsequently, the chimera becomes associated with several tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins, among them the 70-kDa protein tyrosine kinase ZAP70. Mutational data identify the T-cell activation motif as Y(X)2L(X)7Y(X)2L and show that each of the four designated residues is necessary for the above activation events. Recombinant protein containing the two tandem SH2 domains derived from ZAP70 binds to a synthetic peptide corresponding to the above 18-amino acid motif but only when both tyrosines are phosphorylated; in contrast, little or no binding is observed to monophosphorylated or nonphosphorylated analogues. These results imply that after receptor crosslinking in T cells, and by inference also in B cells and mast cells, the motif is phosphorylated on both tyrosine residues, thereafter serving as a docking site for protein tyrosine kinases containing tandem SH2 domains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcover A., Alberini C., Acuto O., Clayton L. K., Transy C., Spagnoli G. C., Moingeon P., Lopez P., Reinherz E. L. Interdependence of CD3-Ti and CD2 activation pathways in human T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1973–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcover A., Weiss M. J., Daley J. F., Reinherz E. L. The T11 glycoprotein is functionally linked to a calcium channel in precursor and mature T-lineage cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2614–2618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigorena S., Salamero J., Davoust J., Fridman W. H., Bonnerot C. Tyrosine-containing motif that transduces cell activation signals also determines internalization and antigen presentation via type III receptors for IgG. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):337–341. doi: 10.1038/358337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A., McConkey D. J., Howard F. D., Clayton L. K., Novick D., Koyasu S., Reinherz E. L. Differential signal transduction via T-cell receptor CD3 zeta 2, CD3 zeta-eta, and CD3 eta 2 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3842–3846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaufils P., Choquet D., Mamoun R. Z., Malissen B. The (YXXL/I)2 signalling motif found in the cytoplasmic segments of the bovine leukaemia virus envelope protein and Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A can elicit early and late lymphocyte activation events. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5105–5112. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Amigorena S., Choquet D., Pavlovich R., Choukroun V., Fridman W. H. Role of associated gamma-chain in tyrosine kinase activation via murine Fc gamma RIII. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2747–2757. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Iwashima M., Turck C. W., Weiss A. ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Shoelson S. E., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):87–91. doi: 10.1038/362087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. G., Sancho J., Terhorst C. Reconstitution of T cell receptor zeta-mediated calcium mobilization in nonlymphoid cells. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.8346442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. D., Moingeon P., Moebius U., McConkey D. J., Yandava B., Gennert T. E., Reinherz E. L. The CD3 zeta cytoplasmic domain mediates CD2-induced T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):139–145. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Chan A. C., Weiss A. Functional characterization of a signal transducing motif present in the T cell antigen receptor zeta chain. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1093–1103. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashima M., Irving B. A., van Oers N. S., Chan A. C., Weiss A. Sequential interactions of the TCR with two distinct cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1136–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.7509083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y. J., Clayton L. K., Howard F. D., Koyasu S., Sieh M., Steinbrich R., Tarr G. E., Reinherz E. L. Molecular cloning of the CD3 eta subunit identifies a CD3 zeta-related product in thymus-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Pallas D. C., DeCaprio J. A., Kaye F. J., Livingston D. M. Identification of cellular proteins that can interact specifically with the T/E1A-binding region of the retinoblastoma gene product. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):521–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90236-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Sutor S. L., Torigoe T., Reed J. C., Bell M. P., McKean D. J., Leibson P. J., Abraham R. T. Effects of p56lck deficiency on the growth and cytolytic effector function of an interleukin-2-dependent cytotoxic T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4521–4530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolanus W., Romeo C., Seed B. T cell activation by clustered tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., McConkey D. J., Clayton L. K., Abraham S., Yandava B., Katagiri T., Moingeon P., Yamamoto T., Reinherz E. L. Phosphorylation of multiple CD3 zeta tyrosine residues leads to formation of pp21 in vitro and in vivo. Structural changes upon T cell receptor stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. T-cell and basophil activation through the cytoplasmic tail of T-cell-receptor zeta family proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Sefton B. M. Activated lck tyrosine protein kinase stimulates antigen-independent interleukin-2 production in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4724–4732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Mak T. W., Van den Elsen P., Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Calman A. F., Terhorst C., Stobo J. D., Weiss A. Reconstitution of an active surface T3/T-cell antigen receptor by DNA transfer. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):606–609. doi: 10.1038/316606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overduin M., Rios C. B., Mayer B. J., Baltimore D., Cowburn D. Three-dimensional solution structure of the src homology 2 domain of c-abl. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90437-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Amiot M., Seed B. Sequence requirements for induction of cytolysis by the T cell antigen/Fc receptor zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):889–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D. Tyrosine kinases and tyrosine-based activation motifs. Current research on activation via the T cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24913–24916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Patel M. D., Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Antigen activation of murine T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a polypeptide associated with the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Hemesath T. J., Pratt J. C., Dintzis R. Z., Dintzis H. M., Acuto O., Shin H. S., Reinherz E. L. Direct evidence for the existence of nominal antigen binding sites on T cell surface Ti alpha-beta heterodimers of MHC-restricted T cell clones. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90439-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölander S., Urbaniczky C. Integrated fluid handling system for biomolecular interaction analysis. Anal Chem. 1991 Oct 15;63(20):2338–2345. doi: 10.1021/ac00020a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Weiss A. Genetic evidence for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90428-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Sizer K. C., Vollmer A. C., Hunkapiller T., Parnes J. R. The T cell differentiation antigen Leu-2/T8 is homologous to immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable regions. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. J., Bonifacino J. S., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Weissman A. M., Saito T., Klausner R. D., Ashwell J. D. Failure to synthesize the T cell CD3-zeta chain: structure and function of a partial T cell receptor complex. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90533-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Kobayashi T., Kondo J., Takahashi K., Nakamura H., Suzuki J., Nagai K., Yamada T., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Molecular cloning of a porcine gene syk that encodes a 72-kDa protein-tyrosine kinase showing high susceptibility to proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15790–15796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Shoelson S. E., Pant N., Cowburn D., Kuriyan J. Binding of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide to the Src SH2 domain: crystal structures of the complexed and peptide-free forms. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90405-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wange R. L., Malek S. N., Desiderio S., Samelson L. E. Tandem SH2 domains of ZAP-70 bind to T cell antigen receptor zeta and CD3 epsilon from activated Jurkat T cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19797–19801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Hou D., Orloff D. G., Modi W. S., Seuanez H., O'Brien S. J., Klausner R. D. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of the human T-cell receptor zeta chain: distinction from the molecular CD3 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9709–9713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]