Abstract
A new inborn error in bile acid synthesis, manifest in identical infant twins as severe intrahepatic cholestasis, is described involving the delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 beta-reductase catalyzed conversion of the key intermediates, 7 alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one and 7 alpha,12 alpha-dihydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one for chenodeoxycholic and cholic acid synthesis, to the respective 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta (H) products. This defect was detected by fast atom bombardment ionization-mass spectrometry from an elevated excretion and predominance of taurine conjugated unsaturated hydroxy-oxo-bile acids. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry confirmed these to be 7 alpha-hydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholenoic and 7 alpha,12 alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholenoic acids (75-92% of total). Fasting serum bile acid concentrations were greater than 37 mumol/liter; chenodeoxycholic acid was the major bile acid, but significant amounts of allo(5 alpha-H)-bile acids (approximately 30%) were present. Biliary bile acid concentration was less than 2 mumol/liter and consisted of chenodeoxycholic, allo-chenodeoxycholic, and allo-cholic acids. These biochemical findings, which were identical in both infants, indicate a defect in bile acid synthesis involving the conversion of the delta 4-3-oxo-C27 intermediates into the corresponding 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta(H)-structures, a reaction that is catalyzed by a delta 4-3-oxosteroid-5 beta reductase enzyme. This defect resulted in markedly reduced primary bile acid synthesis and concomitant accumulation of delta 4-3-oxo-and allo-bile acids. These findings indicate a pathway in bile acid synthesis whereby side chain oxidation can occur despite incomplete alterations to the steroid nucleus, and lend support for an active delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 alpha-reductase catalyzing the conversion of the delta 4-3-oxosteroid intermediates to the respective 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha(H)-structures.
Full text
PDF




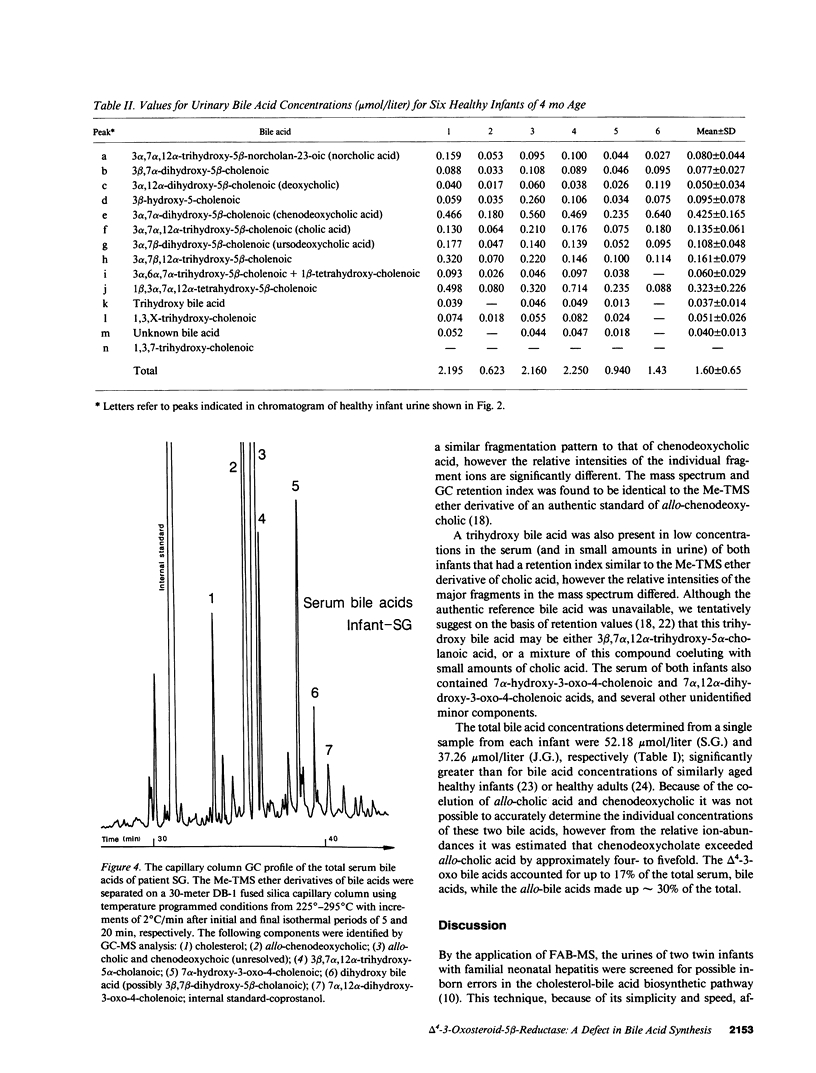

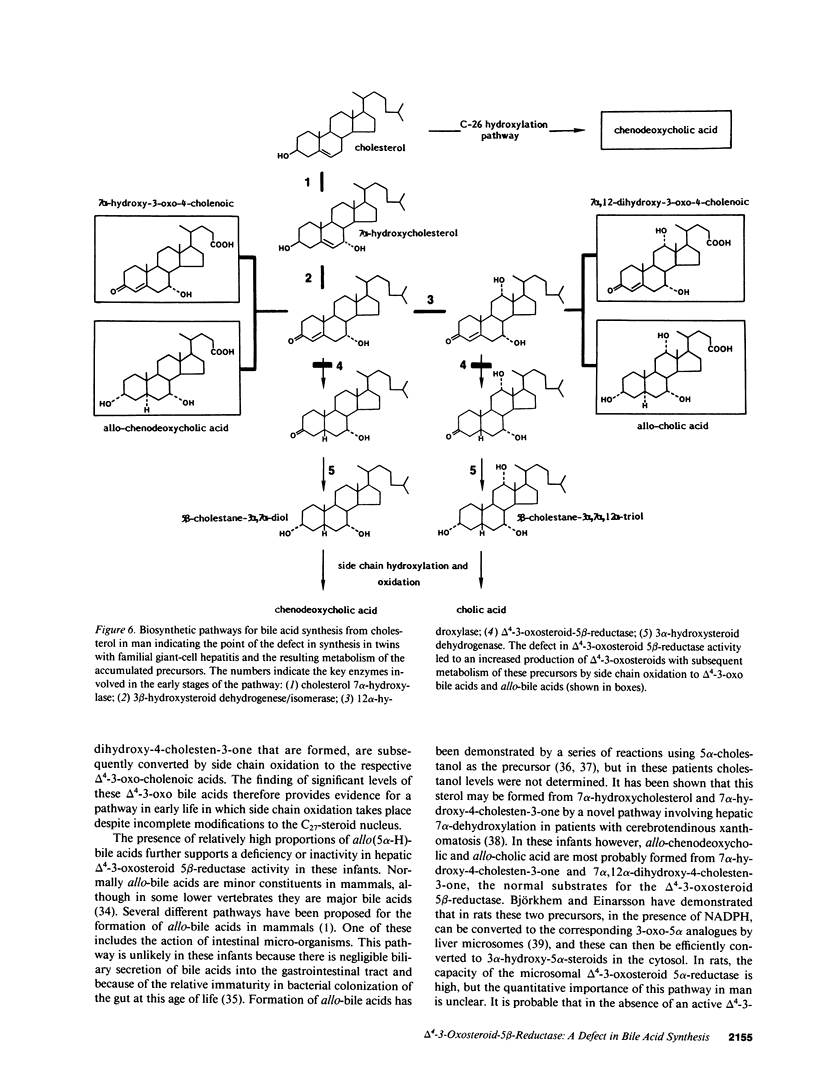


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. E., Kok E., Javitt N. B. Bile acid synthesis in man: metabolism of 7 -hydroxycholesterol- 14 C and 26-hydroxycholesterol- 3 H. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):112–117. doi: 10.1172/JCI106780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Walter K. Developmental pattern of bile acid metabolism as revealed by bile acid analysis of meconium. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew T. C., Summerfield J. A., Billing B. H., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D. Bile acid profiles of human serum and skin interstitial fluid and their relationship to pruritus studied by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Jul;63(1):65–73. doi: 10.1042/cs0630065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batta A. K., Shefer S., Batta M., Salen G. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on biliary and urinary bile acids and bile alcohols in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis; monitoring by high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jun;26(6):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardsson C., Björkhem I., Danielsson H., Wikvall K. 12alpha-hydroxylation of 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one by a reconstituted system from rat liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1030–1038. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90797-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berséus O., Björkhem L. Enzymatic conversion of a delta-4-3-ketosteroid into a 3-alpha-hydroxy-5-beta steroid: mechanism and stereochemistry of hydrogen transfer from NADPH. Bile acids and steroids 190. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):503–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berséus O. Conversion of cholesterol to bile acids in rat: purification and properties of a delta-4-3-ketosteroid 5-beta-reductase and a 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Einarsson K. Formation and metabolism of 7 alpha-hydroxy-5-alpha-cholestan-3-one and 7 alpha, 12 alpha-dihydroxy-5-alpha-cholestan-3-one in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):174–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J. Bile acid profiles in urine of patients with liver diseases. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;9(5):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Leonard J. V., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D., Andersson S., Egestad B., Sjövall J. Familial giant cell hepatitis associated with synthesis of 3 beta, 7 alpha-dihydroxy-and 3 beta,7 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acids. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1031–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI112915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Muller D. P., Lawson A. M. The bile acid composition of gastric contents from neonates with high intestinal obstruction. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):489–498. doi: 10.1042/bj2060489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton P. T., Patel E., Lawson A. M., Carruthers R. A., Tanner M. S., Strandvik B., Egestad B., Sjövall J. 3-Oxo-delta 4 bile acids in liver disease. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Zuliani G., Ronchi M., Breidenstein J., Setchell K. D. Biliary bile acid composition of the human fetus in early gestation. Pediatr Res. 1987 Feb;21(2):197–200. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198702000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Einarsson K., Johansson G. Effect of biliary drainage on individual reactions in the conversion of cholesterol to taurochlic acid. Bile acids and steroids 180. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jul;2(1):44–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Einarsson K. On the conversion of cholesterol to 7-alpha,12-alpha-dihydroxycholest-4-en-3-one. Bile acids and steroids 168. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1449–1454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENCRANTZ J. C., SJOVALL J. On the bile acids in duodenal contents of infants and children. Bile acids and steroids 72. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 Nov;4:793–799. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egestad B., Pettersson P., Skrede S., Sjövall J. Fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Sep;45(5):443–446. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J., Anderson S., Sjövall J. Bile acid metabolism during development: metabolism of lithocholic acid in human fetal liver. Pediatr Res. 1987 Jan;21(1):99–103. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198701000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J., Andersson S., Sjövall J. Bile acid metabolism during development: metabolism of taurodeoxycholic acid in human fetal liver. Biol Neonate. 1985;47(1):26–31. doi: 10.1159/000242087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., MOSBACH E. H. IDENTIFICATION OF ALLODEOXYCHOLIC ACID AS THE MAJOR COMPONENT OF GALLSTONES INDUCED IN THE RABBIT BY 5-ALPHA-CHOLESTAN-3-BETA-OL. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2813–2821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Miyazaki H., Higashidate S., Nakayama F. Analysis of 3-sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids by one-step solvolysis and high performance liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1987 Dec;28(12):1524–1529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida T., Momose T., Tamura T., Matsumoto T., Goto J., Nambara T., Chang F. C. Capillary gas chromatography of hydroxylated bile acid stereoisomers of the allo and normal series. J Chromatogr. 1987 Feb 27;389(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)94419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt N. B., Emerman S. Effect of sodium taurolithocholate on bile flow and bile acid exeretion. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1002–1014. doi: 10.1172/JCI105790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAVOLAS H. J., ELLIOTT W. H., HSIA S. L., DOISY E. A., Jr, MATSCHINER J. T., THAYER S. A., DOISY E. A. BILE ACIDS. XXII. ALLOCHOLIC ACID, A METABOLITE OF 5-ALPHA-CHOLESTAN-3-BET-A-OL IN THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1568–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman B. J., Wolthers B. G., van der Molen J. C., Waterreus R. J. Bile acid therapies applied to patients suffering from cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Oct 31;152(1-2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisans S. K., Thompson S. L., Pena L. A., Kok E., Javitt N. B. Bile acid synthesis in rat liver peroxisomes: metabolism of 26-hydroxycholesterol to 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid. J Lipid Res. 1985 Nov;26(11):1324–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson A. M., Madigan M. J., Shortland D., Clayton P. T. Rapid diagnosis of Zellweger syndrome and infantile Refsum's disease by fast atom bombardment--mass spectrometry of urine bile salts. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 Dec 15;161(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., St Pyrek J., Little J. M., Adcock E. W. Diversity of bile acids in the fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983 May;2(2):355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima S. Studies on the conjugating activity of bile acids in children. Pediatr Res. 1985 Mar;19(3):302–307. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198503000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Dumaswala R., Colombo C., Ronchi M. Hepatic bile acid metabolism during early development revealed from the analysis of human fetal gallbladder bile. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16637–16644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Matsui A. Serum bile acid analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Street J. M. Inborn errors of bile acid synthesis. Semin Liver Dis. 1987 May;7(2):85–99. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Worthington J. A rapid method for the quantitative extraction of bile acids and their conjugates from serum using commercially available reverse-phase octadecylsilane bonded silica cartridges. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 27;125(2):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton C. H. Inborn errors of steroid biosynthesis: detection by a new mass-spectrometric method. Clin Chem. 1983 Feb;29(2):246–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton C. H., Mattox V. R., Honour J. W. Analysis of intact steroid conjugates by secondary ion mass spectrometry (including FABMS) and by gas chromatography. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1A):209–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall J., Lawson A. M., Setchell K. D. Mass spectrometry of bile acids. Methods Enzymol. 1985;111:63–113. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)11006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Raedsch R., Rudolph G., Gundert-Remy U., Senn M. Biliary and urinary excretion of sulfated, glucuronidated and tetrahydroxylated bile acids in cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):492–495. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandvik B., Wikström S. A. Tetrahydroxylated bile acids in healthy human newborns. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;12(4):301–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb02236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel N., Emerman S., Javitt N. B. Metabolism of cholest-5-ene-3 beta, 26-diol in the rat and hamster. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5207–5212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. B., Ingall D., Szczepanik P., Klein P. D., Lester R. Bile-salt metabolism in the newborn. Measurement of pool size and synthesis by stable isotope technic. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 1;288(9):431–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303012880902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitington P. F., Whitington G. L. Partial external diversion of bile for the treatment of intractable pruritus associated with intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):130–136. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikvall K. Purification and properties of a 3 beta-hydroxy-delta 5-C27-steroid oxidoreductase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3376–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



