Abstract
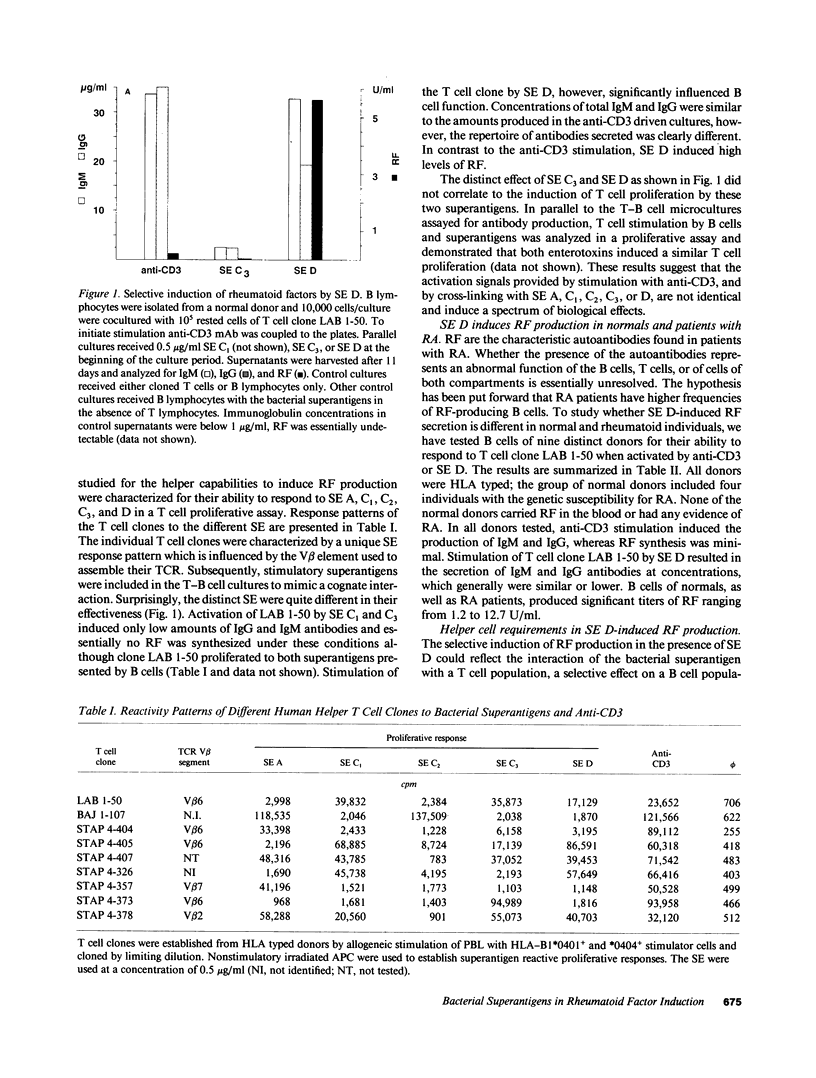
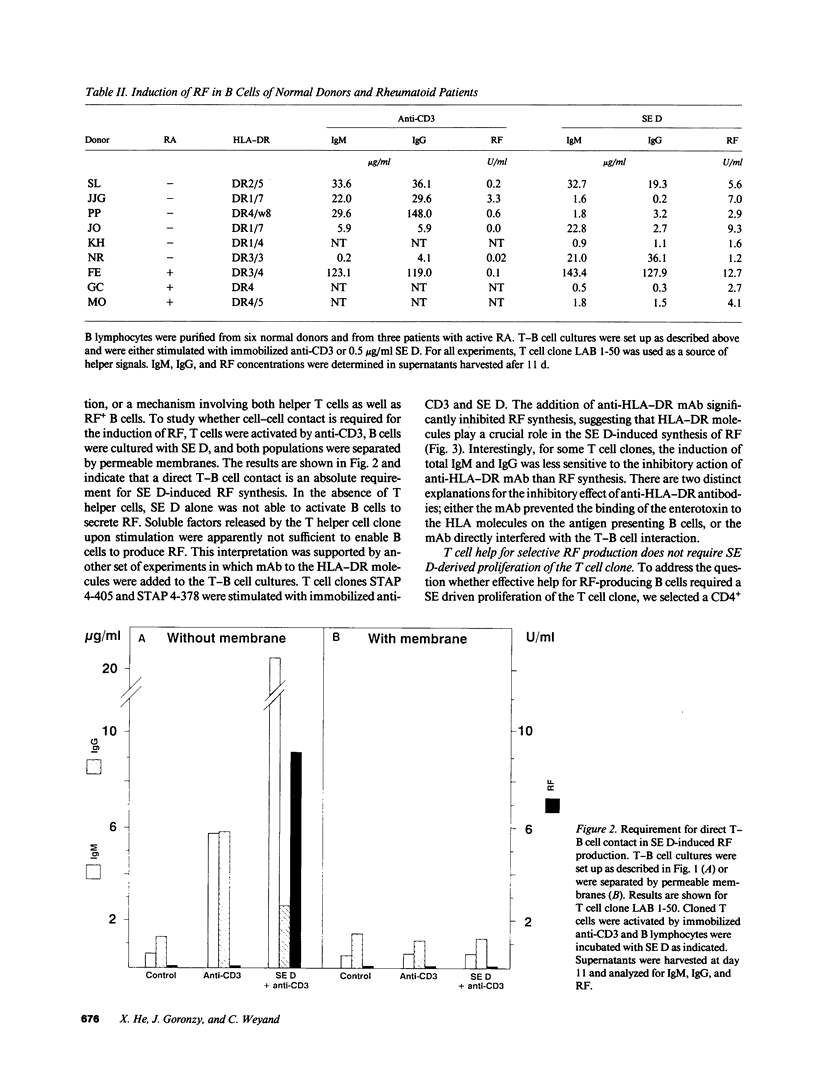
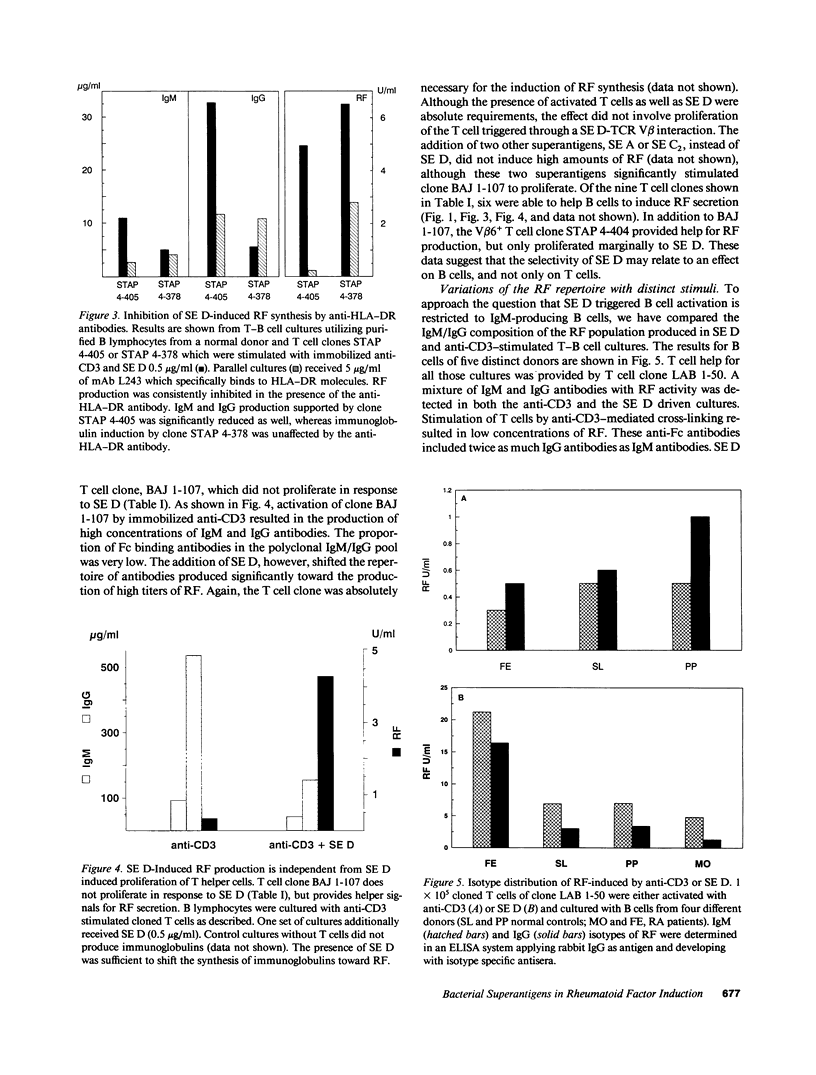
Production of autoantibodies specific for the Fc region of autologous IgG, called rheumatoid factors (RF), is a characteristic finding in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To study the requirements regulating the synthesis of these autoantibodies, we have cloned human helper T cells and co-cultured them with purified B cells. To mimic cognate T-B cell interaction, we have used bacterial superantigens that function by cross-linking HLA molecules on the B cell with selected T cell receptor (TCR) molecules expressing a particular polymorphism of the V beta gene segment. Data presented here demonstrate that the staphylococcal enterotoxin D (SE D), but not other bacterial superantigens, exhibits an ability to induce IgM, IgG, and especially RF production, in B cells from RA patients and normal individuals. Comparison with the polyclonal antibody production in B cell cultures driven by anti-CD3-stimulated T cell clones confirmed that SE D shifted the repertoire of secreted antibodies toward immunoglobulins with Fc binding specificity, suggesting that SE D preferentially stimulates RF+ B lymphocytes. B cells with the potential to secrete RF were highly frequent in RA patients, requiring as few as 150 peripheral B cells/culture to detect RF in the culture supernatants. SE D-induced RF synthesis was strictly dependent on the presence of selected CD4+T helper cells and required a direct membrane contact between B cells and T helper cells. Here, we propose a model that SE D selectively induces RF production depending on the availability of SE D responsive T cells in the TCR repertoire of the responder.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burastero S. E., Casali P., Wilder R. L., Notkins A. L. Monoreactive high affinity and polyreactive low affinity rheumatoid factors are produced by CD5+ B cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):1979–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Chen P. P., Fox R. I., Kipps T. J., Jirik F., Goldfien R. D., Silverman G., Radoux V., Fong S. Rheumatoid factor and immune networks. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:109–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Burastero S. E., Nakamura M., Inghirami G., Notkins A. L. Human lymphocytes making rheumatoid factor and antibody to ssDNA belong to Leu-1+ B-cell subset. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):77–81. doi: 10.1126/science.3105056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Fong S., Carson D. A. Rheumatoid factor. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Dec;13(3):545–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Herman A., DiGiusto D., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. Residues of the variable region of the T-cell-receptor beta-chain that interact with S. aureus toxin superantigens. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):471–473. doi: 10.1038/346471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulie P. G., Van Snick J. Rheumatoid factor (RF) production during anamnestic immune responses in the mouse. III. Activation of RF precursor cells is induced by their interaction with immune complexes and carrier-specific helper T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):88–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuleihan R., Mourad W., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Engagement of MHC-class II molecules by staphylococcal exotoxins delivers a comitogenic signal to human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Shimizu M., Yamasaki K., Kishimoto T. Rheumatoid factor secretion from human Leu-1+ B cells. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3105057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iandolo J. J. Genetic analysis of extracellular toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Yagi J., Conrad P. J., Katz M. E., Jones B., Vroegop S., Buxser S. T-cell responses to Mls and to bacterial proteins that mimic its behavior. Immunol Rev. 1989 Feb;107:61–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Staerz U., White J., Marrack P. C. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mls-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):35–40. doi: 10.1038/332035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Schrohenloher R. E. In vitro synthesis of IgM rheumatoid factor by lymphocytes from healthy adults. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):934–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Schneider R., Lees R. K., Howe R. C., Acha-Orbea H., Festenstein H., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. T-cell receptor V beta use predicts reactivity and tolerance to Mlsa-encoded antigens. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):40–45. doi: 10.1038/332040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourad W., Scholl P., Diaz A., Geha R., Chatila T. The staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 triggers B cell proliferation and differentiation via major histocompatibility complex-unrestricted cognate T/B cell interaction. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2011–2022. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S. Rheumatoid factors are anti-idiotypic antibodies against virus-induced anti-Fc receptor antibodies. A hypothesis for the induction of some rheumatoid factors. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Nov;24(5):485–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Teller D. C., Barber C. V., Mannik M. IgG rheumatoid factors and staphylococcal protein A bind to a common molecular site on IgG. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Hansen J. A., Nepom B. S. The molecular basis for HLA class II associations with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 1987 Jan;7(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00915418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira P., Coutinho A. I-E-linked control of spontaneous rheumatoid factor production in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1825–1835. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J., Heilmann C., Bjerrum O. J., Ingemann-Hansen T., Halkjaer-Kristensen J. IgG rheumatoid factor-secreting lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of a haemolytic plaque-forming cell technique. Scand J Immunol. 1983 May;17(5):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike B. L., Nossal G. J. A high-efficiency cloning system for single hapten-specific B lymphocytes that is suitable for assay of putative growth and differentiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3395–3399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Identification of the region of T cell receptor beta chain that interacts with the self-superantigen MIs-1a. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1365–1374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90700-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasso E. H., Barber C. V., Nardella F. A., Yount W. J., Mannik M. Antigenic specificities of human monoclonal and polyclonal IgM rheumatoid factors. The C gamma 2-C gamma 3 interface region contains the major determinants. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3098–3107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. The immunosuppressive activity of L-leucyl-L-leucine methyl ester: selective ablation of cytotoxic lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1038–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Carson D. A., Fong S., Pasquali J. L., Vaughan J. H. Cellular requirements for pokeweed mitogen-induced autoantibody production rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1125–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Chihara T., Moore T. L., Robbins D. L., Tanimoto K., Johnson J. S., McMillan R. Rheumatoid factor-producing cells detected by direct hemolytic plaque assay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):933–941. doi: 10.1172/JCI108546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Fong S., Vaughan J., Carson D. Increased frequency of rheumatoid factor precursor B lymphocytes after immunization of normal adults with tetanus toxoid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):299–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Goronzy J. J. Disease-associated human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen determinants in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Functional role in antigen-specific and allogeneic T cell recognition. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1051–1057. doi: 10.1172/JCI114535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Goronzy J. J. Nonrandom selection of T cell specificities in anti-HLA-DR responses. Sequence motifs of the responder HLA-DR allele influence T cell recruitment. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):70–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withrington R. H., Teitsson I., Valdimarsson H., Seifert M. H. Prospective study of early rheumatoid arthritis. II. Association of rheumatoid factor isotypes with fluctuations in disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):679–685. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]