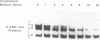Abstract
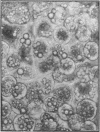
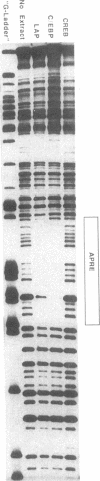
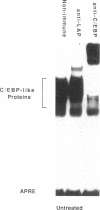
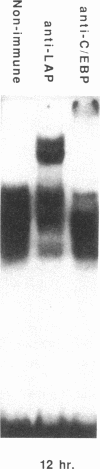
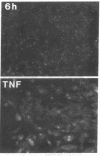
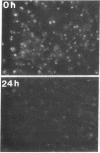
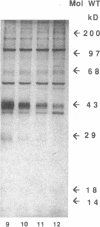
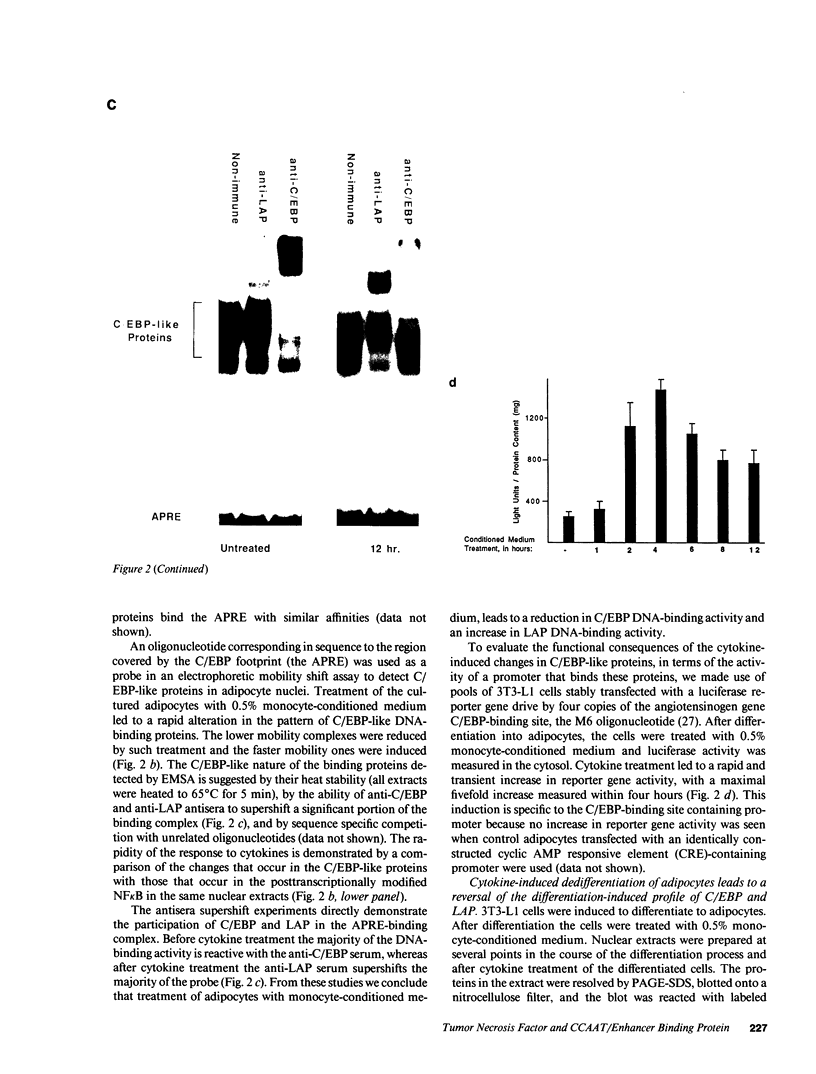
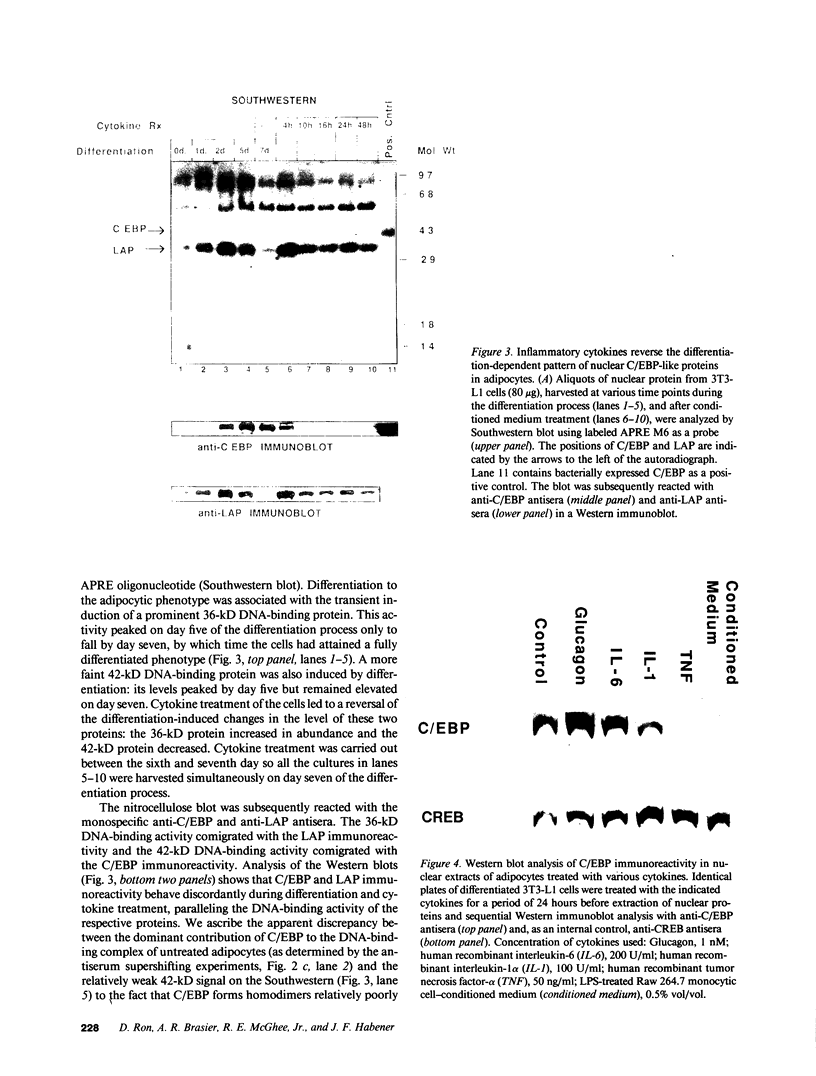
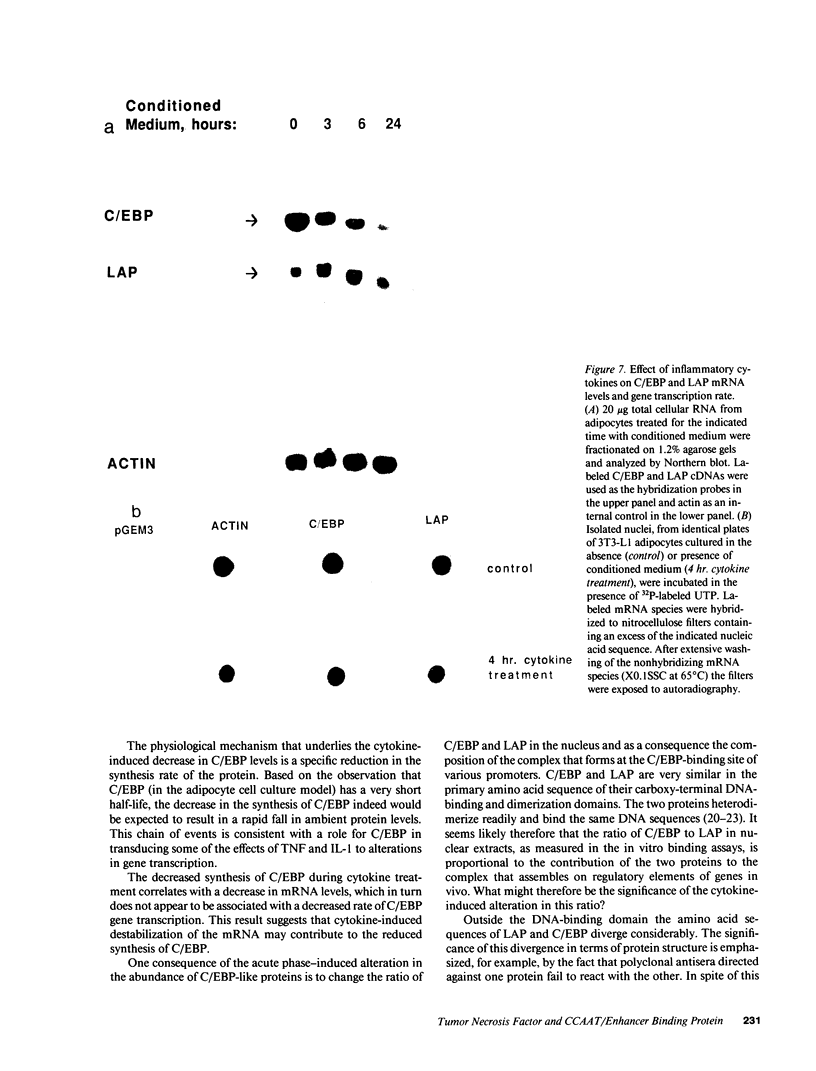
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were used as a model for studying the effects of systemic inflammation on adipose tissue. Lipopolysaccharide-treated monocyte-conditioned medium or recombinant human TNF alpha induced morphological dedifferentiation of the adipocytes and led to loss of adipocyte specific gene expression. Gel shift, Southwestern and Western immunoblot analysis demonstrated that dedifferentiation was preceded by a decrease in the DNA binding activity and protein level of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP). Liver activating protein, a related protein that binds identical DNA sequences, increased during cytokine treatment. Both proteins activate specific enhancer elements located in the promoter region of many genes whose transcription is altered during systemic inflammation. Pulse-chase labeling followed by immunoprecipitation demonstrated that C/EBP is a rapidly turning over protein in adipocytes and that cytokine treatment led to a specific, time dependent decrease in its rate of synthesis. Because C/EBP binding sites have been shown to play an important role in regulating the expression of genes involved in adipocyte metabolism, we propose that the TNF-induced changes in the complement of transcription factors binding those sites may be important in the pathogenesis of inflammation-induced atrophy of adipose tissue.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F., Osborne R., Burke F., Naylor S., Talbot D., Durbin H., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Evidence for tumour necrosis factor/cachectin production in cancer. Lancet. 1987 Nov 28;2(8570):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91850-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch H. E., Schreiber G. Transcriptional regulation of plasma protein synthesis during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8077–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. A family of constitutive C/EBP-like DNA binding proteins attenuate the IL-1 alpha induced, NF kappa B mediated trans-activation of the angiotensinogen gene acute-phase response element. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3933–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Synergistic enhansons located within an acute phase responsive enhancer modulate glucocorticoid induction of angiotensinogen gene transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1921–1933. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Ron D., Habener J. F. Multiple cis-acting DNA regulatory elements mediate hepatic angiotensinogen gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;3(6):1022–1034. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-6-1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Buck M., Feitelberg S. P., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits albumin gene expression in a murine model of cachexia. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI114419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. Identification of two polypeptide segments of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein required for transcriptional activation of the serum albumin gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1416–1426. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Ro H. S., Robinson G. S., Xanthopoulos K. G., Spiegelman B. M. A direct role for C/EBP and the AP-I-binding site in gene expression linked to adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5331–5339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Cerami A. Studies of endotoxin-induced decrease in lipoprotein lipase activity. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):631–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Q., Yun Y. D., Hoeffler J. P., Habener J. F. Cyclic-AMP-responsive transcriptional activation of CREB-327 involves interdependent phosphorylated subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4455–4465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Levine B., Kalman J., Mayer L., Fillit H. M., Packer M. Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):236–241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J., Maury C. P., Teppo A. M., Repo H. Elevated levels of circulating cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Lane M. D., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Is CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein a central regulator of energy metabolism? Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2021–2024. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Defeo-Jones D., Boyer M., Martinez D., Kiefer D., Vuocolo G., Wolfe A., Socher S. H. Tumors secreting human TNF/cachectin induce cachexia in mice. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekala P. H., Kawakami M., Angus C. W., Lane M. D., Cerami A. Selective inhibition of synthesis of enzymes for de novo fatty acid biosynthesis by an endotoxin-induced mediator from exudate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Chapman A. B., Knight D. M., Navre M., Torti F. M. Hormonal control of adipocyte differentiation and adipocyte gene expression. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1988;44:115–140. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571144-9.50008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Habener J. F. The permissive role of glucocorticoids on interleukin-1 stimulation of angiotensinogen gene transcription is mediated by an interaction between inducible enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4389–4395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye J. A., Cassis L. A., Sturgill T. W., Lynch K. R., Peach M. J. Angiotensinogen gene expression in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C448–C451. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Pöll-Jordan G., Löffler G. Adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells in a serum-free culture system depends on epidermal growth factor, insulin-like growth factor I, corticosterone, and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15489–15495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi P., Sterling K. E., Lam K. S., Finley P. R., Ryan K. J., Ray C. G., Petersen E., Slymen D. J., Salmon S. E. Raised serum levels of tumour necrosis factor in parasitic infections. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. L., Foss N. T. Tumor necrosis factor in leprosy patients. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):787–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Frank M., Green H. Molecular cloning of mRNA from 3T3 adipocytes. Regulation of mRNA content for glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and other differentiation-dependent proteins during adipocyte development. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10083–10089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G. H., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Regulation of fatty acid synthetase concentration and activity during adipocyte differentiation. Studies on 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4751–4757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Kuo C. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Cell-specific transcriptional control of the mouse DNA-binding protein mC/EBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4117–4121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]