Abstract
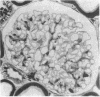
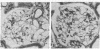
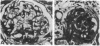
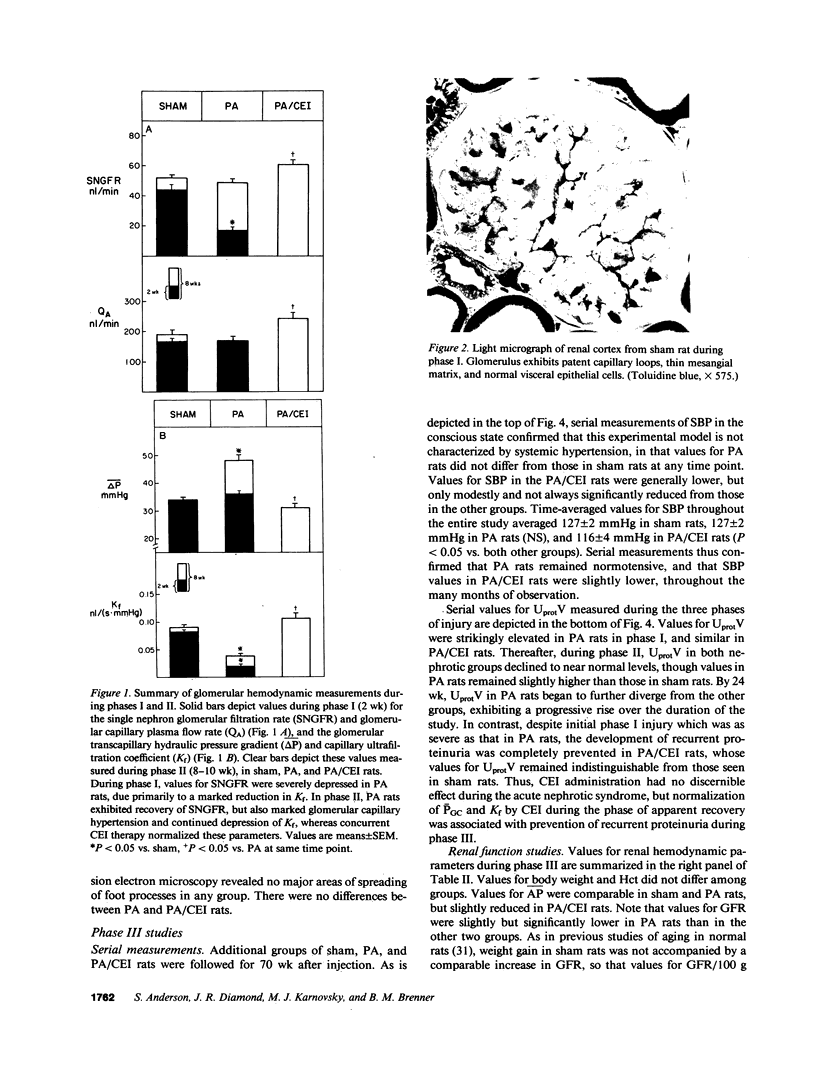
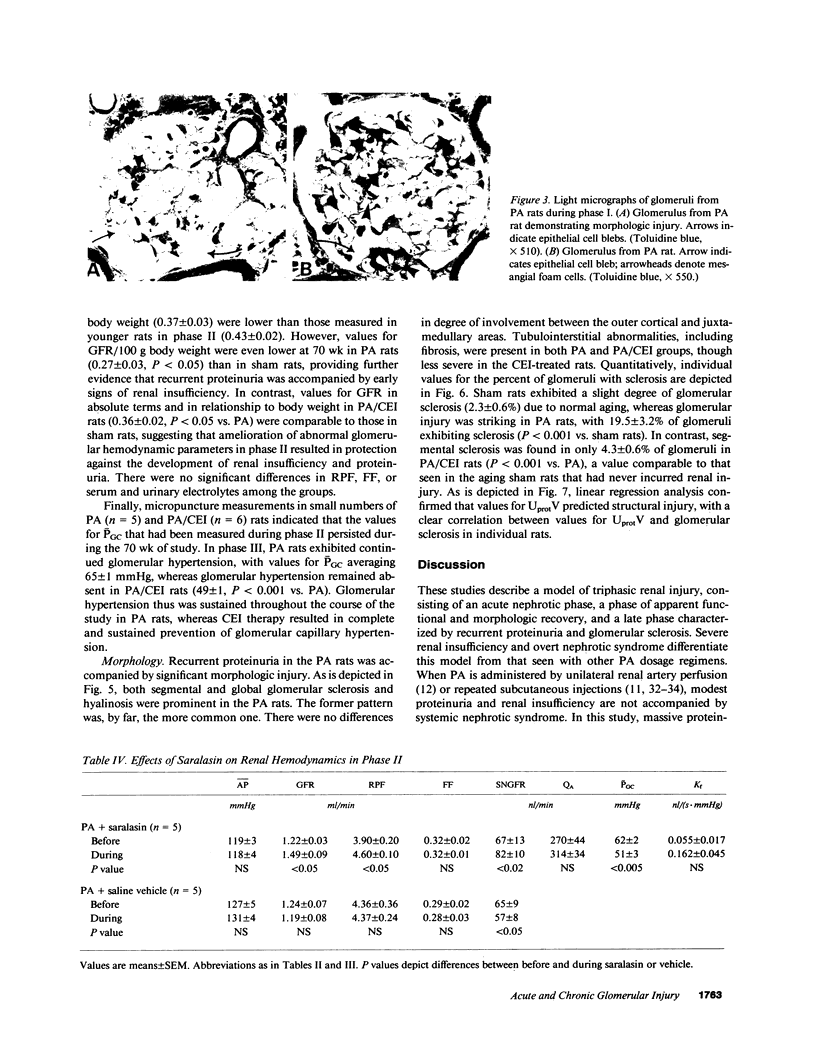
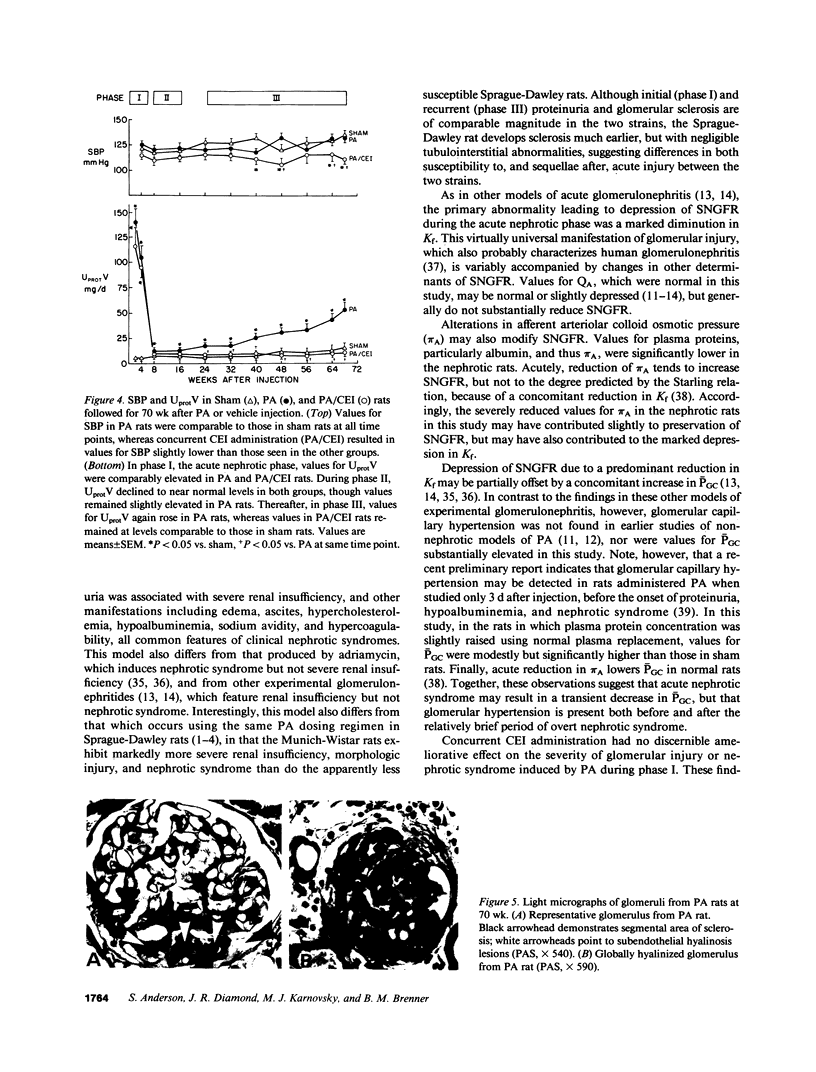
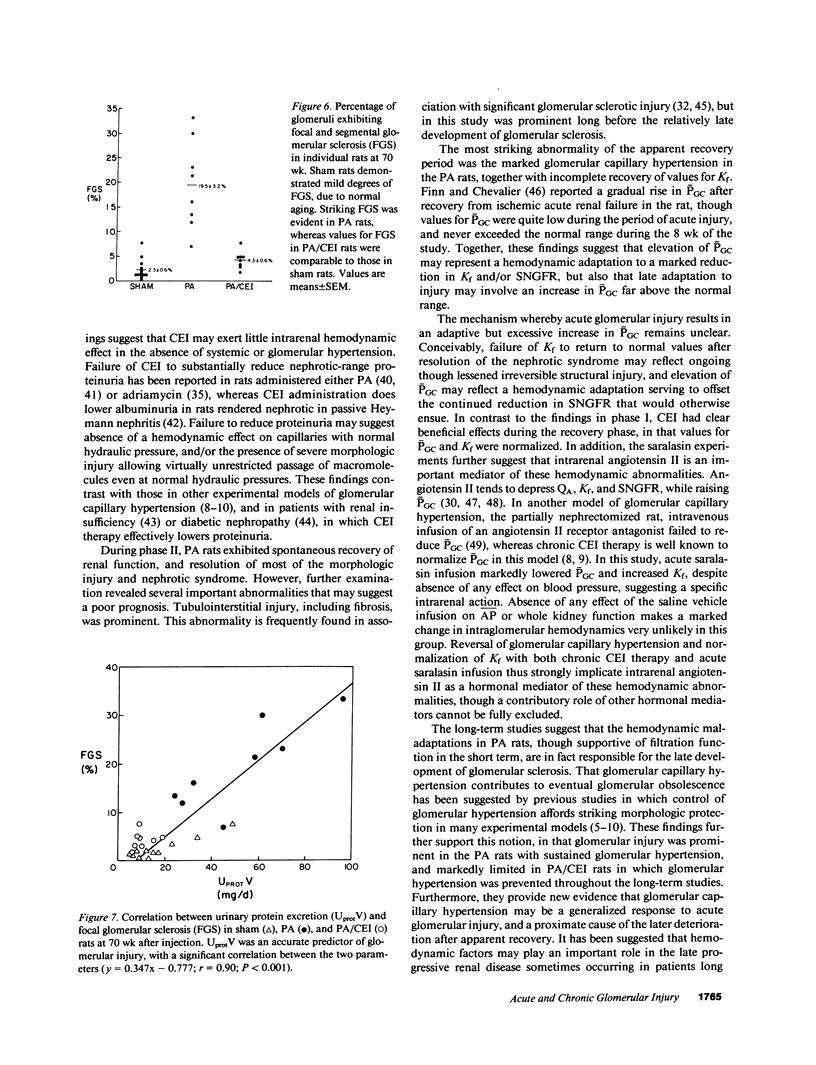
Functional and morphologic measurements were performed in Munich-Wistar rats after a single central venous injection of puromycin aminonucleoside (PA) or saline vehicle (sham). During phase I, PA rats exhibited overt nephrotic syndrome and impaired glomerular filtration, primarily due to a reduction in the glomerular capillary ultrafiltration coefficient. The morphologic counterpart of the latter consisted of effacement of glomerular epithelial cell foot processes and decrease in the number of filtration slit diaphragms. Administration of the angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitor (CEI) enalapril to PA rats did not ameliorate glomerular dysfunction. During phase II, PA rats exhibited spontaneous resolution of proteinuria, impaired function, and morphologic abnormalities. However, PA rats now demonstrated marked glomerular capillary hypertension and continued, albeit lesser, reductions in the ultrafiltration coefficient. Concurrent CEI administration modestly lowered systemic arterial pressure, and normalized the glomerular capillary hydraulic pressure and ultrafiltration coefficient. Additional rats were studied during phase III, 70 wk after injection. In PA rats, prior glomerular hypertension was associated with development of recurrent proteinuria and extensive glomerular sclerosis, whereas concurrent CEI administration limited these parameters to values comparable to those in sham rats. Glomerular hypertension thus may explain the development of glomerular sclerosis and renal failure long after an episode of acute glomerular injury.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Meyer T. W., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):612–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Therapeutic advantage of converting enzyme inhibitors in arresting progressive renal disease associated with systemic hypertension in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1993–2000. doi: 10.1172/JCI112528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin D. S. Chronic glomerulonephritis: nonimmunologic mechanisms of progressive glomerular damage. Kidney Int. 1982 Jan;21(1):109–120. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertani T., Cutillo F., Zoja C., Broggini M., Remuzzi G. Tubulo-interstitial lesions mediate renal damage in adriamycin glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 1986 Oct;30(4):488–496. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Konnen K. S., Tucker B. J. Angiotensin II effects upon the glomerular microcirculation and ultrafiltration coefficient of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):419–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI108293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohrer M. P., Baylis C., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Willis W. T. Mechanisms of the puromycin-induced defects in the transglomerular passage of water and macromolecules. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):152–161. doi: 10.1172/JCI108751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu P. J., Brown A. D. Effect of captopril on pre-existing and aminonucleoside-induced proteinuria in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;31(3):419–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corman B., Michel J. B. Renin-angiotensin system, converting-enzyme inhibition and kidney function in aging female rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):R450–R455. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.3.R450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Ameliorative effects of dietary protein restriction in chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 May;109(5):538–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Exacerbation of chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis by dietary cholesterol supplementation. Kidney Int. 1987 Nov;32(5):671–677. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis following a single intravenous dose of puromycin aminonucleoside. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):481–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis: analogies to atherosclerosis. Kidney Int. 1988 May;33(5):917–924. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Nonanticoagulant protective effect of heparin in chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis. Ren Physiol. 1986;9(6):366–374. doi: 10.1159/000173102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn W. F., Chevalier R. L. Recovery from postischemic acute renal failure in the rat. Kidney Int. 1979 Aug;16(2):113–123. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser R. J., Velosa J. A., Michael A. F. Experimental model of focal sclerosis. I. Relationship to protein excretion in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grond J., Koudstaal J., Elema J. D. Mesangial function and glomerular sclerosis in rats with aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1985 Feb;27(2):405–410. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grond J., Weening J. J., Elema J. D. Glomerular sclerosis in nephrotic rats. Comparison of the long-term effects of adriamycin and aminonucleoside. Lab Invest. 1984 Sep;51(3):277–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeg J. E., de Jong P. E., van der Hem G. K., de Zeeuw D. Reduction of proteinuria by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. Kidney Int. 1987 Jul;32(1):78–83. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel E., Parving H. H., Mathiesen E., Edsberg B., Damkjaer Nielsen M., Giese J. Effect of captopril on kidney function in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with nephropathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 23;293(6545):467–470. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6545.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F85–F93. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Glomerular hemodynamics in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1981 Mar;19(3):410–415. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. N., Schambelan M., Kaysen G. A. Modulation of albuminuria by dietary protein and converting enzyme inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F719–F725. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Hoyer J. R., Seiler M. W., Brenner B. M. Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance in the setting of heterogeneous glomerular injury. Preservation of a close functional linkage between individual nephrons and surrounding microvasculature. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):185–198. doi: 10.1172/JCI110430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Miele J. F., Brenner B. M. Reversal of renal cortical actions of angiotensin II by verapamil and manganese. Kidney Int. 1979 Aug;16(2):137–147. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Rennke H. G., Hoyer J. R., Badr K. F., Schor N., Troy J. L., Lechene C. P., Brenner B. M. Role for intrarenal mechanisms in the impaired salt excretion of experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):91–103. doi: 10.1172/JCI110756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jha R. K. An improved polychrome staining method for thick epoxy sections. Stain Technol. 1976 May;51(3):159–162. doi: 10.3109/10520297609116692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasten F. H., Lala R. The Feulgen reaction after glutaraldehyde fixation. Stain Technol. 1975 May;50(3):197–201. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane W. F., Raij L. Relationship among altered glomerular barrier permselectivity, angiotensin II, and mesangial uptake of macromolecules. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):599–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Daugharty T. M., Brenner B. M. Determinants of glomerular filtration in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):305–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI107934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Price D. C., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of surgery on plasma volume and salt and water excretion in rats. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F600–F606. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinides G. N., Groggel G. C., Cohen A. H., Cook T., Baranowski R. L., Westenfelder C., Border W. A. Failure of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition to affect the course of chronic puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 1987 Nov;129(2):394–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marre M., Leblanc H., Suarez L., Guyenne T. T., Ménard J., Passa P. Converting enzyme inhibition and kidney function in normotensive diabetic patients with persistent microalbuminuria. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jun 6;294(6585):1448–1452. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6585.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. L., Meyer T. W. Plasma protein concentration and colloid osmotic pressure in nephrotic rats. Kidney Int. 1988 Aug;34(2):220–223. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncloa F., Sromovsky J. A., Walker J. F., Davies R. O. Enalapril in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Overall review of efficacy and safety. Drugs. 1985;30 (Suppl 1):82–89. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198500301-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers B. D., Deen W. M., Brenner B. M. Effects of norepinephrine and angiotensin II on the determinants of glomerular ultrafiltration and proximal tubule fluid reabsorption in the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Jul;37(1):101–110. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers B. D., Okarma T. B., Friedman S., Bridges C., Ross J., Asseff S., Deen W. M. Mechanisms of proteinuria in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):732–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI110669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. P., Michels L., Kasiske B., Raij L., Keane W. F. Adriamycin-induced chronic proteinuria: a structural and functional study. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer J. M., Pfeffer M. A., Frohlich E. D. Validity of an indirect tail-cuff method for determining systolic arterial pressure in unanesthetized normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Dec;78(6):957–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Iturbe B., Herrera J., García R. Response to acute protein load in kidney donors and in apparently normal postacute glomerulonephritis patients: evidence for glomerular hyperfiltration. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):461–464. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Karnovsky M. J. An ultrastructural study of the mechanisms of proteinuria in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1975 Oct;8(4):219–232. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velosa J. A., Glasser R. J., Nevins T. E., Michael A. F. Experimental model of focal sclerosis. II. Correlation with immunopathologic changes, macromolecular kinetics, and polyanion loss. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets J. W., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Determination of serum protein concentration in nanoliter blood samples using fluorescamine or 9-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger M. H. Antihypertensive therapy and lipids. Evidence, mechanisms, and implications. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Jun;145(6):1102–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., Dunn B. R., Meyer T. W., Anderson S., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Prevention of diabetic glomerulopathy by pharmacological amelioration of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1925–1930. doi: 10.1172/JCI112521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Nahas A. M., Zoob S. N., Evans D. J., Rees A. J. Chronic renal failure after nephrotoxic nephritis in rats: contributions to progression. Kidney Int. 1987 Aug;32(2):173–180. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]