Abstract
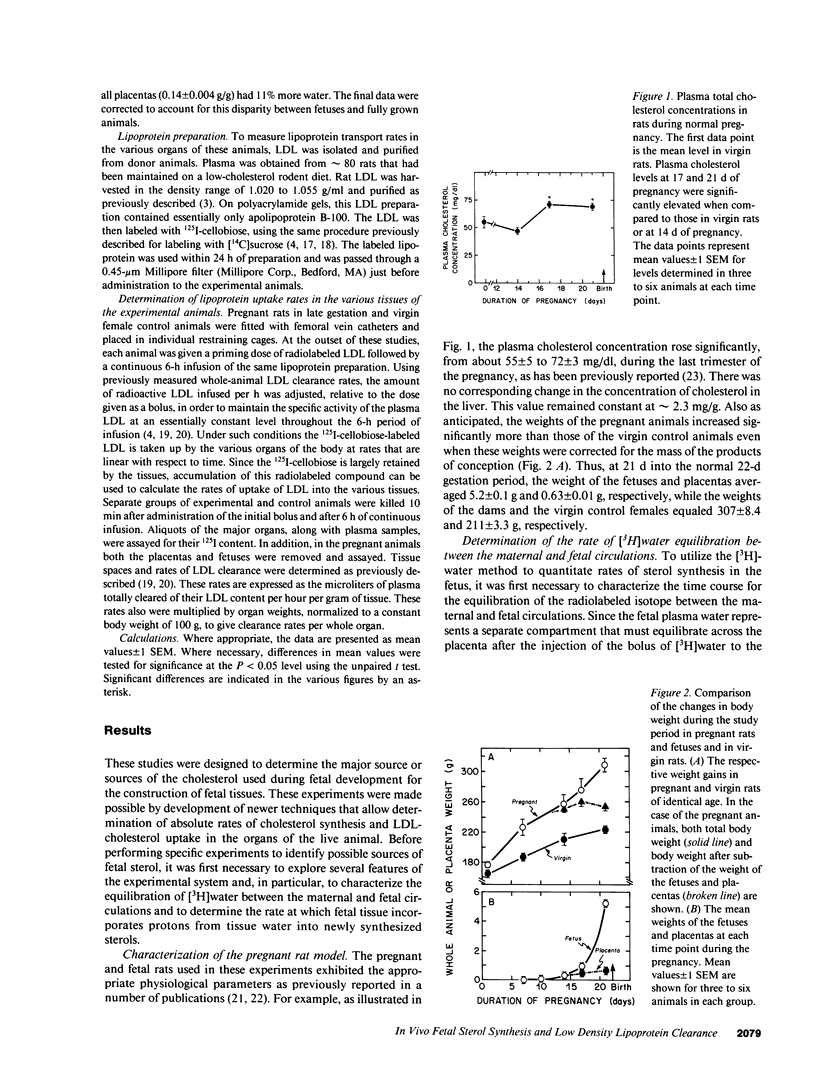
Whereas the greatest relative increase in body mass occurs during the third trimester of fetal life, the source of the cholesterol that supports this growth is uncertain. These studies used [3H]water and 125I-cellobiose-labeled low density lipoproteins to quantitate absolute rates of cholesterol acquisition in vivo by the fetus of the rat. Preliminary studies demonstrated that [3H]water administered intravenously to the mother rapidly equilibrated with the body pool of water in the fetus and that 22-microgram atoms of H from the water pool were incorporated into each micromole of newly synthesized cholesterol. After administration of [3H]water to pregnant rats, the rates of sterol synthesis per 100 g of whole body weight were severalfold higher in the fetus than in the dams. Individual organs of the dam such as the liver, however, had much higher synthetic rates than those in the fetus. When maternal hepatic cholesterol synthesis was suppressed by cholesterol feeding, newly synthesized cholesterol disappeared from the maternal blood yet there was essentially no change in the rate of appearance of newly synthesized sterol in the fetus, placenta, and fetal membranes. The placenta did take up low density lipoproteins at rates equal to about one-third of that seen in the maternal liver, but none of the apolipoprotein or cholesterol was transferred to the fetus. These studies indicate that the rat fetus receives little or no cholesterol from the mother but, rather, satisfies its need for cholesterol during fetal development through local synthesis. Furthermore, the fetal membranes appear to be an important site for sterol synthesis in the fetal compartment.
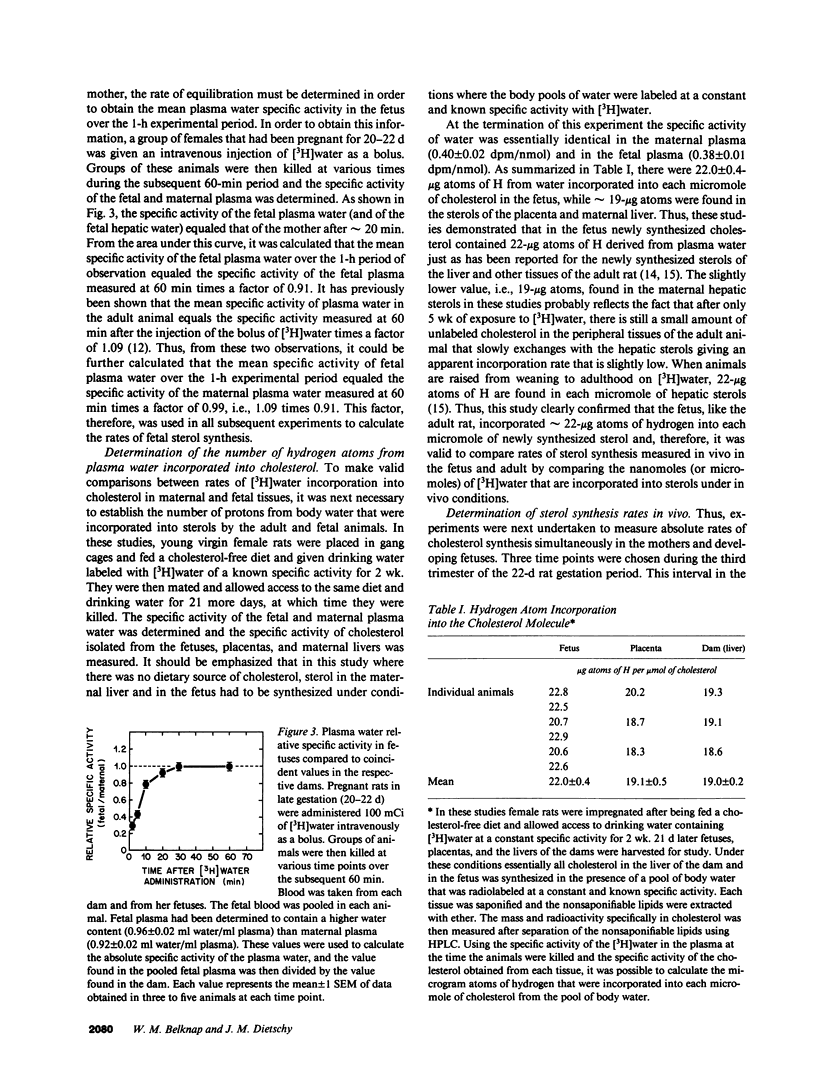
Full text
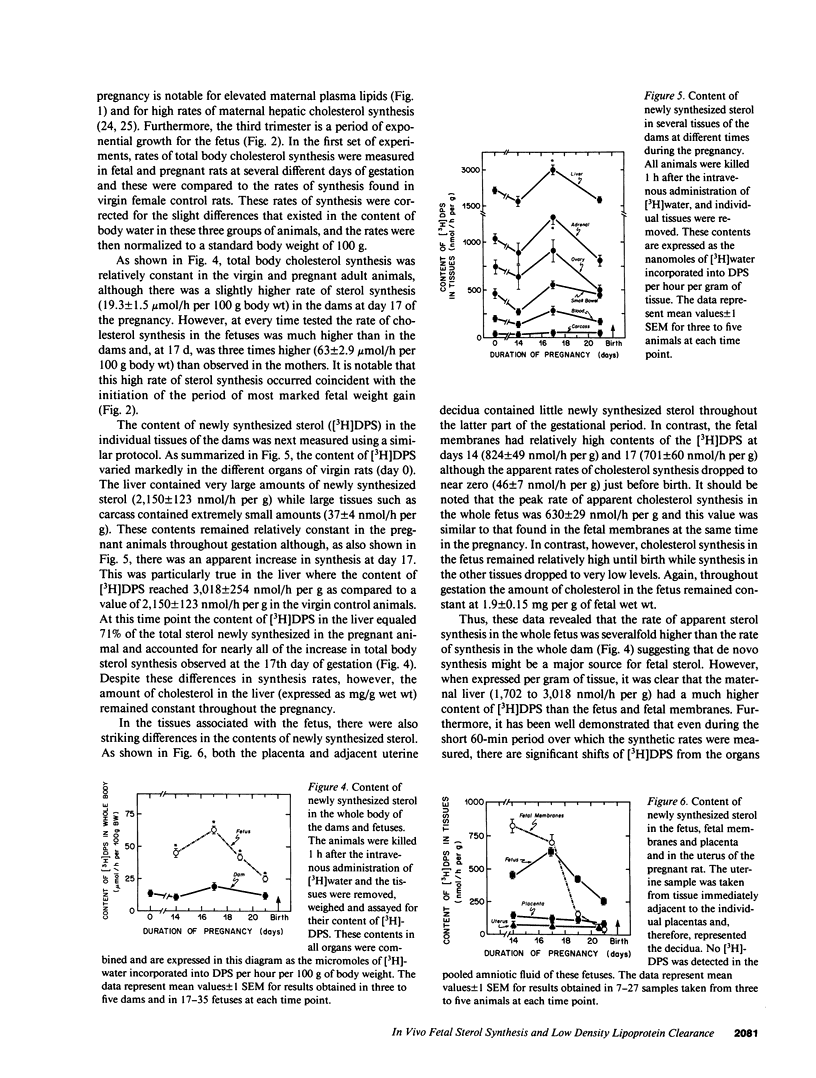
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Absolute rates of cholesterol synthesis in extrahepatic tissues measured with 3H-labeled water and 14C-labeled substrates. J Lipid Res. 1979 Aug;20(6):740–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argiles J., Herrera E. Lipids and lipoproteins in maternal and fetus plasma in the rat. Biol Neonate. 1981;39(1-2):37–44. doi: 10.1159/000241390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botte V., Materazzi G., Chieffi G. Histochemical distribution of 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17-alpha-and 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in the placenta and foetal membranes of the rat. J Endocrinol. 1966 Feb;34(2):179–183. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0340179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr B. R., Rainey W. E., Mason J. I. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in anencephalic and normal human fetal liver. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1946–1949. doi: 10.1172/JCI112192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr B. R., Simpson E. R. Cholesterol synthesis in human fetal tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):447–452. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. C., Minor R. R., Koszalka T. R., Brent R. L., Kefalides N. A. The embryonic rat parietal yolk sac. Changes in the morphology and composition of its basement membrane during development. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. C., Tomichek E. A., Koszalka T. R., Minor R. R., Kefalides N. A. The embryonic rat parietal yolk sac. The role of the parietal endoderm in the biosynthesis of basement membrane collagen and glycoprotein in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5259–5267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor W. E., Johnston R., Lin D. S. Metabolism of cholesterol in the tissues and blood of the chick embryo. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):388–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmer L. A., Levin M. S., Elovson J., Reuben M. A., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. Tissue-specific expression and developmental regulation of the rat apolipoprotein B gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8102–8106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Kita T., Suckling K. E., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Cholesterol synthesis in vivo and in vitro in the WHHL rabbit, an animal with defective low density lipoprotein receptors. J Lipid Res. 1983 Apr;24(4):469–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Spady D. K. Measurement of rates of cholesterol synthesis using tritiated water. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1469–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Spady D. K., Stange E. F. Quantitative importance of different organs for cholesterol synthesis and low-density-lipoprotein degradation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):639–641. doi: 10.1042/bst0110639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Wiley T., Moser A. H., Lear S. R., Wiley M. H. De novo cholesterogenesis in pregnancy. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensh R. P., Koszalka T. R., Jensen M., Biddle L., Brent R. L. Morphologic alterations in the parietal yolk-sac of the rat from the 12th to the 19th day of gestation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Jun;39:9–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeske D. J., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J Lipid Res. 1980 Mar;21(3):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayden H. J., Dancis J., Money W. L. Transfer of lipids across the guinea pig placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Jun 15;104(4):564–572. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Sherrill B. C., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Correlation of low and high density lipoprotein binding in vivo with rates of lipoprotein degradation in the rat. A comparison of lipoproteins of rat and human origin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8061–8072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D. S., Pitkin R. M., Connor W. E. Placental transfer of cholesterol into the human fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Aug 1;128(7):735–739. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(77)90713-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkin R. M., Connor W. E., Lin D. S. Cholesterol metabolism and placental transfer in the pregnant Rhesus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2584–2592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Attie A. D., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Tissue sites of degradation of low density lipoprotein: application of a method for determining the fate of plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Taylor C. A., Jr Methods for assessment of tissue sites of lipoprotein degradation. Methods Enzymol. 1986;129:612–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)29094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Bilheimer D. W., Dietschy J. M. Rates of receptor-dependent and -independent low density lipoprotein uptake in the hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Dietary saturated triacylglycerols suppress hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor activity in the hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4526–4530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Rates of cholesterol synthesis and low-density lipoprotein uptake in the adrenal glands of the rat, hamster and rabbit in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 11;836(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Dietschy J. M. Sterol synthesis in vivo in 18 tissues of the squirrel monkey, guinea pig, rabbit, hamster, and rat. J Lipid Res. 1983 Mar;24(3):303–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Huettinger M., Bilheimer D. W., Dietschy J. M. Role of receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the maintenance of tissue cholesterol balance in the normal and WHHL rabbit. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jan;28(1):32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the rat in vivo. Quantitation, characterization, and metabolic consequences. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1113–1122. doi: 10.1172/JCI112066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stange E. F., Dietschy J. M. Age-related decreases in tissue sterol acquisition are mediated by changes in cholesterol synthesis and not low density lipoprotein uptake in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jul;25(7):703–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Rates of sterol synthesis and uptake in the major organs of the rat in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):551–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel C. A., MacDonald P. C., Hemsell P. G., Simpson E. R. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by human trophoblastic cells in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1981 Oct;109(4):1084–1090. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-4-1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



