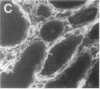
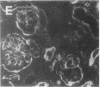
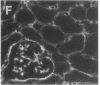
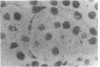
Abstract
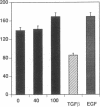
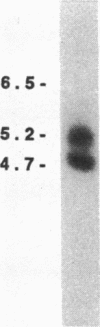
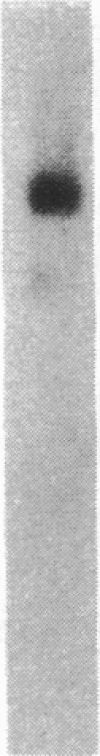
We have been studying immune interactions with somatic cells using a tubular antigen-binding protein (ThF) secreted by helper T lymphocytes harvested from mice that have an autoimmune form of interstitial nephritis called anti-tubular basement membrane disease. This ThF, although characterized originally because of its ability to induce effector T cells, additionally recognizes the nephritogenic 3M-1 antigen expressed by its target renal tubular epithelium. We believe these proteins, in general, may modulate directly some homeostatic functions in organ-derived cells, and now report that our ThF represses specifically the cellular transcription and secretion of basement membrane type IV collagen in tubular epithelium. These in vitro findings of reduced levels of mRNA encoding type IV collagen correlate well with in situ hybridization studies performed on kidneys expressing early autoimmune lesions, and predict a progressive drop in the expression of type IV collagen in the interstitium. Such a novel and unexpected repression of transcription of type IV collagen might easily impart or facilitate permanent change in the infrastructure of kidney architecture during autoimmune injury and, perhaps, contributes to the process of tubular atrophy attendant to prolonged renal inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appling W. D., O'Brien W. R., Johnston D. A., Duvic M. Synergistic enhancement of type I and III collagen production in cultured fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta and ascorbate. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80792-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A., Michaud L., Alper R., Mann R., Kefalides N. A., Neilson E. G. Isolation and characterization of the nephritogenic antigen producing anti-tubular basement membrane disease. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):290–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Sun M. J., Michaud L., Brill-Dashoff J., Riblet R., Neilson E. G. Clonotypic heterogeneity in experimental interstitial nephritis. Restricted specificity of the anti-tubular basement membrane B cell repertoire is associated with a disease-modifying crossreactive idiotype. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1296–1312. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P. Developmentally regulated conversion of mesenchyme to epithelium. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2141–2150. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2666230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Watanabe M., Neilson E. G., Kelly C. J. Protective modulation of class II MHC gene expression in tubular epithelium by target antigen-specific antibodies. Cell-surface directed down-regulation of transcription can influence susceptibility to murine tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1133–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall R. H. Pathology of end-stage kidney disease. Am J Med. 1968 May;44(5):656–663. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines W. H., Haverty T. P., Elias J. A., Neilson E. G., Kelly C. J. T cell recognition of epithelial self. Autoimmunity. 1989;5(1-2):37–47. doi: 10.3109/08916938909029141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines W. H., Mann R. A., Kelly C. J., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IX. Induction of the nephritogenic effector T cell repertoire with an antigen-specific T cell cytokine. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkavelas G., Kefalides N. A., Amenta P. S., Martinez-Hernandez A. Comparative ultrastructural localization of collagen types III, IV, VI and laminin in rat uterus and kidney. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Aug;100(2):137–155. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuncio G. S., Neilson E. G., Haverty T. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int. 1991 Mar;39(3):550–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Yamada Y., de Crombrugghe B. Coordinate regulation of the levels of type III and type I collagen mRNA in most but not all mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Clayman M. D., Blanchard N., Sun M. J., Neilson E. G. Effector T cell differentiation in experimental interstitial nephritis. I. The development and modulation of effector lymphocyte maturation by I-J+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4200–4208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Zakheim B., Clayman M., McCafferty E., Michaud L., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IV. Long-term cultured L3T4+ T cell lines transfer delayed expression of disease as I-A-restricted inducers of the effector T cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Brinker J. M., Kefalides N. A., Rosenbloom J., Wang S. Y., Gudas L. J. Discrimination among multiple AATAAA sequences correlates with interspecies conservation of select 3' untranslated nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4499–4517. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Jimenez S. A., Phillips S. M. Cell-mediated immunity in interstitial nephritis. III. T lymphocyte-mediated fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis: an immune mechanism for renal fibrogenesis. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1708–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Murine interstitial nephritis. I. Analysis of disease susceptibility and its relationship of pleiomorphic gene products defining both immune-response genes and a restrictive requirement for cytotoxic T cells at H-2K. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Sun M. J., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Haverty T. P., Clayman M. D., Cooke N. E. Molecular characterization of a major nephritogenic domain in the autoantigen of anti-tubular basement membrane disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2006–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson E. G., Phillips S. M., Jimenez S. Lymphokine modulation of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1484–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Growth factor control of myoepithelial-cell differentiation in cultures of human mammary gland. Differentiation. 1988 Dec;39(3):197–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Dziadek M. Structure, development, and molecular pathology of basement membranes. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;29:1–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Gudas L. J. Isolation of cDNA clones specific for collagen IV and laminin from mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5880–5884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim B., McCafferty E., Phillips S. M., Clayman M., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. II. The adoptive transfer of disease with immune T lymphocytes produces a phenotypically complex interstitial lesion. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]