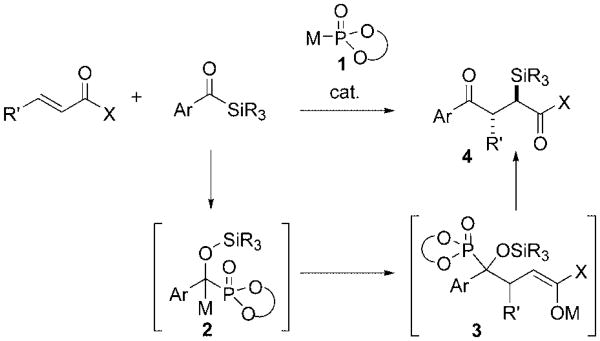
Nucleophilic acylation of enones and enoates catalyzed by cyanide ions or heterazolium carbenes, commonly known as the Stetter reaction, is a useful method for the synthesis of 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds.[1] The key feature of this reaction is the carbonyl-polarity reversal initiated by the addition of a cyanide ion or a heterazolium carbene to an aldehyde facilitating subsequent 1,4-addition to an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound. Although this reaction has proven fruitful with a variety of acceptors, its success has been largely limited to aryl or unsubstituted[2] substrates. Acceptors bearing a β-alkyl group normally give the 1,4-addition product in 30–40% yield,[3] and achieving enantioselectivity in the intermolecular Stetter reaction has also proven to be difficult.[4] Herein, we provide a strategy to address both of these issues through metallophosphite-catalyzed acylations of α,β-unsaturated amides. These reactions are enabled by an unusual [1,2] Brook rearrangement/conjugate addition/retro [1,4] Brook rearrangement sequence that proceeds with good anti diastereoselectivity and allows access to a range of stable α-silyl-γ-ketoamides (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
Metallophosphite-catalyzed alkene acylation. X=OR, NR2.
Acyl silanes are effective aldehyde surrogates that confer unique advantages in umpolung reactions. The acyl anion equivalent formed on nucleophilic addition and subsequent [1,2] Brook rearrangement[5,6] undergoes addition to a number of electrophiles. Degl'Innocenti et al. found that the 1,4-addition of benzoyl trimethylsilane to cyclohexenone can be catalyzed by cyanide ions,[7] whereas Scheidt and coworkers recently described the successful conjugate addition of acyl silanes to unsaturated esters and ketones by using thiazolium carbene catalysis.[8,9] The substrate scope of the latter process mirrors the classic Stetter reaction, and conjugate acceptors bearing a β-alkyl substituent have not been reported. Metallophosphites[10,11] can be considered as an alternative to cyanide ions and thiazolium carbenes, and they have recently been described as carbonyl-umpolung catalysts in the context of a new enantioselective cross-benzoin reaction.[12] We projected that this catalysis concept might be applicable to alkene electrophiles as well.
The conjugate addition of acyl silanes (benzoyl trimethylsilane, benzoyl triethylsilane, and benzoyl dimethylphenylsilane) to Michael acceptors (ethyl crotonate, methyl cinnamate, and cyclohexenone) catalyzed by the Enders phosphite 5 was initially examined. Potassium hydride gave the best reactivity of the bases screened in these reactions; however, few reactions provided appreciable quantities of the desired acylation product. The 1H NMR spectra of the reactions typically revealed incorporation of the phosphite in the acyl silane/acceptor adduct, thus indicating that the proposed cycle was initiated but not completed. Exposure of the reaction mixture to tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) afforded the desired γ-ketoester. Ethyl crotonate provided the best yields of the acceptors screened, but even under optimized conditions these were unacceptably low [≤ 37 % of 6, Eq. (1)].
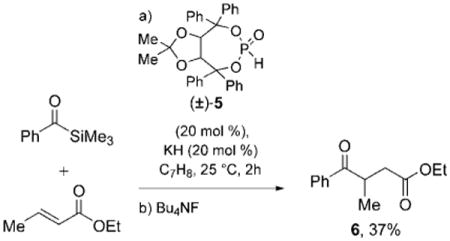 |
(1) |
The low turnover and aforementioned observations suggested that enolate 3 did not undergo efficient silyl transfer. We hoped that replacement of the unsaturated ester (X=OR) with an amide (X=NR2) would enhance the nucleophilicity of the derived enolate, promote the desired silyl transfer, and regenerate the metallophosphite catalyst.
Evaluation of this hypothesis revealed that amides did indeed facilitate catalyst turnover (Table 1). We had expected that O→O 1,6 transfer of the silyl group to form a silylketene aminal might be energetically feasible but were surprised to find that the O→C 1,4 silyl transfer was dominant to the exclusion of the former. Furthermore, the derived α-silyl- amide was unexpectedly delivered with good diastereoselectivity in a number of cases. Acceptors bearing a (β-alkyl substituent for these metallophosphite-catalyzed reactions[13] are now synthetically useful substrates that generate alkene acylation products in moderate to high yields (62–91 %, entries 1–3 and 7–10). A number of acyl silanes are competent in the addition and show only subtle changes in reactivity upon variation of the silyl group (entries 1, 7, and 8) but exhibit more significant differences in reactivity between the electron-rich and electron-poor acyl silanes (entries 9 and 10).
Table 1.
Catalytic conjugate addition of acyl silanes to unsaturated amides.[a]
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| Entry | Ar | SiR3 | R′ | Z | d.r.[b] of 4 | t [h] | Yield [%][c] |
| 1[d] | Ph | SiMe2Ph | Me | CH2 | 7:1 (4a) | 2 | 73 (7a) |
| 2 | Ph | SiMe2Ph | Me | O | 4:1 (4b) | 0.5 | 81 (7b) |
| 3 | Ph | SiMe2Ph | Et | CH2 | 1.3:1 (4c) | 0.75 | 74 (7c) |
| 4[e] | Ph | SiMe2Ph | Ph | O | 10:1 (4d)[f] | 0.5[g] | 81 (7d) |
| 5[e] | Ph | SiMe2Ph | 4-MeOPh | O | 11:1 (4e) | 0.5[g] | 57 (7e) |
| 6[e] | Ph | SiMe2Ph | 4-ClPh | O | 8:1 (4f) | 0.5[g] | 80 (7f) |
| 7 | Ph | SiMe3 | Me | CH2 | 10:1 (4g) | 3 | 80 (7a) |
| 8 | Ph | SiEt3 | Me | CH2 | 4:1 (4h) | 2.5 | 91 (7a) |
| 9 | 4-MeOPh | SiEt3 | Me | CH2 | 3.5:1 (4i) | 1 | 87 (7i) |
| 10 | 4-ClPh | SiEt3 | Me | CH2 | 3:1 (4j) | 2 | 62 (7j) |
ArC(O)SiR3 (1.0 equiv), R′CH=CHC(O)NC4H8Z (1.1 equiv) unless otherwise stated.
anti/syn isomers as determined by 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis unless otherwise stated.
Yield of the isolated, analytically pure 7; average of at least two experiments.
Phosphite catalyst loading = 10 mol%.
R′CH=CHC(O)NC4H8O (1.5 equiv).
As determined by yield of isolated product.
Including slow addition of acyl silane to other reagents.
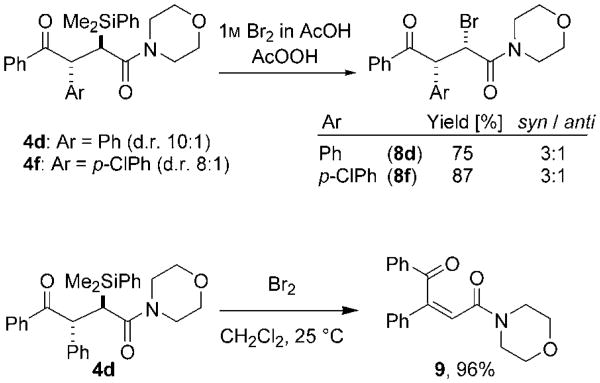
The α-silyl-γ-ketoamides 4 were stable and could be easily isolated by column chromatography. We were naturally attracted to the stereospecific transformation of the functionalized silane to its derived secondary alcohol through the Tamao–Fleming oxidation,[14,15] but were aware of only two reported examples of such oxidations of α-silylcarbonyl compounds.[16,17] Attempts to activate the C(sp2)—Si bond by a variety of protocols led to either desilylation, which yielded 7, or bromination through cleavage of the Ca—Si bond. The α-bromo-γ-ketoamides 8d and 8 f were obtained in 75 and 87 % yields, respectively, with a diastereomeric ratio of 3:1 in each case (Scheme 2). An X-ray diffraction study of 8d revealed that the major diastereomer exhibits syn stereochemistry.[18] Interestingly, the addition of bromine to 4d in the absence of AcOH/AcO2H induces elimination to give the (Z)-α,β-unsaturated ketoamide 9 exclusively in 96% yield (Scheme 2). The olefin geometry was determined by NOESY analysis.
Scheme 2.
Functionalization of α-silyl-γ-ketoamides.
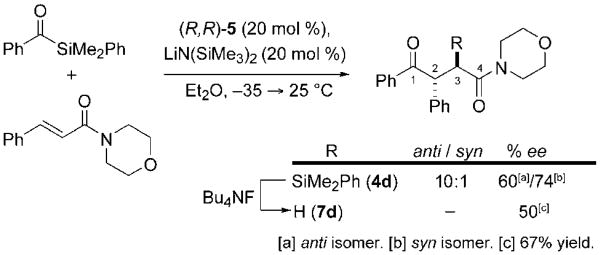
Finally, we found that this new catalyzed acylation provides an attractive platform for enantioselective catalysis. The enantiopure Enders phosphite (R,R)-5 was employed and the major anti diastereomer was delivered in 60 % ee, whereas the minor syn isomer was obtained in 74 % ee (Scheme 3). Desilylation gave γ-ketoamide (2R)-7d in 67% yield and 50% ee.[19] Although the enantioselectivity is moderate, it already eclipses the highest enantioselectivity of which we are aware for intermolecular Stetter-type reactions (4% yield, 39% ee).[20] We further note that the structure of 1,1,4,4-tetraphenyl-2,3-O-iso-propylidene-l-threitol (TADDOL) phosphite is readily amenable to modifications that we project will deliver more highly enantioselective catalysts.
Scheme 3.
Enantioselective metallophosphite-catalyzed alkene acylation.
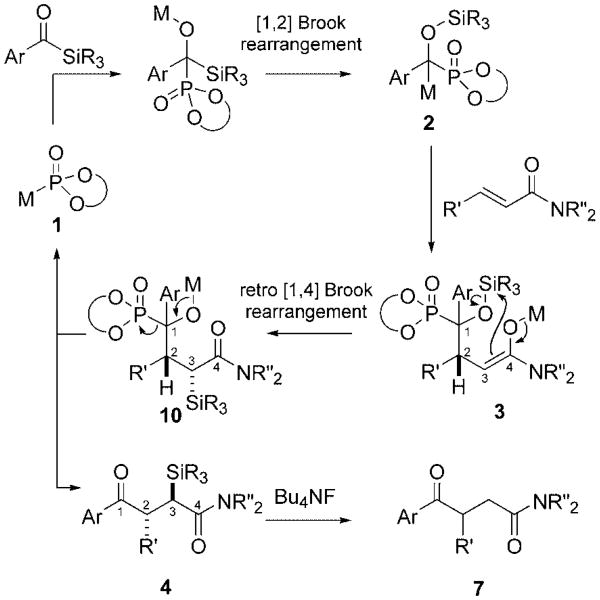
The proposed catalytic cycle is depicted in Scheme 4 and is initiated by phosphite addition and the [1,2] Brook rearrange- ment.[21] Catalyst release is apparently trig gered after conjugate addition by an unusual diastereoselective retro [1,4] Brook rearrangement (3→10).[22] The fact that the major enantiomer possesses the same C3 configuration in both the syn and anti diastereomers (Scheme 3) suggests that the chiral phosphite may be the dominant diastereocontrol element rather than a preferred transition-state topology.
Scheme 4.
Proposed catalytic cycle.
A metallophosphite-catalyzed intermo-lecular alkene acylation has been achieved employing the Enders TADDOL phosphite, thus giving γ-ketoamides in generally good yields. These reactions allow access to synthetically interesting α-silyl-γ-ketoamides and provide an attractive platform for enantioselective variants. Ongoing work in our laboratory is directed toward the development of 1) those strategies that take advantage of the high diastereoselectivity of the retro [1,4] Brook rearrangement and 2) phosphite catalysts that deliver more highly enantioenriched products.
Experimental Section
7a (entry 1, representative procedure): The acyl silane (0.42 mmol) and amide (0.46 mmol, 1.1 equiv) were added to a dry pear-shaped flask in the glovebox, while the TADDOL phosphite (0.084 mmol, 0.2 equiv) and lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LHMDS; 0.29 mmol, 0.7 equiv) were added to a dry round-bottom flask with a magnetic stirring bar. The flasks were removed from the glovebox and Et2O (3.0 mL) was added to the metallophosphite and stirred in an N2 atmosphere. The acyl silane/amide mixture was added to the metallophosphite by cannula and the delivery flask was rinsed with Et2O (7 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred in an N2 atmosphere at room temperature until the starting material was consumed (TLC analysis). The solvent was removed in vacuo and an aliquot was taken to determine the diastereoselectivity by 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis. The residue was redissolved in THF. The reaction mixture was treated with a solution of tetrabutylammonium fluoride in THF (TBAF; 1m, 0.84 mmol, 2.0 equiv) and immediately quenched with several milliliters of a saturated aqueous solution of NH4Cl. The product was then extracted with Et2O, washed with water (2×10 mL), and washed with a saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3 (2 × 10 mL). The organic extracts were combined and dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated. The product then was purified by flash chromatography with ethyl acetate/hexanes (30:70) as the eluent to afford the pure 1,4-dicarbonyl compound in 76% yield. Analytical data for 7a: IR (thin film): ṽ = 3061, 2933, 2856, 1684, 1639, 1444, 1369, 1223, 1196, 1122, 1016, 978, 706 cm−1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.07–7.98 (m, 2H), 7.54–7.47 (m, 1H), 7.47–7.39 (m, 2H), 4.10–4.00 (m, 1H), 3.53–3.36 (m, 4H), 3.02 (dd, J = 16.0, 8.8 Hz, 1H), 2.40 (dd, J = 16.4, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 1.66–1.49 (m, 6H), 1.17 ppm (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H); 13CNMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 203.9, 169.3, 136.1, 132.6, 128.41, 128.40, 46.4, 42.6, 37.0, 36.9, 26.2, 25.4, 24.4, 17.8 ppm; TLC (ethyl acetate/hexanes, 40:60) Rf = 0.32; elemental analysis (%) calcd for C16H21NO2: C 74.10, H 8.16, N 5.40; found: C 74.21, H 8.27, N 5.29.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
We thank the National Institutes of Health (National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM068443)) for support of this research. J.S.J. is an Eli Lilly Grantee and a 3 m Nontenured Faculty Awardee.
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.angewandte.org or from the author.
References
- 1.a) Stetter H, Schreckenberg M. Angew Chem. 1973;85:89. [Google Scholar]; Angew Chem Int Ed. 1973;12:81. [Google Scholar]; b) Stetter H, Kuhlmann H. Org React. 1991;40:407–496. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gong JH, Im YJ, Lee KY, Kim JN. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002;43:1247–1251. [Google Scholar]
- 3.a) Stetter H. Angew Chem. 1976;88:695–736. [Google Scholar]; Angew Chem Int Ed. 1976;15:639–647. [Google Scholar]; b) Stetter H, Kuhlmann H. Chem Ber. 1976;109:2890–2896. [Google Scholar]; c) Stetter H, Schreckenberg M, Wiemann K. Chem Ber. 1976;109:541–545. [Google Scholar]; d) Stetter H, Bender HJ. Chem Ber. 1981;114:1226–1233. [Google Scholar]; e) Stetter H, Simons L. Chem Ber. 1985;118:3172–3187. [Google Scholar]; f) Stetter H, Skobel H. Chem Ber. 1987;120:643–645. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Enders D, Breuer K. In: Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis. Jacobsen EN, Pfaltz A, Yamamoto H, editors. Vol. 3. Springer; New York: 1999. pp. 1093–1102.for examples of enantioselective intramolecular Stetter reactions, see: Enders D, Breuer K, Runsink J, Teles JH. Helv Chim Acta. 1996;79:1899–1902.Kerr MS, Readde Alaniz J, Rovis T. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:10298–10299. doi: 10.1021/ja027411v.Kerr MS, Rovis T. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:8876–8877. doi: 10.1021/ja047644h.Mennen SM, Blank JT, Tran-Dube MB, Imbriglio JE, Miller SJ. Chem Commun. 2005:195–197. doi: 10.1039/b414574g.
- 5.Brook AG. Acc Chem Res. 1974;7:77–84. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moser WH. Tetrahedron. 2001;57:2065–2084. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Degl'Innocenti A, Ricci A, Mordini A, Reginato G, Colotta V. Gazz Chim Ital. 1987;117:645–648. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mattson AE, Bharadwaj AR, Scheidt KA. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:2314–2315. doi: 10.1021/ja0318380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bharadwaj AR, Scheidt KA. Org Lett. 2004;6:2465–2468. doi: 10.1021/ol049044t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Takeda K, Tanaka T. Synlett. 1999:705–708. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Enders D, Tedeschi L, Bats JW. Angew Chem. 2000;112:4774–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:4605–4607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Linghu X, Potnick JR, Johnson JS. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:3070–3071. doi: 10.1021/ja0496468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.The racemic TADDOL phosphite 5 regularly provided higher yields than simpler phosphites, for example, diethyl phosphite.
- 14.Jones GR, Landais Y. Tetrahedron. 1996;52:7599–7662. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fleming I. Chemtracts: Org Chem. 1996;9:1–64. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mader MM, Edel JC. J Org Chem. 1998;63:2761–2764. doi: 10.1021/jo9721960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dakin LA, Schaus SE, Jacobsen EN, Panek JS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:8947–8950. [Google Scholar]
- 18.CCDC-253985 (4d) and -253984 (8d) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- 19.The 2R configuration of 7d was assigned through chemical correlation (see the Supporting Information).
- 20.Enders D, Balensiefer T. Acc Chem Res. 2004;37:534–541. doi: 10.1021/ar030050j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.(Silyloxy) phosphonate anion 2 has been previously prepared stoichiometrically: Koenigkramer RE, Zimmer H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980;21:1017–1020.
- 22.Gibson C, Buck T, Noltemeyer M, Bruckner R. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997;38:2933–2936. and references therein. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.