Abstract
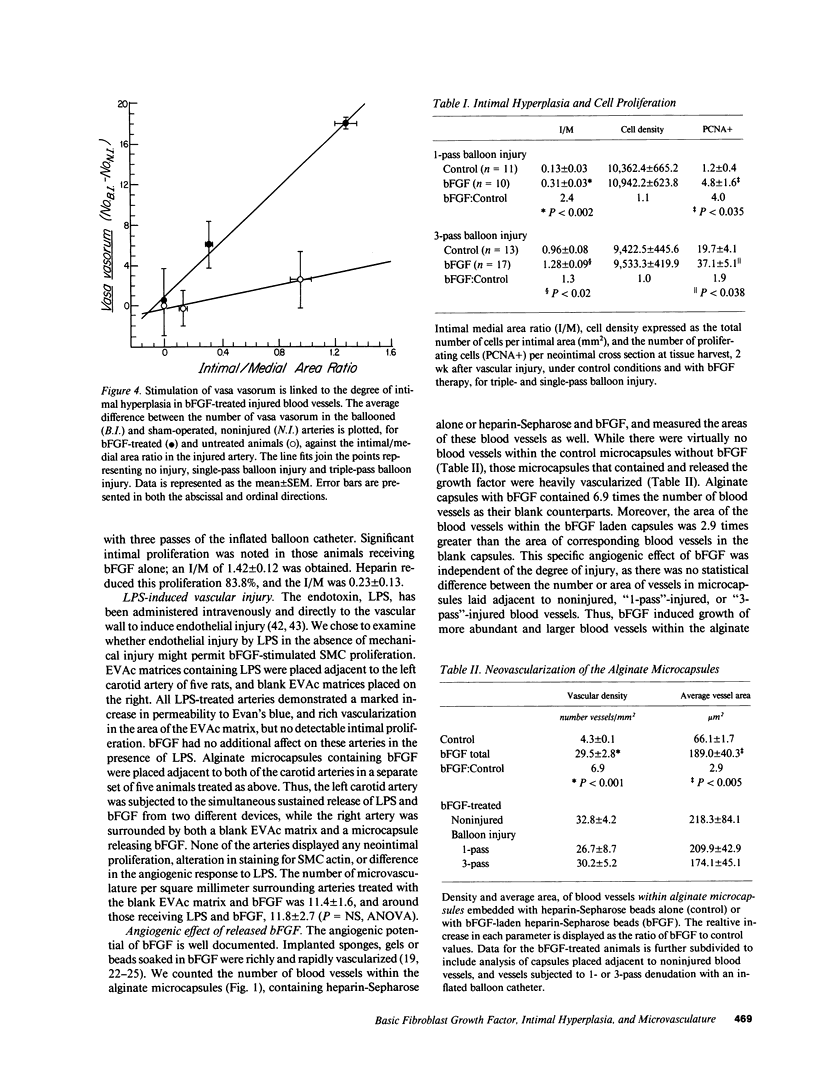
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is mitogenic for smooth muscle cells (SMC) and angiogenic. We examined the in vivo effects of bFGF in balloon denuded carotid arteries of laboratory rats. bFGF was administered continuously from polymer-based devices at 34 ng/d into the periadventitial space of rat carotid arteries for 2 wk. Intimal hyperplasia was not observed in the absence of injury or with lipopolysaccharide induced endothelial dysfunction. Different degrees of vascular injury produced proportionally more intimal hyperplasia. bFGF increased the intimal hyperplastic response 1.3-fold with severe vascular injury, and 2.4-fold with more mild injury. Increased cell proliferation, not extracellular matrix production, accounted for these effects. Cell density was unchanged for the control and bFGF-treated groups, and the number of proliferating intimal cells at 2 wk rose to an amount equivalent to the increase in mass; 1.9- and 4.0-fold for severe and lesser injury, respectively. The relative ability of heparin to reduce SMC proliferation was not altered by the presence of bFGF.bFGF also induced profound angiogenesis within and surrounding the polymeric releasing device, and in the vasa vasorum immediately around the injured arteries. bFGF's effect on vasa was linearly related to the amount of SMC proliferation within the blood vessel. Thus, the in vivo mitogenic and angiogenic potential of bFGF are coupled, and may be similarly modulated by the products of local injury and/or factors in the vessel wall.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird A., Ling N. Fibroblast growth factors are present in the extracellular matrix produced by endothelial cells in vitro: implications for a role of heparinase-like enzymes in the neovascular response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):428–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barger A. C., Beeuwkes R., 3rd, Lainey L. L., Silverman K. J. Hypothesis: vasa vasorum and neovascularization of human coronary arteries. A possible role in the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):175–177. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashkin P., Doctrow S., Klagsbrun M., Svahn C. M., Folkman J., Vlodavsky I. Basic fibroblast growth factor binds to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1737–1743. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Webb R. C. Vasoconstriction: a new activity for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.3485309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkerud S. Reaction of the aortic wall of the rabbit after superficial, longitudinal, mechanical trauma. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1969;347(3):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00543107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Wright T. C., Karnovsky M. J. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by heparin and heparan sulfates. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1987 Oct;13(4):489–503. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Karnowsky M. J. Suppression by heparin of smooth muscle cell proliferation in injured arteries. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):625–626. doi: 10.1038/265625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A., Clowes M. M. Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I. Smooth muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):327–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Stoddard B. L., Harakas N. K., Feder J. Human fibroblast-derived growth factor is a mitogen and chemoattractant for endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):705–712. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro P. G., Seckel B. R., Lipton S. A., D'Amore P. A., Wagner J., Madison R. Acidic fibroblast growth factor enhances peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989 Jun;83(6):1013–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Flores L., Dominguez C. Relation between arterial intimal thickening and the vasa-vasorum. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;406(2):165–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00737083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman E. R., Adams D. H., Karnovsky M. J. Effect of controlled adventitial heparin delivery on smooth muscle cell proliferation following endothelial injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3773–3777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman E. R., Mathiowitz E., Langer R., Klagsbrun M. Controlled and modulated release of basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. 1991 Sep;12(7):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(91)90107-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIRINGER E. Intimal vascularization and atherosclerosis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Apr;63(2):201–211. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J. Heparin protects basic and acidic FGF from inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):475–484. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G., Schweigerer L. Fibroblast growth factor: structural and biological properties. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1987;Suppl 5:15–26. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisler H. P., Klosak J. J., Steinam S. J., Lam T. M., Burgess W. H., Kim D. U. Effects of class I heparin binding growth factor and fibronectin on platelet adhesion and aggregation. J Vasc Surg. 1990 May;11(5):665–674. doi: 10.1067/mva.1990.19423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Rosenberg R. D., Clowes A. W., Karnovsky M. J. Inhibition of rat arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation by heparin. In vivo studies with anticoagulant and nonanticoagulant heparin. Circ Res. 1980 May;46(5):625–634. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Van Valen R. G., Melden M. K., Saunders R. N. Suppression of rat carotid lesion development by the calcium channel blocker PN 200-110. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):88–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek A., Culler F. L., Beattie G. M., Lopez A. D., Cuevas P., Baird A. An in vivo model for study of the angiogenic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):876–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip J. H., Fuster V., Badimon L., Badimon J., Taubman M. B., Chesebro J. H. Syndromes of accelerated atherosclerosis: role of vascular injury and smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Jun;15(7):1667–1687. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)92845-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Hansson G. K. Cyclosporin A inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in the vascular response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2303–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Edelman E. R. Biological and biochemical properties of fibroblast growth factors. Implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer R., Siegel R., Brown L., Leong K., Kost J., Edelman E. Controlled release and magnetically modulated systems for macromolecular drugs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;446:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb18386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Lappi D. A., Baird A., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in vascular lesion formation. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):106–113. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates endothelial regrowth and proliferation in denuded arteries. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2004–2008. doi: 10.1172/JCI114665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner V., Reidy M. A. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells after vascular injury is inhibited by an antibody against basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. W., Roubin G. S., King S. B., 3rd Restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Potential biologic determinants and role of intimal hyperplasia. Circulation. 1989 Jun;79(6):1374–1387. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.6.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. W., Roubin G. S., Robinson K. A., Black A. J., Hearn J. A., Siegel R. J., King S. B., 3rd Trapidil in preventing restenosis after balloon angioplasty in the atherosclerotic rabbit. Circulation. 1990 Mar;81(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.3.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Baird A., Guillemin R., Orci L. Basic fibroblast growth factor induces angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott M. F., McBride C. K., Court M. Development of intimal lesions after leukocyte migration into the vascular wall. Am J Pathol. 1989 Nov;135(5):835–846. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Maier J. A., Rusnati M., Ragnotti G. Basic fibroblast growth factor is released from endothelial extracellular matrix in a biologically active form. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):68–74. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial injury and regeneration. IV. Endotoxin: a nondenuding injury to aortic endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial regeneration. III. Time course of intimal changes after small defined injury to rat aortic endothelium. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Silver M. Endothelial regeneration. VII. Lack of intimal proliferation after defined injury to rat aorta. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):173–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarembock I. J., LaVeau P. J., Sigal S. L., Timms I., Sussman J., Haudenschild C., Ezekowitz M. D. Influence of inflation pressure and balloon size on the development of intimal hyperplasia after balloon angioplasty. A study in the atherosclerotic rabbit. Circulation. 1989 Oct;80(4):1029–1040. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Neufeld G., Friedman J., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C., Gospodarowicz D. Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):257–259. doi: 10.1038/325257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Anderson K. D., DiPietro J. M., Zwiebel J. A., Zametta M., Anderson W. F., Maciag T. Site-directed neovessel formation in vivo. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1349–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.2457952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Fridman R., Sullivan R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Aortic endothelial cells synthesize basic fibroblast growth factor which remains cell associated and platelet-derived growth factor-like protein which is secreted. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jun;131(3):402–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen G. F., Shing Y., Folkman J. The fate of intravenously administered bFGF and the effect of heparin. Growth Factors. 1989;1(2):157–164. doi: 10.3109/08977198909029125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkles J. A., Friesel R., Burgess W. H., Howk R., Mehlman T., Weinstein R., Maciag T. Human vascular smooth muscle cells both express and respond to heparin-binding growth factor I (endothelial cell growth factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir M., Silver M. D. Vasculature in the walls of human coronary arteries. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Jul;109(7):659–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sanadiki M. N., Cross K. S., Murray J. J., Schuman R. W., Mikat E., McCann R. L., Hagen P. O. Reduction of intimal hyperplasia and enhanced reactivity of experimental vein bypass grafts with verapamil treatment. Ann Surg. 1990 Jul;212(1):87–96. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199007000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]