Abstract
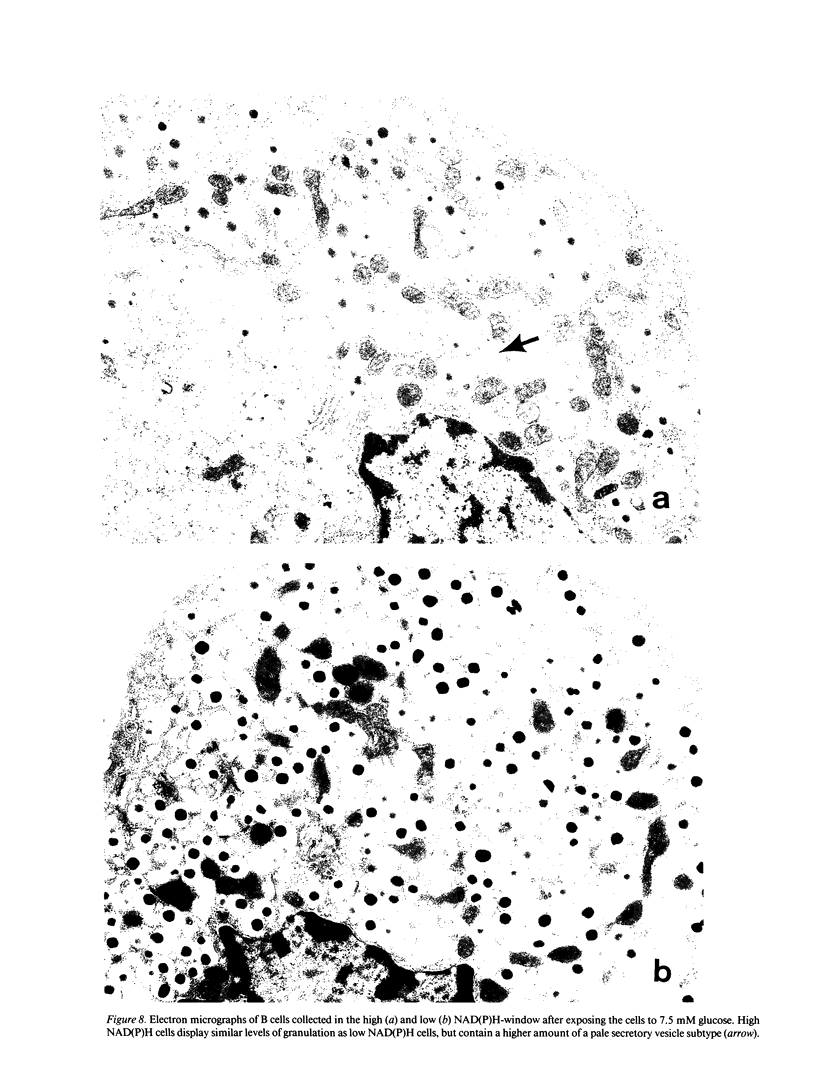
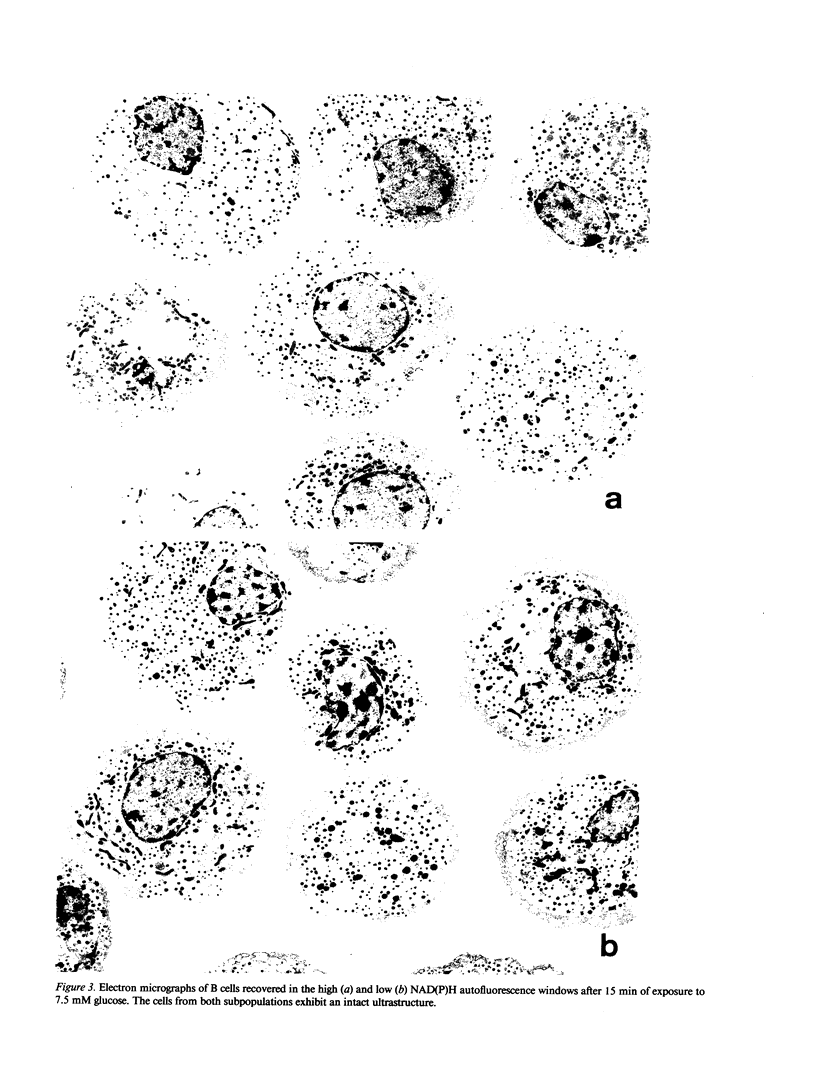
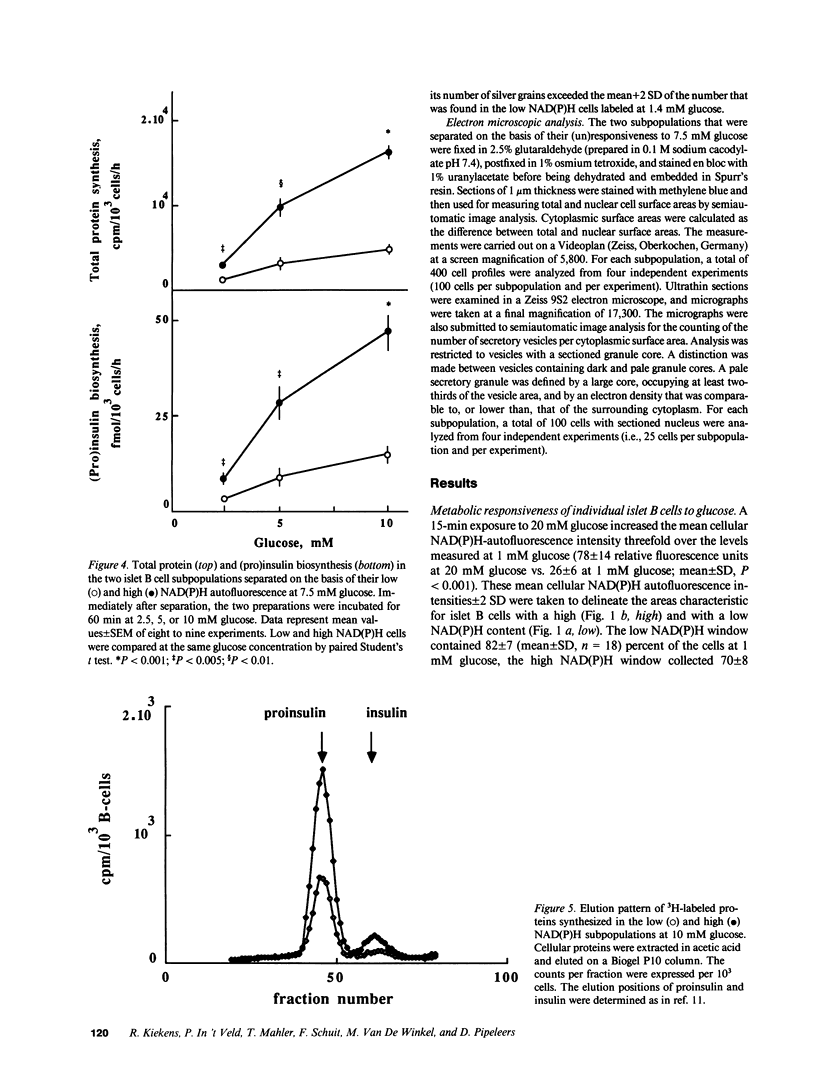
In vitro incubated rat islet B cells differ in their individual rates of protein synthesis. The number of cells in biosynthetic activity increases with the glucose concentration. Flow cytometric monitoring of the cellular redox states indicated that islet B cells differ in their individual metabolic responsiveness to glucose. A shift from basal to increased NAD(P)H fluorescence occurred for 18% of the cells at 1 mM glucose, for 43% at 5 mM, and for 70% at 20 mM. The functional significance of this metabolic heterogeneity was assessed by comparing protein synthesis in metabolically responsive and unresponsive subpopulations, shortly after their separation by autofluorescence-activated cell sorting. The glucose-sensitive subpopulation exhibited four- to fivefold higher rates of insulin synthesis during 60-min incubations at 2.5-10 mM glucose. Its higher biosynthetic activity was mainly caused by recruitment of cells into active synthesis and, to a lesser extent, by higher biosynthetic activity per recruited cell. Cells from the glucose-sensitive subpopulation were larger, and presented a threefold higher density of a pale secretory vesicle subtype, which is thought to contain unprocessed proinsulin. It is concluded that intercellular differences in metabolic responsiveness result in functional heterogeneity of the pancreatic B cell population.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Möbius G., Seitz H. J., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Tissue-specific expression of glucokinase: identification of the gene product in liver and pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):1998–2001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. J., Nagy B. R., Haist R. E. Effect of various concentrations of glucose on insulin biosynthesis. Endocrinology. 1972 Jul;91(1):309–311. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-1-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Hutton J. C. Insulin release: the fuel hypothesis. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Burch P. T., Berner D. K., Najafi H., Vogin A. P., Matschinsky F. M. Chromatographic resolution and kinetic characterization of glucokinase from islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):85–89. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Like A. A., Amherdt M., Blondel B., Kanazawa Y., Marliss E. B., Lambert A. E., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Monolayer cell culture of neonatal rat pancreas: an ultrastructural and biochemical study of functioning endocrine cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 May;43(3):270–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Madsen O., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Direct identification of prohormone conversion site in insulin-secreting cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):671–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Kipnis D. M. Insulin biosynthesis. I. On the mechanism of glucose stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Marichal M., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XIV. Glucose regulation of insular biosynthetic activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Nov;93(5):1001–1011. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-5-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A. A method for the purification of single A, B and D cells and for the isolation of coupled cells from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00257436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., in't Veld P. A., Van de Winkel M., Maes E., Schuit F. C., Gepts W. A new in vitro model for the study of pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):806–816. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit F. C., In't Veld P. A., Pipeleers D. G. Glucose stimulates proinsulin biosynthesis by a dose-dependent recruitment of pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3865–3869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Chan S. J., Welsh J. M., Nielsen D., Michael J., Tager H. S., Rubenstein A. H. Models of peptide biosynthesis: the molecular and cellular basis of insulin production. Clin Invest Med. 1986 Nov;9(4):328–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Winkel M., Pipeleers D. Autofluorescence-activated cell sorting of pancreatic islet cells: purification of insulin-containing B-cells according to glucose-induced changes in cellular redox state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Winkle M., Maes E., Pipeleers D. Islet cell analysis and purification by light scatter and autofluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Florholmen J., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Studies of the Ca2+ requirements for glucose- and carbachol-induced augmentation of inositol trisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in digitonin-permeabilized islets. Evidence for a glucose recognition site in insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3565–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











