Figure 1.
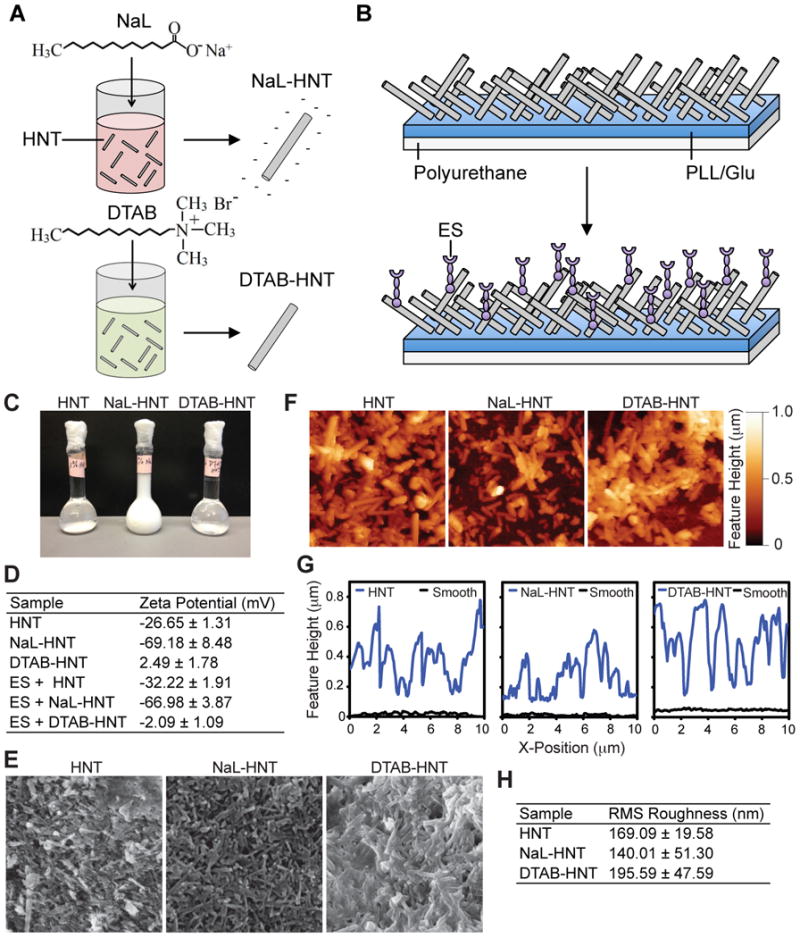
Functionalization of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) with surfactants to fabricate nanostructured surfaces of altered surface charge for flow-based cell capture assays. (A) Negative charge of HNT is enhanced via mixing and functionalization with sodium dodecanoate (NaL) surfactant (NaL-HNT). Intrinsic negative charge of HNT is attenuated via hmixing and functionalization of decyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB) surfactant (DTAB-HNT). (B) HNTs are immobilized onto polyurethane flow device surfaces coated with poly-L-lysine (for HNT and NaL-HNT) or glutamic acid (for DTAB-HNT) for cell capture assays. Surfaces can be further functionalized with adhesion proteins, such as E-selectin (ES) to facilitate cell capture. (C) Stability of HNT, NaL-HNT, and DTAB-HNT dispersions (1.1 wt %) 24 h after mixing. (D) Zeta potential (mV) measurements of HNT samples, incubated with and without E-selectin (ES), using dynamic light scattering. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent measurements. (E) SEM images of polyurethane substrates with immobilized HNT samples. Scale bar = 2 μm. (F) AFM images of HNT samples immobilized on polyurethane substrates. Scale bar = 2 μm. (G) Representative surface feature height profiles of HNT samples immobilized onto polyurethane substrates, compared to smooth surfaces. Nanotube profiles have been shifted up by 100 nm for ease of viewing. (H) Root-mean-square (RMS) roughness measurements of HNT surfaces. Data are mean ± standard deviation of three independent measurements.
