Abstract
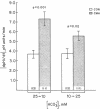
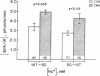
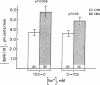
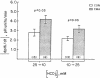
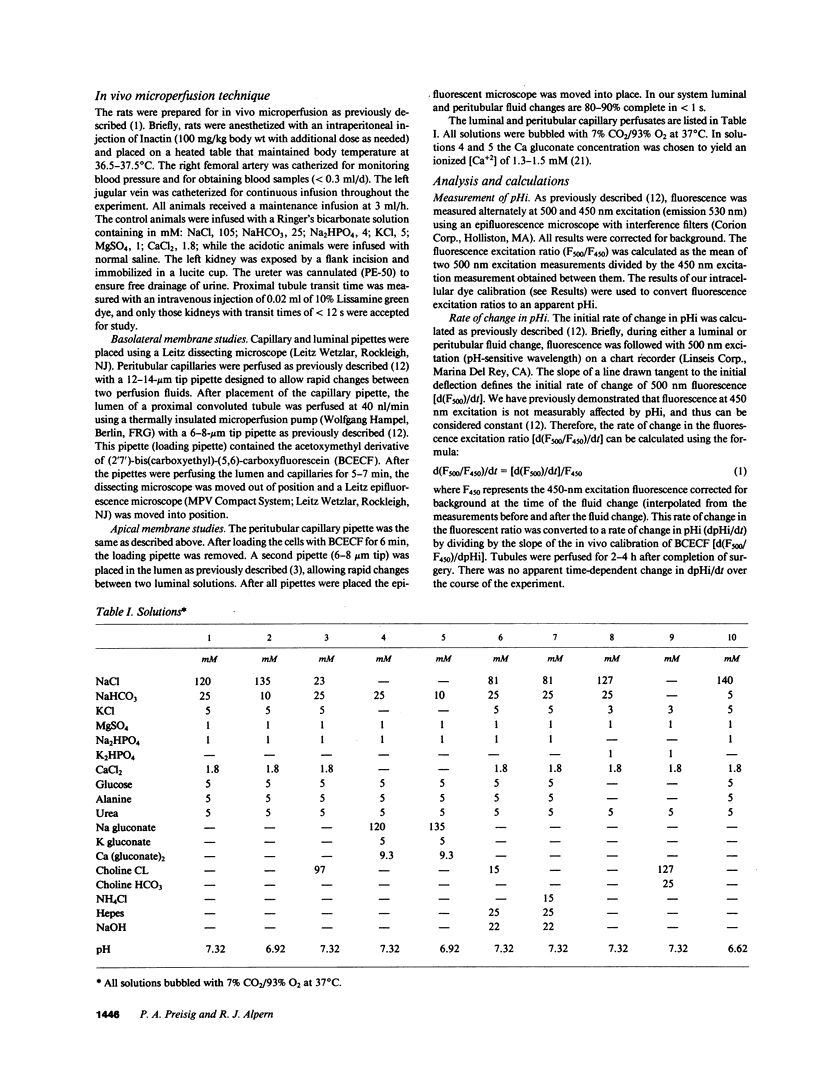
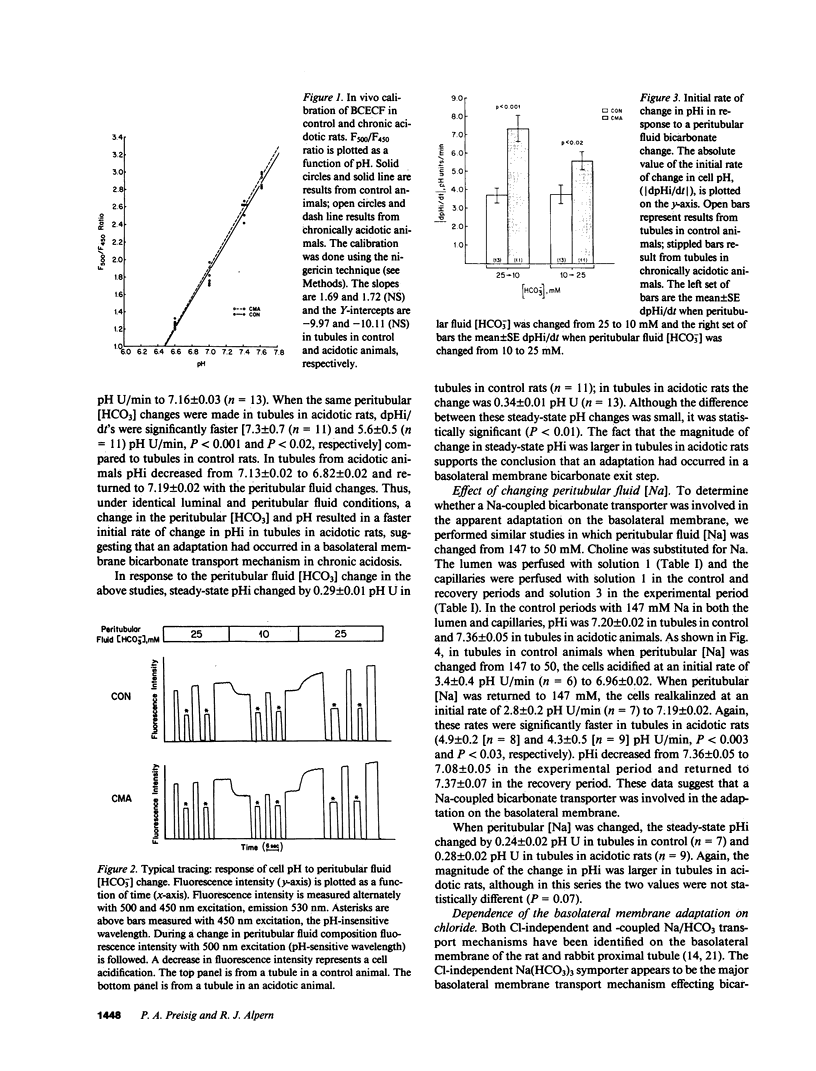
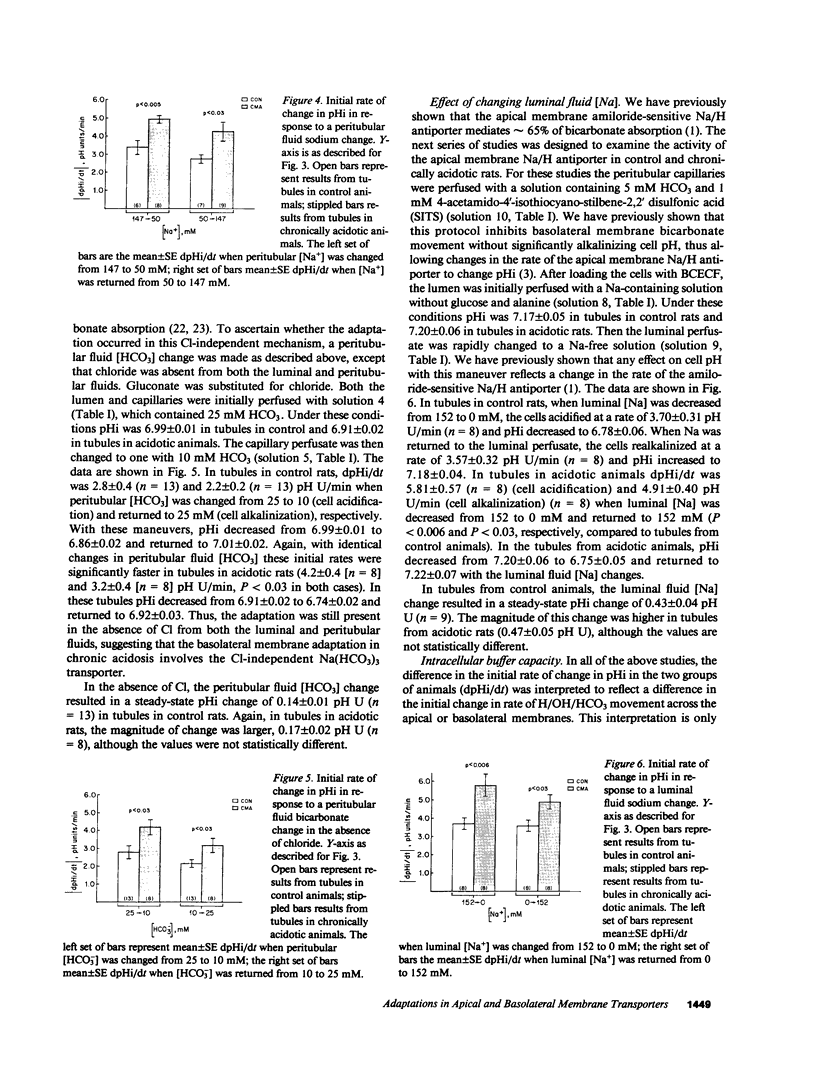
The effect of chronic dietary acid on the apical membrane Na/H antiporter and basolateral membrane Na(HCO3)3 symporter was examined in the in vivo microperfused rat proximal tubule. Transporter activity was assayed with the epifluorescent measurement of cell pH using the intracellular, pH-sensitive fluorescent dye, (2'7')-bis(carboxyethyl)-(5,6)-carboxy-fluorescein (BCECF). BCECF was calibrated intracellularly, demonstrating similar pH-sensitivity of the dye in control and acidotic animals. In subsequent studies, lumen and peritubular capillaries were perfused to examine Na/H and Na(HCO3)3 transporter activity in the absence of contact with native fluid. The initial rate of change in cell pH (dpHi/dt) was 97, 50, and 44% faster in tubules from acidotic animals when peritubular [HCO3] was changed from 25 to 10 mM in the presence or absence of chloride, or peritubular [Na] was changed from 147 to 50 mM, respectively. dpHi/dt was 57% faster in tubules from acidotic animals when luminal [Na] was changed from 152 to 0 mM. Buffer capacities, measured using NH3/NH+4 addition, were similar in the two groups. The results demonstrate that chronic metabolic acidosis causes an adaptation in the intrinsic properties of both the apical membrane Na/H antiporter and basolateral membrane Na(HCO3)3 symporter.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiba T., Alpern R. J., Eveloff J., Calamina J., Warnock D. G. Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransport in rabbit renal cortical basolateral membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1472–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI112738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiba T., Rocco V. K., Warnock D. G. Parallel adaptation of the rabbit renal cortical sodium/proton antiporter and sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):308–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI113074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Basolateral membrane Cl/HCO3 exchange in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Na-dependent and -independent modes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Apr;89(4):581–598. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Chambers M. Cell pH in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Regulation by luminal and peritubular pH and sodium concentration. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):502–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI112602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):F53–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.1.F53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of extracellular fluid volume and plasma bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI110821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH-/HCO-3 transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. A sodium-coupled electrogenic process. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):613–636. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Sohtell M. Electrophysiology of basolateral bicarbonate transport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 2):F267–F272. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.2.F267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal S. S., Ware R. A., Kleinman J. G. Proximal tubule hydrogen ion transport processes in diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Na-H exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):29–52. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Intracellular pH transients in giant barnacle muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):C61–C73. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.233.3.C61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Green N. Bicarbonate transport by isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F307–F314. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Giebisch G. Relationship between sodium and bicarbonate transport in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):F222–F230. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.3.F222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Proximal reabsorption during metabolic acidosis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F499–F507. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Metabolic acidosis and parathyroidectomy increase Na+-H+ exchange in brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F217–F222. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., DuBose T. D., Jr Ammonia transport by early and late proximal convoluted tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):684–691. doi: 10.1172/JCI112871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Aronson P. S. Na+/HCO3-co-transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8778–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassl S. M., Holohan P. D., Ross C. R. HCO3- transport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rat renal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Brenner B. M., Seifter J. L. Sodium-hydrogen exchange and glucose transport in renal microvillus membrane vesicles from rats with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):724–733. doi: 10.1172/JCI112367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Seifter J. L., Brenner B. M. Adaptation of Na+-H+ exchange in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Role of dietary protein and uninephrectomy. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1979–1987. doi: 10.1172/JCI111619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen C., Kragh-Hansen U., Sheikh M. I. Na+-H+ exchange in luminal-membrane vesicles from rabbit proximal convoluted and straight tubules in response to metabolic acidosis. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):411–416. doi: 10.1042/bj2390411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne-Saffran E., Beauwens R., Kinne R. An ATP-driven proton pump in brush-border membranes from rat renal cortex. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(1-2):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01870769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Interaction of NH4+ and Li+ with the renal microvillus membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):C220–C226. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.5.C220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F461–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange activity in renal brush border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis: The role of glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Berry C. A. Basolateral membrane Na/base cotransport is dependent on CO2/HCO3 in the proximal convoluted tubule. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Dec;90(6):833–853. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Hart J. I., Walker K. A. Effect of metabolic acidosis on proximal tubular total CO2 absorption. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 2):F62–F68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.1.F62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I. Apical Na+/H+ antiporter and glycolysis-dependent H+-ATPase regulate intracellular pH in the rabbit S3 proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):928–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI113184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes A. G., Siebens A. W., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransport across basolateral membrane of isolated perfused Necturus proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F340–F350. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U., Kinne R. Sodium/proton antiport in brush-border-membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine and kidney. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):597–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami G. T. Luminal secretion of ammonia in the mouse proximal tubule perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):159–164. doi: 10.1172/JCI113287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Hafezi A., Kaunitz J. D., Trizna W., Fine L. G. pH gradient-dependent increased Na+-H+ antiport capacity of the rabbit remnant kidney. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 2):F90–F98. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.1.F90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Ives H. E., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr Role of the Na+/H+ antiporter in rat proximal tubule bicarbonate absorption. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):970–978. doi: 10.1172/JCI113190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Berry C. A. Mechanism of bicarbonate exit across basolateral membrane of the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F889–F896. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Shigai T., Takeuchi J. Intracellular pH in the isolated perfused rabbit proximal straight tubule. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F417–F423. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Grassi S. M., Aronson P. S. Stoichiometry of Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1172/JCI112948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talor Z., Yang W. C., Shuffield J., Sack E., Arruda J. A. Chronic hypercapnia enhances Vmax of Na-H antiporter of renal brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F394–F400. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. J., Ives H. E., Alpern R. J., Yee V. J., Warnock D. G., Rector F. C., Jr Increased Vmax for Na+/H+ antiporter activity in proximal tubule brush border vesicles from rabbits with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F339–F343. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Reenstra W. W., Yee V. J. Na+/H+ antiporter of brush border vesicles: studies with acridine orange uptake. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F733–F739. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Burckhardt B. C., Frömter E. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):360–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00595689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]