Abstract
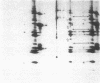
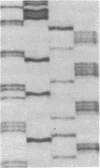
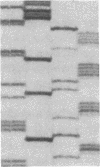
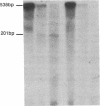
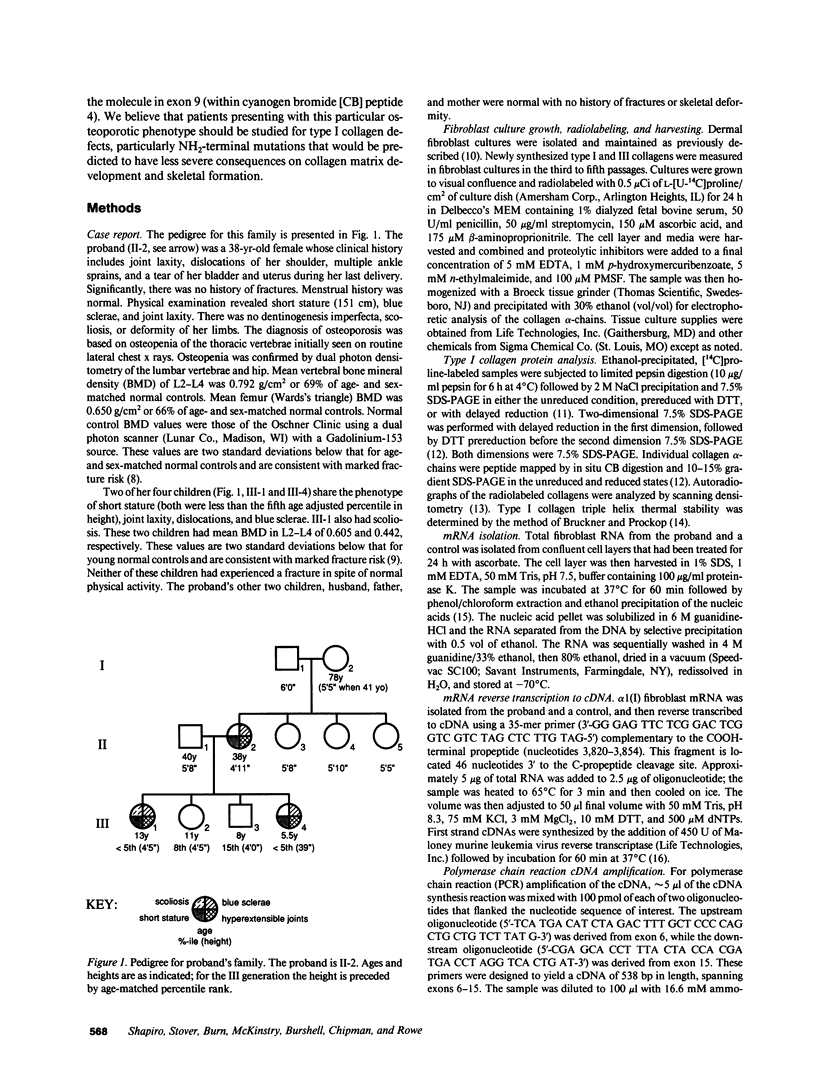
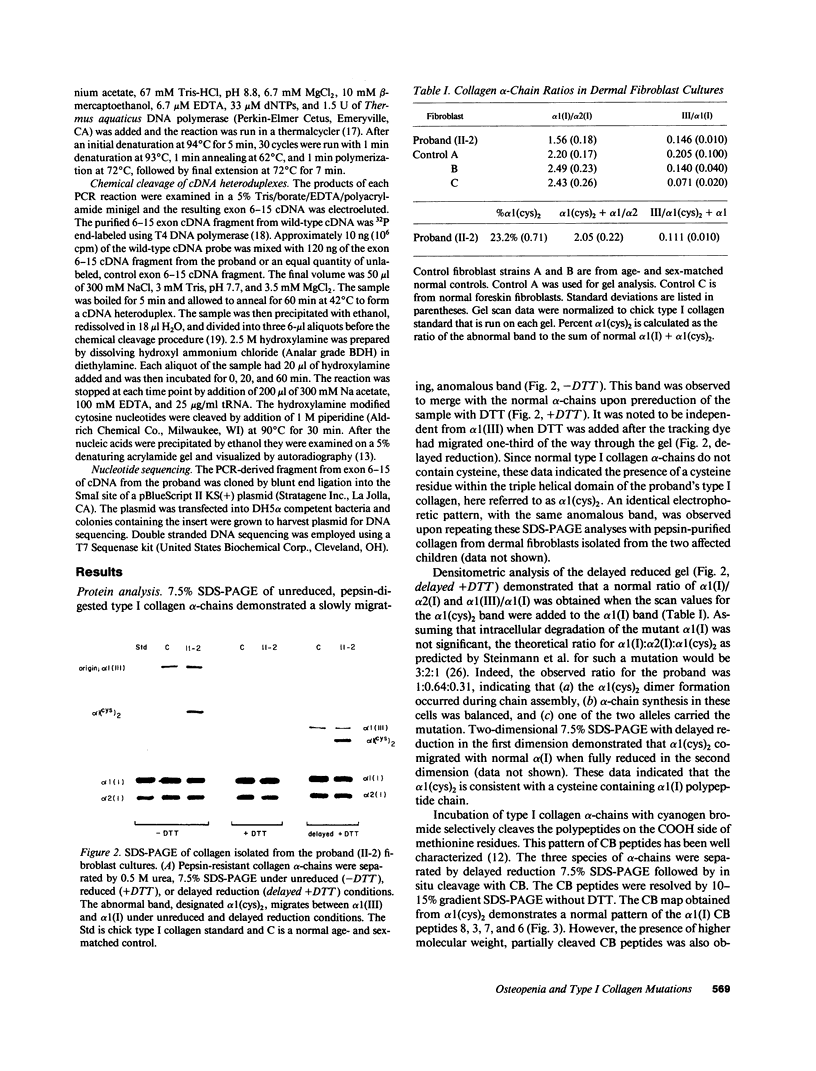
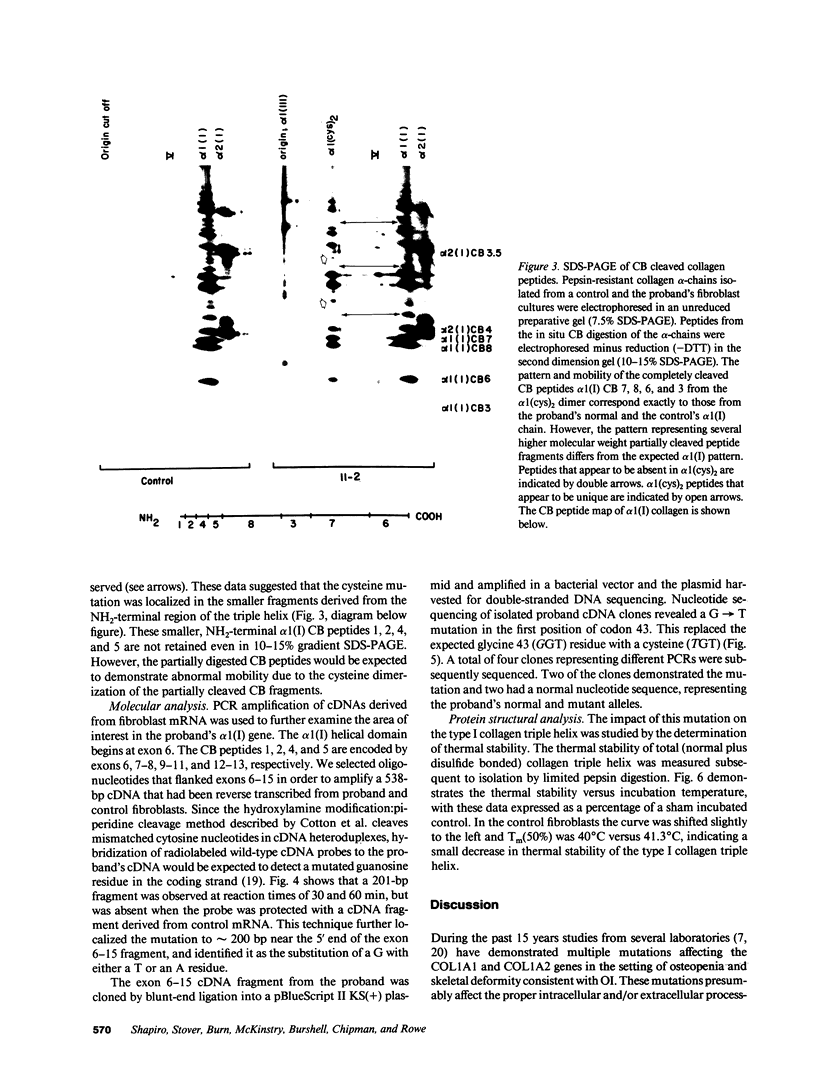
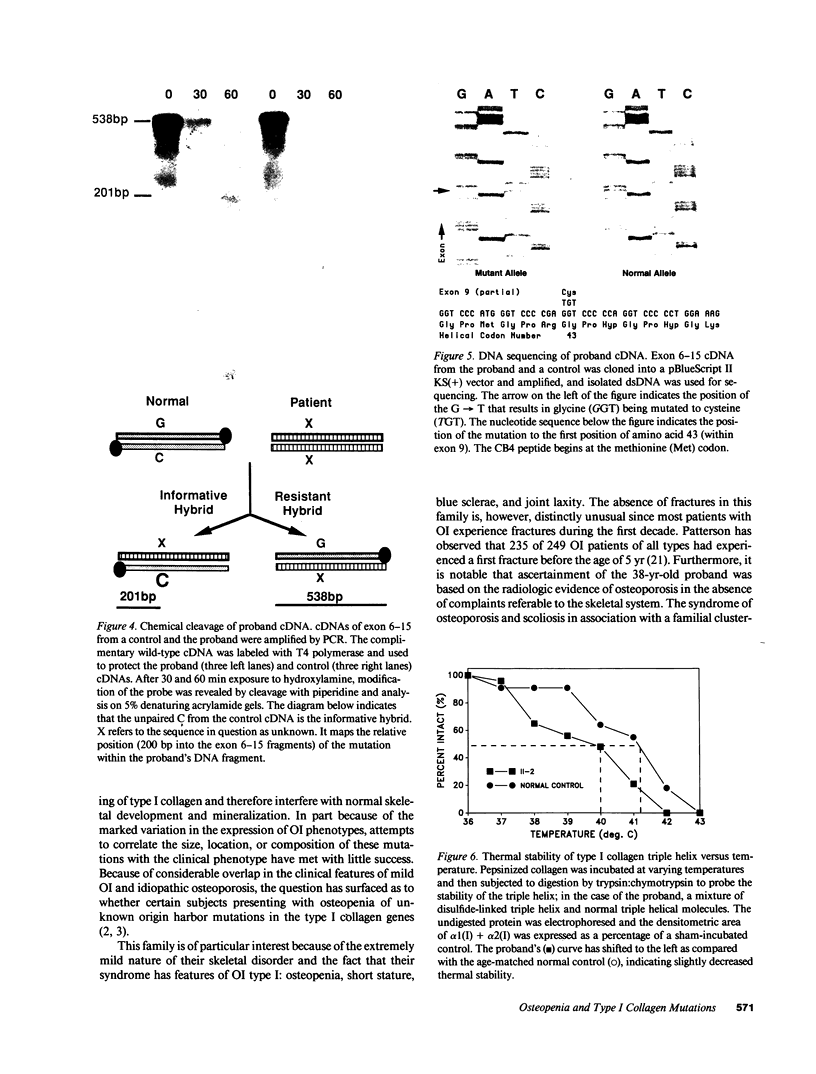
Mutations affecting the pro alpha 1(I) or pro alpha 2(I) collagen genes have been identified in each of the major clinical types of osteogenesis imperfecta. This study reports the presence of a heritable connective tissue disorder in a family with an osteopenic syndrome which has features of mild osteogenesis imperfecta but was considered idiopathic osteoporosis in the proband. At age 38, while still premenopausal, she was found to have osteopenia, short stature, hypermobile joints, mild hyperelastic skin, mild scoliosis, and blue sclerae. There was no history of vertebral or appendicular fracture. Hip and vertebral bone mineral density measurements were consistent with marked fracture risk. Delayed reduction SDS-PAGE of pepsin-digested collagens from dermal fibroblast cultures demonstrated an anomalous band migrating between alpha 1(I) and alpha 1(III). This band merged with the normal alpha-chains upon prereduction, indicating an unexpected cysteine residue. Cyanogen bromide peptide mapping suggested that the mutation was in the smaller NH2-terminal peptides. cDNA was reverse transcribed from mRNA and amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. A basepair mismatch between proband and control alpha 1(I) cDNA hybrids was detected by chemical cleavage with hydroxylamine:piperidine. The cysteine substitution was thus localized to alpha 1(I) exon 9 within the cyanogen bromide 4 peptide. Nucleotide sequence analysis localized a G----T point mutation in the first position of helical codon 43, replacing the expected glycine (GGT) residue with a cysteine (TGT). The prevalence of similar NH2-terminal mutations in subjects with this phenotype which clinically overlaps idiopathic osteoporosis remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruckner P., Prockop D. J. Proteolytic enzymes as probes for the triple-helical conformation of procollagen. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 15;110(2):360–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Bonadio J. F., Cohn D. H., Starman B. J., Wenstrup R. J., Willing M. C. Osteogenesis imperfecta: the molecular basis of clinical heterogeneity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;543:117–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb55324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H. Brittle bones--fragile molecules: disorders of collagen gene structure and expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Sep;6(9):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Apone S., Eyre D. R., Starman B. J., Andreassen P., Charbonneau H., Nicholls A. C., Pope F. M., Byers P. H. Substitution of cysteine for glycine within the carboxyl-terminal telopeptide of the alpha 1 chain of type I collagen produces mild osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14605–14607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou C. D., Nielsen K. B., Prockop D. J. A lethal variant of osteogenesis imperfecta has a single base mutation that substitutes cysteine for glycine 904 of the alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen. The asymptomatic mother has an unidentified mutation producing an overmodified and unstable type I procollagen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):574–584. doi: 10.1172/JCI113920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivaniemi H., Tromp G., Prockop D. J. Mutations in collagen genes: causes of rare and some common diseases in humans. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2052–2060. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.2010058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhard M. E., Wirtz M. K., Pope F. M., Nicholls A. C., Hollister D. W. A cysteine for glycine substitution at position 1017 in an alpha 1(I) chain of type I collagen in a patient with mild dominantly inherited osteogenesis imperfecta. Mol Biol Med. 1988 Dec;5(3):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikodem V., Fresco J. R. Protein fingerprinting by SDS-gel electrophoresis after partial fragmentation with CNBr. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 1;97(2):382–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin B. E. The definition and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 1987 Feb;40(2):57–58. doi: 10.1007/BF02555705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. R. Osteogenesis imperfecta and fractures in childhood. Health Visit. 1978 May;51(5):174–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J. Osteogenesis imperfecta. A model for genetic causes of osteoporosis and perhaps several other common diseases of connective tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Kream B. E. Regulation of collagen synthesis in fetal rat calvaria by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8009–8015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. R., Burn V. E., Chipman S. D., Jacobs J. B., Schloo B., Reid L., Larsen N., Louis F. Pulmonary hypoplasia and osteogenesis imperfecta type II with defective synthesis of alpha I(1) procollagen. Bone. 1989;10(3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(89)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. R., Burn V. E., Chipman S. D., Velis K. P., Bansal M. Osteoporosis and familial idiopathic scoliosis: association with an abnormal alpha 2(I) collagen. Connect Tissue Res. 1989;21(1-4):117–124. doi: 10.3109/03008208909050002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W. Imperfect osteogenesis and osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 28;310(26):1738–1740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406283102610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. O., Senn A., Danks D. M. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979 Apr;16(2):101–116. doi: 10.1136/jmg.16.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spotila L. D., Constantinou C. D., Sereda L., Ganguly A., Riggs B. L., Prockop D. J. Mutation in a gene for type I procollagen (COL1A2) in a woman with postmenopausal osteoporosis: evidence for phenotypic and genotypic overlap with mild osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5423–5427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starman B. J., Eyre D., Charbonneau H., Harrylock M., Weis M. A., Weiss L., Graham J. M., Jr, Byers P. H. Osteogenesis imperfecta. The position of substitution for glycine by cysteine in the triple helical domain of the pro alpha 1(I) chains of type I collagen determines the clinical phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1206–1214. doi: 10.1172/JCI114286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Nicholls A., Pope F. M. Clinical variability of osteogenesis imperfecta reflecting molecular heterogeneity: cysteine substitutions in the alpha 1(I) collagen chain producing lethal and mild forms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8958–8964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Puddle B., Francis M., Smith R. The estimation of two collagens from human dermis by interrupted gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1472–1480. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W., Steinmann B. Structural study of a mutant type I collagen from a patient with lethal osteogenesis imperfecta containing an intramolecular disulfide bond in the triple-helical domain. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80407-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velis K. P., Healey J. H., Schneider R. Peak skeletal mass assessment in young adults with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989 Jul;14(7):706–711. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198907000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel B. E., Doelz R., Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Engel J., Prockop D. J. A substitution of cysteine for glycine 748 of the alpha 1 chain produces a kink at this site in the procollagen I molecule and an altered N-proteinase cleavage site over 225 nm away. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19249–19255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W. N., de Wet W. J. The molecular defect in an autosomal dominant form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Synthesis of type I procollagen containing cysteine in the triple-helical domain of pro-alpha 1(I) chains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9056–9064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]