Abstract
Abetalipoproteinemia (ABL) is a recessive disorder in which affected individuals have extremely low or undetectable levels of serum apo B-containing lipoproteins. Using restriction fragment length polymorphisms, we have studied two families, each with two children with classical ABL born of normal parents. In each of these families, the two affected children have inherited different apo B alleles from at least one parent, whereas the siblings would be anticipated to share common alleles if this disorder were due to an apo B gene mutation. This linkage study shows that in these families, the apo B gene is discordant with ABL and therefore the disorder is caused by a defect in another gene, which is important for the normal synthesis or secretion of apo B-containing lipoproteins from both the liver and intestine.
Full text
PDF

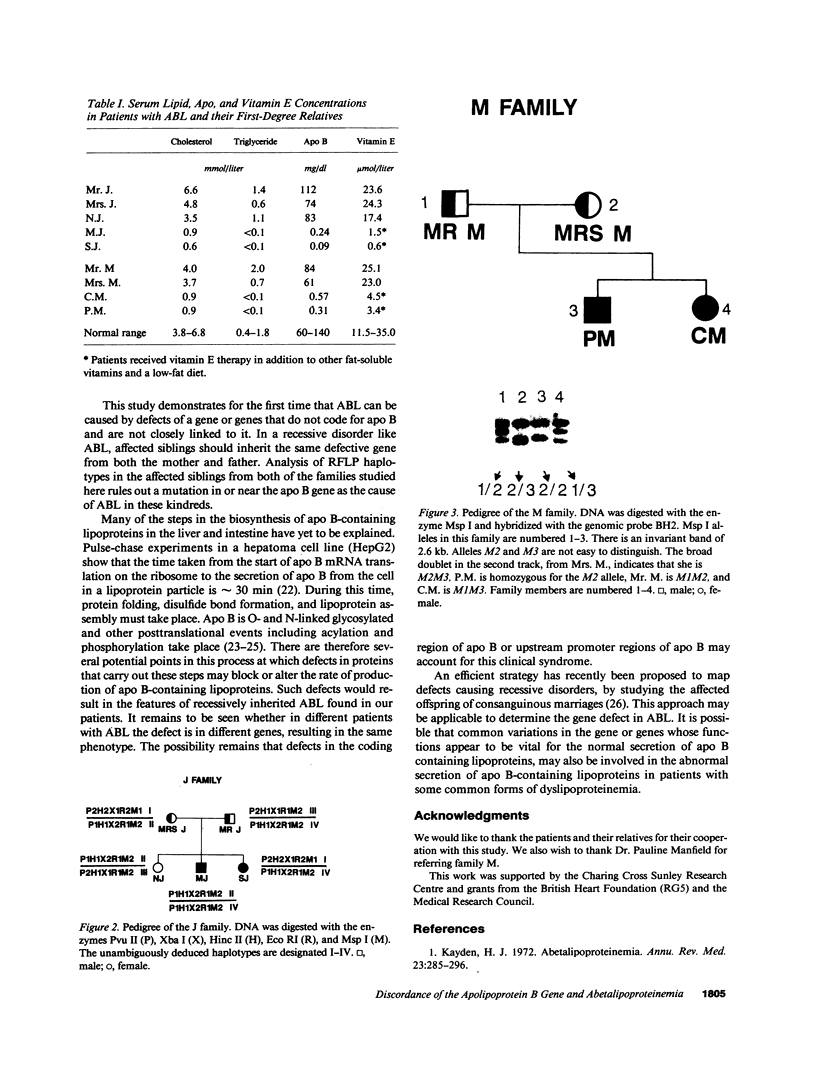

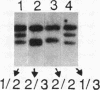
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barni N., Talmud P. J., Carlsson P., Azoulay M., Darnfors C., Harding D., Weil D., Grzeschik K. H., Bjursell G., Junien C. The isolation of genomic recombinants for the human apolipoprotein B gene and the mapping of three common DNA polymorphisms of the gene--a useful marker for human chromosome 2. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):313–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00279093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemer J. J., McCammon R. E. The genetic relationship of abetalipoproteinemia and hypobetalipoproteinemia: a report of the occurence of both diseases within the same family. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):556–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Witt K. R., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Donaldson V. H., Jackson R. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein B-100 of human plasma low density lipoproteins by tissue and plasma kallikreins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8522–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. R., Knott T. J., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Robertson S., Pullinger C. R., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Humphries S. E. Truncated variants of apolipoprotein B cause hypobetalipoproteinaemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8361–8375. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnfors C., Nilsson J., Protter A. A., Carlsson P., Talmud P. J., Humphries S. E., Whalström J., Wiklund O., Bjursell G. RFLPs for the human apolipoprotein B gene: HincII and PvuII. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7135–7135. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dullaart R. P., Speelberg B., Schuurman H. J., Milne R. W., Havekes L. M., Marcel Y. L., Geuze H. J., Hulshof M. M., Erkelens D. W. Epitopes of apolipoprotein B-100 and B-48 in both liver and intestine. Expression and evidence for local synthesis in recessive abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1397–1404. doi: 10.1172/JCI112727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H., Lees R. S., Lux S. E., Kilgore A. Immunofluorescence studies of apolipoprotein B in intestinal mucosa. Absence in abetalipoproteinemia. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):288–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G., Lee D. M., Singh S. Identification of the thiol ester linked lipids in apolipoprotein B. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayden H. J. Abetalipoproteinemia. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:285–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessling A. M., Horsthemke B., Humphries S. E. A study of DNA polymorphisms around the human apolipoprotein AI gene in hyperlipidaemic and normal individuals. Clin Genet. 1985 Oct;28(4):296–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Scott J. A hypervariable region 3' to the human apolipoprotein B gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9215–9216. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner K. J., Monge J. C., Gregg R. E., Hoeg J. M., Triche T. J., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Analysis of the apolipoprotein B gene and messenger ribonucleic acid in abetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1707–1712. doi: 10.1172/JCI112766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2884728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Grey V. L., Roy C. C. Absence of intestinal synthesis of apolipoprotein B-48 in two cases of abetalipoproteinemia. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1119–1126. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90577-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Bird A. C. Long-term management of abetalipoproteinaemia. Possible role for vitamin E. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Mar;52(3):209–214. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K. Effect of large oral doses of vitamin E on the neurological sequelae of patients with abetalipoproteinemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;393:133–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Wolff O. H. Vitamin E and neurological function. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):225–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S. O., Bjursell G., Boström K., Carlsson P., Elovson J., Protter A. A., Reuben M. A., Bondjers G. Apolipoprotein B: structure, biosynthesis and role in the lipoprotein assembly process. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Nov;68(1-2):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. S., Gregg R. E., Law S. W., Monge J. C., Grant S. M., Higuchi K., Triche T. J., Jefferson J., Brewer H. B., Jr Homozygous hypobetalipoproteinemia: a disease distinct from abetalipoproproteinemia at the molecular level. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):590–595. doi: 10.1172/JCI113357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmud P. J., Barni N., Kessling A. M., Carlsson P., Darnfors C., Bjursell G., Galton D., Wynn V., Kirk H., Hayden M. R. Apolipoprotein B gene variants are involved in the determination of serum cholesterol levels: a study in normo- and hyperlipidaemic individuals. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Sep;67(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrift R. N., Forte T. M., Cahoon B. E., Shore V. G. Characterization of lipoproteins produced by the human liver cell line, Hep G2, under defined conditions. J Lipid Res. 1986 Mar;27(3):236–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauhkonen M., Viitala J., Parkkinen J., Rauvala H. High-mannose structure of apolipoprotein-B from low-density lipoproteins of human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whayne T. F., Alaupovic P., Curry M. D., Lee E. T., Anderson P. S., Schechter E. Plasma apolipoprotein B and VLDL-, LDL-, and HDL-cholesterol as risk factors in the development of coronary artery disease in male patients examined by angiography. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jun;39(3):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Dubois B. W., Witztum J. L. Genetic analysis of a kindred with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. Evidence for two separate gene defects: one associated with an abnormal apolipoprotein B species, apolipoprotein B-37; and a second associated with low plasma concentrations of apolipoprotein B-100. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1842–1851. doi: 10.1172/JCI113026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Characterization of an abnormal species of apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B-37, associated with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI113025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]