Abstract
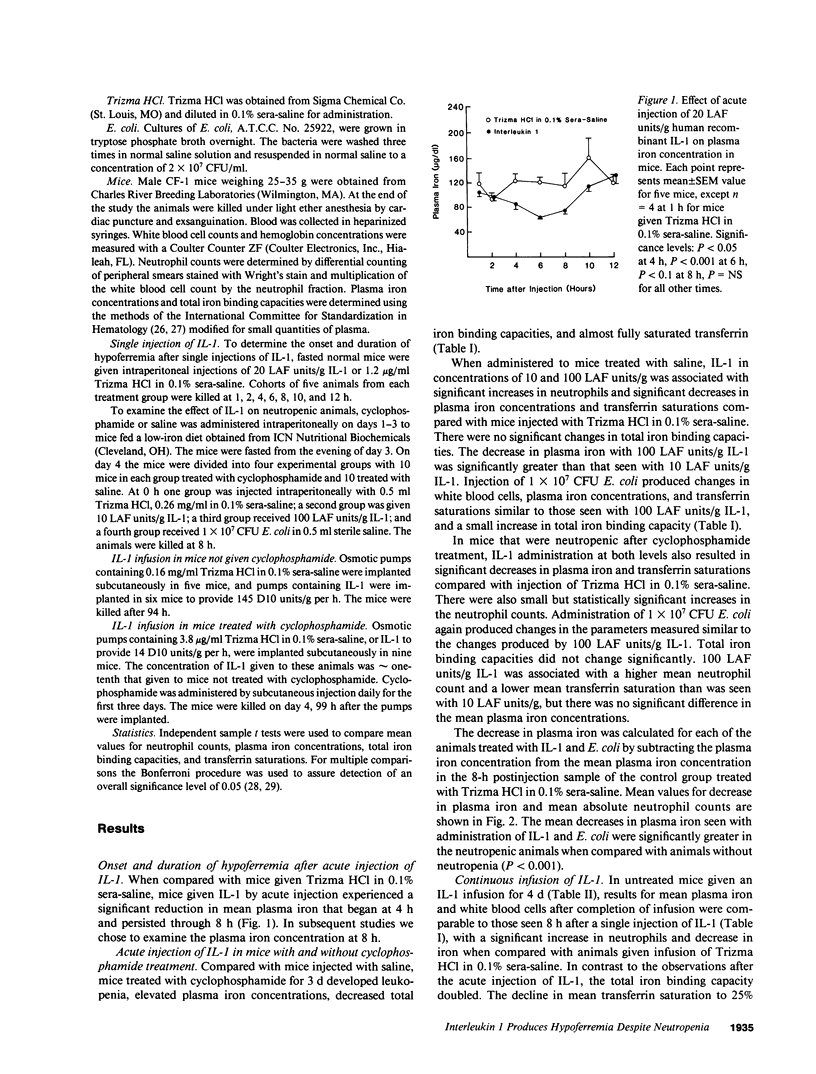
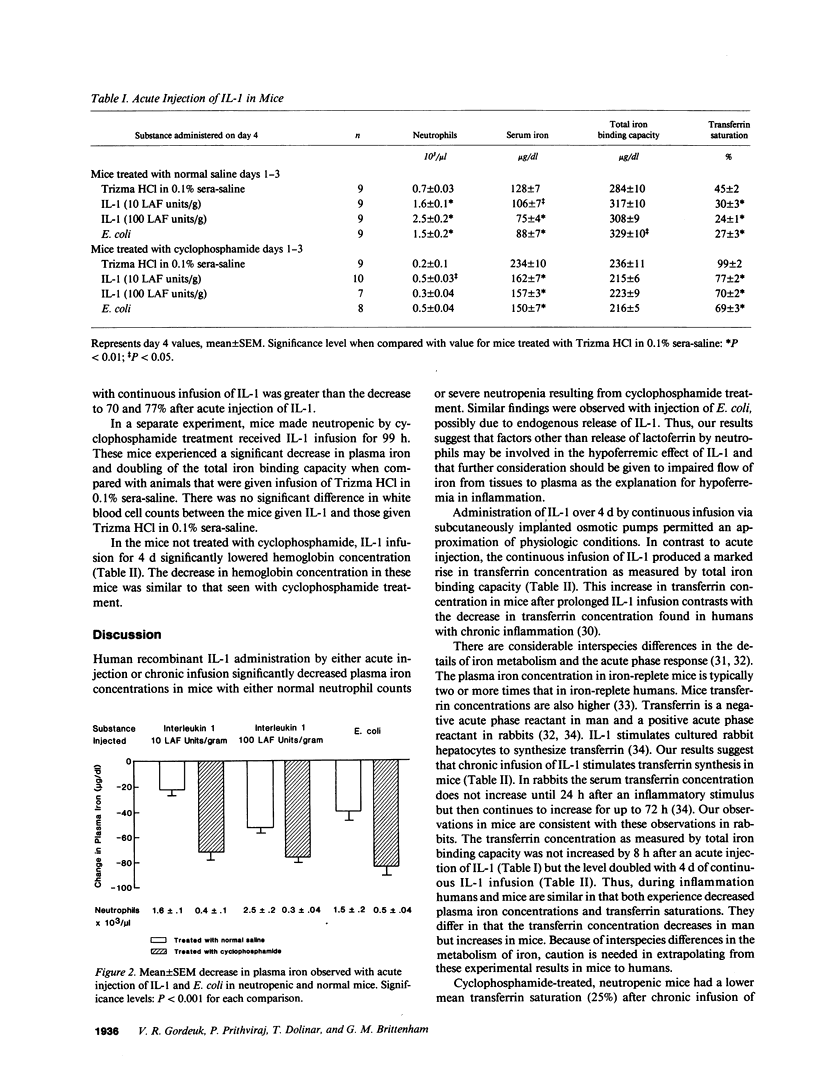
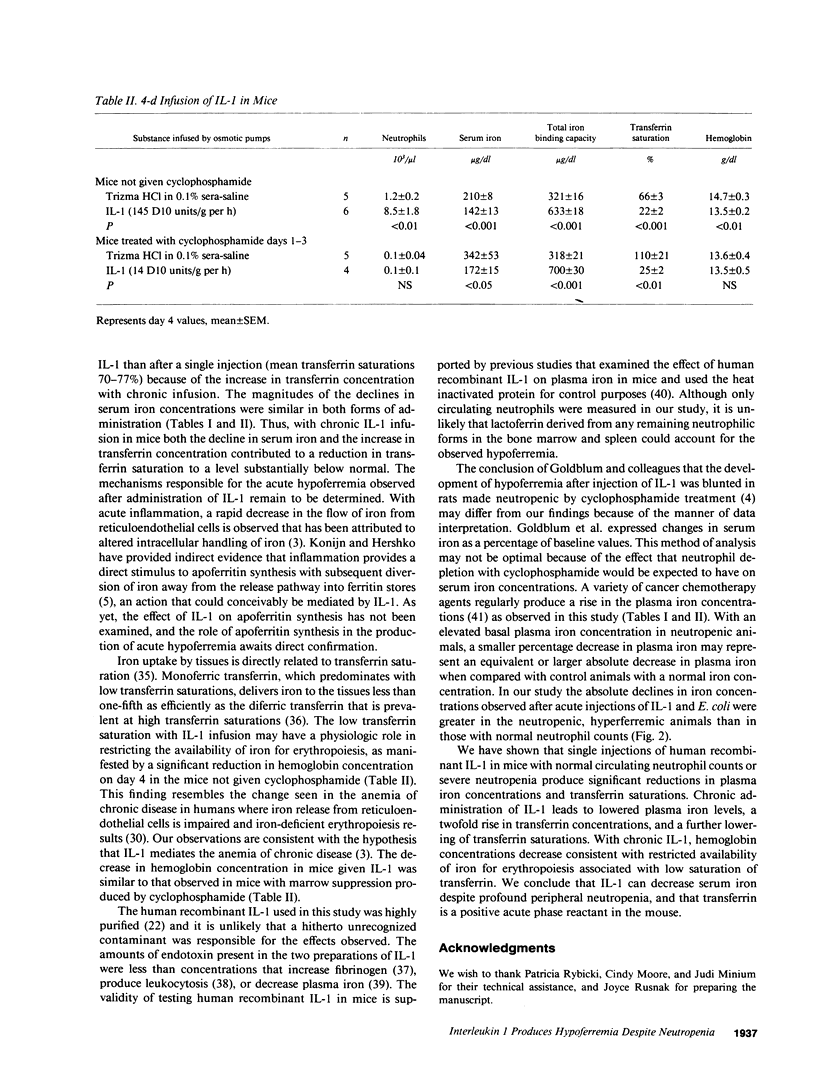
To determine whether the hypoferremic response to inflammation requires neutrophils, we administered human recombinant IL-1 to mice made neutropenic with cyclophosphamide. With single intraperitoneal injections of IL-1 the plasma iron concentrations decreased significantly in mice with either normal neutrophil counts or neutropenia. After single injections transferrin concentrations were not significantly changed, but the decrease in serum iron lowered mean transferrin saturations from a baseline of 45 to 24-30% in nonneutropenic mice, and from 99 to 70-77% in neutropenic mice. Similar changes were observed after intraperitoneal injections of Escherichia coli. 4-d continuous infusions of IL-1 also led to reductions in serum iron concentrations, but transferrin concentrations doubled. The combination of a decrease in serum iron and an increase in transferrin concentration after chronic infusion in neutropenic mice led to a greater decline in mean transferrin saturations, from a baseline of 110 to 25%. In mice not given cyclophosphamide, chronic IL-1 infusion was associated with a reduction in mean hemoglobin concentrations from 14.7 to 13.5 g/dl, consistent with restricted availability of iron for erythropoiesis associated with low saturation of transferrin. We conclude that IL-1 can decrease the serum iron despite profound peripheral neutropenia and that transferrin in a positive acute phase reactant in the mouse.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., De Duve C., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Association of lactoferrin with specific granules in rabbit heterophil leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baynes R., Bezwoda W., Bothwell T., Khan Q., Mansoor N. The non-immune inflammatory response: serial changes in plasma iron, iron-binding capacity, lactoferrin, ferritin and C-reactive protein. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;46(7):695–704. doi: 10.3109/00365518609083733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Kokocinski T. Lactoferrin content of peripheral blood cells. Br J Haematol. 1978 Aug;39(4):509–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright G. E., Lee G. R. The anaemia of chronic disorders. Br J Haematol. 1971 Aug;21(2):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzola M., Huebers H. A., Sayers M. H., MacPhail A. P., Eng M., Finch C. A. Transferrin saturation, plasma iron turnover, and transferrin uptake in normal humans. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):935–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtoy P. J., Moguilevsky N., Retegui L. A., Castracane C. E., Masson P. L. Uptake of lactoferrin by the liver. II. Endocytosis by sinusoidal cells. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):329–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancey J. T., Brubaker L. H. Neutrophil marrow cellularity in neutropenia. Am J Hematol. 1982 Jun;12(4):309–322. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Mier J. W., Bernheim H. A., LoPreste G., Lynn D. L., Love R. N., Webb A. C., Auron P. E., Reuben R. C. Multiple biological activities of human recombinant interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1734–1739. doi: 10.1172/JCI112495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Cohen D. A., Jay M., McClain C. J. Interleukin 1-induced depression of iron and zinc: role of granulocytes and lactoferrin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 1):E27–E32. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.1.E27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordeuk V. R., Brittenham G. M., McLaren G. D., Spagnuolo P. J. Hyperferremia in immunosuppressed patients with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia and the risk of infection. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Nov;108(5):466–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Chua A. O., Stern A. S., Hellmann C. P., Vitek M. P., DeChiara T. M., Benjamin W. R., Collier K. J., Dukovich M., Familletti P. C. Recombinant human interleukin 1 alpha: purification and biological characterization. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen N. E., Malmquist J., Thorell J. Plasma myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin measured by radioimmunoassay: relations to neutrophil kinetics. Acta Med Scand. 1975 Dec;198(6):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1975.tb19572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebers H., Csiba E., Huebers E., Finch C. A. Molecular advantage of diferric transferrin in delivering iron to reticulocytes: a comparative study. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jun;179(2):222–226. doi: 10.3181/00379727-179-42090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter R. L., Bennett B., Towns M., Vogler W. R. Transferrin in disease II: defects in the regulation of transferrin saturation with iron contribute to susceptibility to infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;81(6):748–753. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.6.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMPSCHMIDT R. F., UPCHURCH H. F. Effects of bacteria endotoxin on plasma iron. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 May;110:191–193. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Upchurch H. F. Neutrophil release after injections of endotoxin or leukocytic endogenous mediator into rats. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Aug;28(2):191–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Upchurch H. Lowering of plasma iron concentration in the rat with leukocytic extracts. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jun;216(6):1287–1291. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.6.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasing K. C. Effect of inflammatory agents and interleukin 1 on iron and zinc metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):R901–R904. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.5.R901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Human leukocytic pyrogen induces release of specific granule contents from human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1330–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI109050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn A. M., Hershko C. Ferritin synthesis in inflammation. I. Pathogenesis of impaired iron release. Br J Haematol. 1977 Sep;37(1):7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Mackiewicz A. Acute phase proteins as disease markers. Dis Markers. 1987 Mar;5(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lash J. A., Coates T. D., Lafuze J., Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A. Plasma lactoferrin reflects granulocyte activation in vivo. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):885–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. R. The anemia of chronic disease. Semin Hematol. 1983 Apr;20(2):61–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. The Limulus test and bacterial endotoxins: some perspectives. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;93:7–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozoff B., Brittenham G. M. Behavioral aspects of iron deficiency. Prog Hematol. 1986;14:23–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Samols D., Reese J., Kushner I. Regulation of rabbit acute phase protein biosynthesis by monokines. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):851–857. doi: 10.1042/bj2530851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by the macrophage cell line, P388D1. I. Enhancement of LAF production by activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson T., Olsson I., Venge P., Elgefors B. Serum myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin in neutropenia. Scand J Haematol. 1977 Jan;18(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1977.tb01480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieels J. P., Pizzo S. V., Glasgow L. R., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Hepatic receptor that specifically binds oligosaccharides containing fucosyl alpha1 leads to 3 N-acetylglucosamine linkages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2215–2219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Chindemi P. A., Debanne M. T., Prieels J. P. Lactoferrin catabolism in the rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):G8–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.1.G8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Speziale S. C., Bowman B. J. Properties of interleukin-1 as a complete secretagogue for human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1233–1240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91746-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L. The binding of human lactoferrin to mouse peritoneal cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1568–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wycoff H. D. Production of fibrinogen following an endotoxin injection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):940–943. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Snick J. L., Markowetz B., Masson P. L. The ingestion and digestion of human lactoferrin by mouse peritoneal macrophages and the transfer of its iron into ferritin. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):817–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



