Abstract
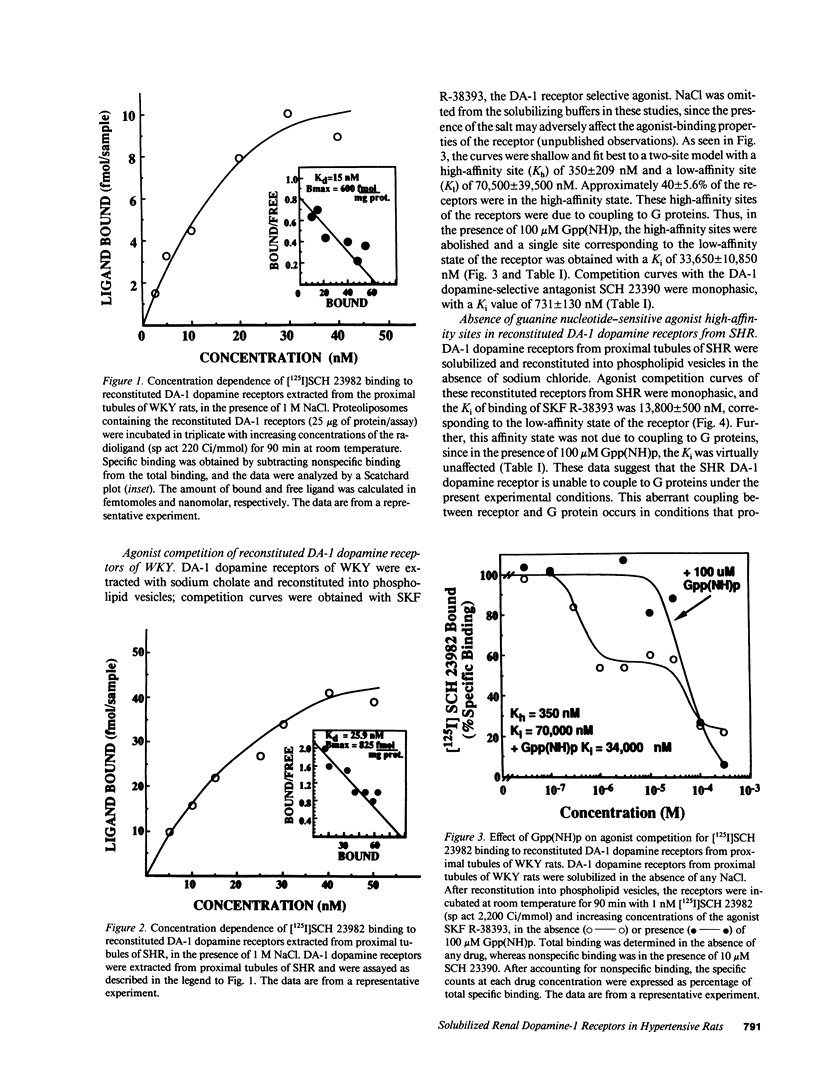
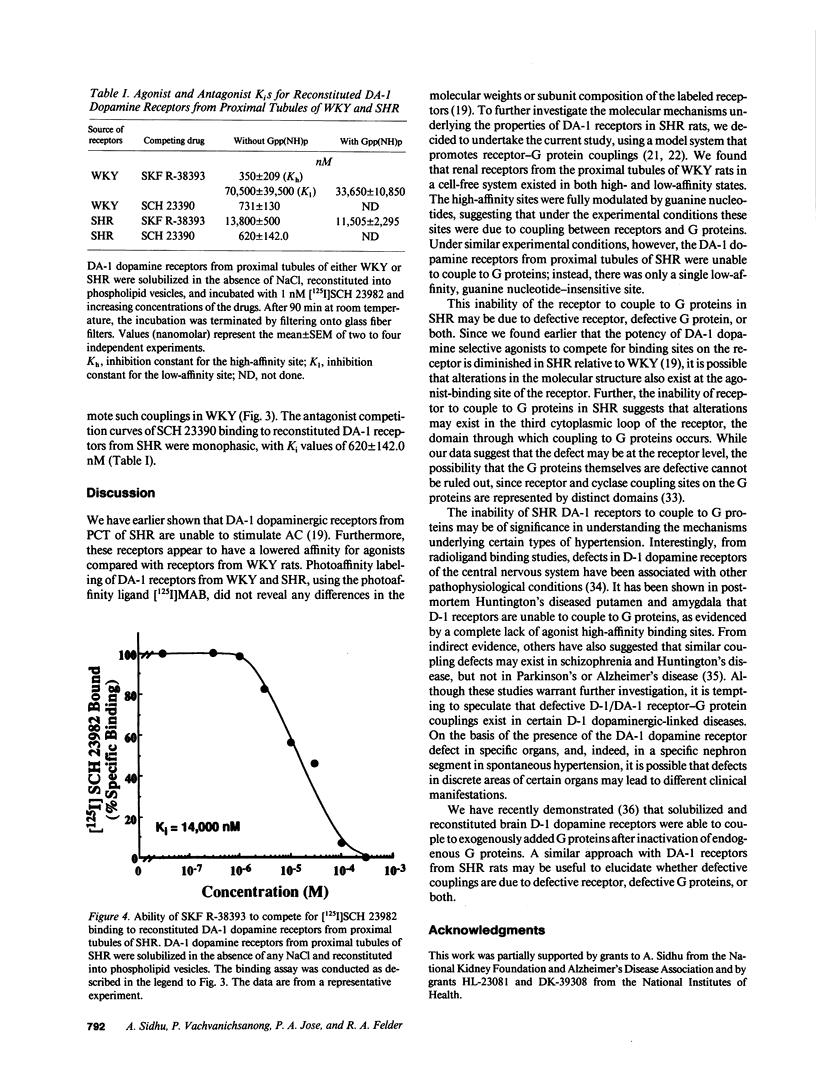
The natriuretic effect of dopamine-1 (DA-1) agonists is reduced in spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR), partly because of defective DA-1 receptor-adenylate cyclase (AC) coupling in renal proximal convoluted tubules. To investigate this defective coupling, DA-1 dopamine receptors from renal proximal tubules were solubilized and reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. The binding of DA-1-selective ligand [125I]SCH 23982 was specific and saturable, with no differences in receptor density or Kd between SHR and normotensive rats (Wistar-Kyoto rats; WKY). Competition experiments of the reconstituted DA-1 dopamine receptors in WKY with a DA-1-selective agonist, SKF R-38393, revealed the presence of high- (Kh = 350 +/- 209 nM) and low-affinity (Kl = 70,500 +/- 39,500 nM) binding sites. 100 microM Gpp(NH)p abolished the agonist high-affinity sites, converting them to a low-affinity state (Ki = 33,650 +/- 10,850 nM). In SHR, one affinity site was noted (Ki = 13,800 +/- 500) and was not modulated by Gpp(NH)p (Ki = 11,505 +/- 2,295). The absence of guanine nucleotide-sensitive agonist high-affinity sites may explain the defective DA-1/AC coupling mechanism in the SHR.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P. H., Gingrich J. A., Bates M. D., Dearry A., Falardeau P., Senogles S. E., Caron M. G. Dopamine receptor subtypes: beyond the D1/D2 classification. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Bertorello A., Seri I. Dopamine causes inhibition of Na+-K+-ATPase activity in rat proximal convoluted tubule segments. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):F39–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.1.F39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A., Aperia A. Na+-K+-ATPase is an effector protein for protein kinase C in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F370–F373. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Keyser J., De Backer J. P., Ebinger G., Vauquelin G. Coupling of D1 dopamine receptors to the guanine nucleotide binding protein Gs is deficient in Huntington's disease. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 4;496(1-2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Blecher M., Jose P. A. Dopamine-1-mediated stimulation of phospholipase C activity in rat renal cortical membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8739–8745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Campbell T., Albrecht F., Jose P. A. Dopamine inhibits Na(+)-H+ exchanger activity in renal BBMV by stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F297–F303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., Jose P. A., Axelrod J. The dopamine-1 agonist, SKF 82526, stimulates phospholipase-C activity independent of adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):171–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder R. A., Blecher M., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. Cortical tubular and glomerular dopamine receptors in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F557–F568. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder R. A., Felder C. C., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. The dopamine receptor in adult and maturing kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F315–F327. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder R. A., Seikaly M. G., Cody P., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. Attenuated renal response to dopaminergic drugs in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1990 Jun;15(6 Pt 1):560–569. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.6.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Sidhu A., Felder R. A. Defective dopamine-1 receptor adenylate cyclase coupling in the proximal convoluted tubule from the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1849–1856. doi: 10.1172/JCI114371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, Mahan L. C., McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsma F. J., Jr, McVittie L. D., Gerfen C. R., Mahan L. C., Sibley D. R. Multiple D2 dopamine receptors produced by alternative RNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):926–929. doi: 10.1038/342926a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. R., Hnatowich M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Adrenergic receptors. Models for regulation of signal transduction processes. Hypertension. 1990 Feb;15(2):119–131. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Guan H. C., Booth G., Ulpian C. Link between D1 and D2 dopamine receptors is reduced in schizophrenia and Huntington diseased brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10156–10160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A. A novel affinity purification of D-1 dopamine receptors from rat striatum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10065–10072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A., Felder R. A., Jose P. A., Fishman P. H. Comparison of the central and renal dopamine-1 receptor. Am J Hypertens. 1990 Jun;3(6 Pt 2):37S–39S. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.6.37s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A., Fishman P. H. Solubilization of the D-1 dopamine receptor from rat striatum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):943–949. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A., Kebabian J. W. An iodinated ligand identifying the D-1 dopamine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A. Solubilization and reconstitution of the D-1 dopamine receptor: potentiation of the agonist high-affinity state of the receptor. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8768–8776. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A., Sullivan M., Kohout T., Balen P., Fishman P. H. D1 dopamine receptors can interact with both stimulatory and inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding proteins. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu A., van Oene J. C., Dandridge P., Kaiser C., Kebabian J. W. [125I]SCH 23982: the ligand of choice for identifying the D-1 dopamine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 9;128(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90768-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Guan H. C., O'Dowd B. F., Seeman P., Laurier L. G., Ng G., George S. R., Torchia J., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):614–619. doi: 10.1038/350614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunahara R. K., Niznik H. B., Weiner D. M., Stormann T. M., Brann M. R., Kennedy J. L., Gelernter J. E., Rozmahel R., Yang Y. L., Israel Y. Human dopamine D1 receptor encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 5. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):80–83. doi: 10.1038/347080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



