Abstract
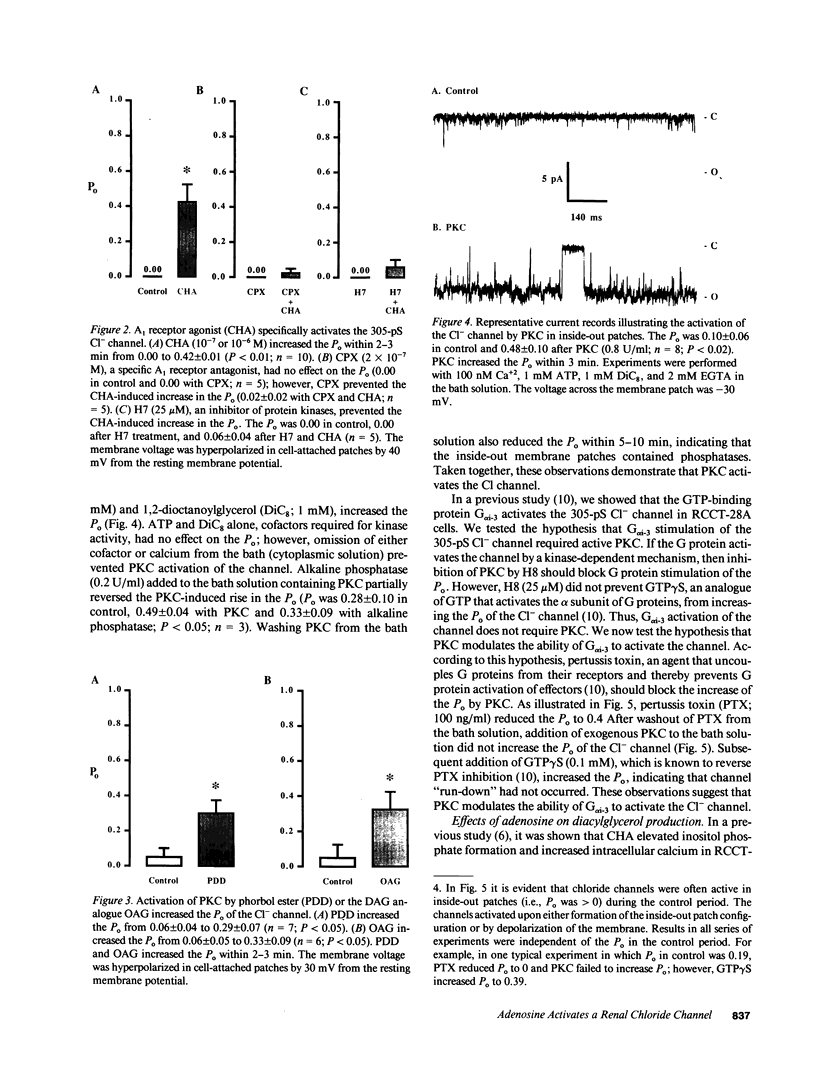
We examined the regulation by adenosine of a 305-pS chloride (Cl-) channel in the apical membrane of a continuous cell line derived from rabbit cortical collecting duct (RCCT-28A) using the patch clamp technique. Stimulation of A1 adenosine receptors by N6-cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) activated the channel in cell-attached patches. Phorbol 12,13-didecanoate and 1-oleoyl 2-acetylglycerol, activators of protein kinase C (PKC), mimicked the effect of CHA, whereas the PKC inhibitor H7 blocked the action of CHA. Stimulation of A1 adenosine receptors also increased the production of diacylglycerol, an activator of PKC. Exogenous PKC added to the cytoplasmic face of inside-out patches also stimulated the Cl- channel. Alkaline phosphatase reversed PKC activation. These results show that stimulation of A1 adenosine receptors activates a 305-pS Cl-channel in the apical membrane by a phosphorylation-dependent pathway involving PKC. In previous studies, we showed that the protein G alpha i-3 activated the 305-pS Cl- channel (Schwiebert et al. 1990. J. Biol. Chem. 265:7725-7728). We, therefore, tested the hypothesis that PKC activates the channel by a G protein-dependent pathway. In inside-out patches, pertussis toxin blocked PKC activation of the channel. In contrast, H7 did not prevent G protein activation of the channel. We conclude that adenosine activates a 305-pS Cl- channel in the apical membrane of RCCT-28A cells by a membrane-delimited pathway involving an A1 adenosine receptor, phospholipase C, diacylglycerol, PKC, and a G protein. Because we have shown, in previous studies, that this Cl- channel participates in the regulatory volume decrease subsequent to cell swelling, adenosine release during ischemic cell swelling may activate the Cl-channel and restore cell volume.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend L. J., Burnatowska-Hledin M. A., Spielman W. S. Adenosine receptor-mediated calcium mobilization in cortical collecting tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C581–C588. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend L. J., Handler J. S., Rhim J. S., Gusovsky F., Spielman W. S. Adenosine-sensitive phosphoinositide turnover in a newly established renal cell line. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1067–F1074. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend L. J., Sonnenburg W. K., Smith W. L., Spielman W. S. A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in rabbit cortical collecting tubule cells. Modulation of hormone-stimulated cAMP. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):710–714. doi: 10.1172/JCI112875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauldry S. A., Wykle R. L., Bass D. A. Phospholipase A2 activation in human neutrophils. Differential actions of diacylglycerols and alkylacylglycerols in priming cells for stimulation by N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16787–16795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Yatani A., Okabe K., Mattera R., Graf R., Sanford J., Codina J., Brown A. M. Roles of G proteins in coupling of receptors to ionic channels and other effector systems. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(4):225–244. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Ionic channels and their regulation by G protein subunits. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:197–213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Yatani A., Imoto Y., Codina J., Mattera R., Birnbaumer L. Direct G-protein regulation of Ca2+ channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:373–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Localization of membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase type IV in kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7457–7461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M. Diacylglycerol stimulates phospholipase A2 from Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnatowska-Hledin M. A., Spielman W. S. Immunodissection of mitochondria-rich cells from rabbit outer medullary collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):F907–F911. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.6.F907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Yatani A., Grenet D., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The alpha subunit of the GTP binding protein Gk opens atrial potassium channels. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2436299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson R., Johnson R. A., Olsson R. A., Cooper D. R., Scheinman S. J. Adenosine stimulates phosphate and glucose transport in opossum kidney epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):F921–F928. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.6.F921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. P., Gandhi R., Le Hir M., Kaissling B. Ecto-5'-nucleotidase: localization in rat kidney by light microscopic histochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Jan;37(1):39–47. doi: 10.1177/37.1.2535703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillingham M. A., Anderson R. J. Purinergic regulation of basal and arginine vasopressin-stimulated hydraulic conductivity in rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(3):277–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01871091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J. W., Laurenson J. P., Forrest J. N., Jr Adenosine and adenosine analogues stimulate adenosine cyclic 3', 5'-monophosphate-dependent chloride secretion in the mammalian ileum. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):929–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI111511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasl M., Turnheim K. Stimulation of electrolyte secretion in rabbit colon by adenosine. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:93–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K., Rittenhouse S. E., Brock T. A., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5901–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., MacDonald R. L. Activators of protein kinase C selectively enhance inactivation of a calcium current component of cultured sensory neurons in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jun;61(6):1259–1269. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.6.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L., Ryan-Jastrow T. 2-Chloroadenosine reduces the N calcium current of cultured mouse sensory neurones in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:585–595. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Clancy G. P., Adams-Brotherton A., Stokes J. B. Inhibition of Na transport by 2-chloroadenosine: dissociation from production of cyclic nucleotides. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;68(10):1357–1362. doi: 10.1139/y90-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Aosaki T. Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00580956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley G. G., Poeschla E. M., Barron H. V., Forrest J. N., Jr A1 adenosine receptors inhibit chloride transport in the shark rectal gland. Dissociation of inhibition and cyclic AMP. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1629–1636. doi: 10.1172/JCI114614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M. Electrophysiological identification of principal and intercalated cells in the rabbit outer medullary collecting duct. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jun;409(1-2):138–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00584761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang M. A., Preston A. S., Handler J. S., Forrest J. N., Jr Adenosine stimulates sodium transport in kidney A6 epithelia in culture. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C330–C336. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeHir M., Kaissling B., Koeppen B. M., Wade J. B. Binding of peanut lectin to specific epithelial cell types in kidney. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C117–C120. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., McCann F. V., Keller T. M., Stanton B. A. Amiloride-sensitive cation channel in apical membrane of inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F278–F286. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Schwiebert E. M., Fejes-Toth G., Naray-Fejes-Toth A., Karlson K. H., McCann F. V., Stanton B. A. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of cortical collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F273–F280. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager R., Ferroni S., Schubert P. Adenosine modulates a voltage-dependent chloride conductance in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 5;532(1-2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91741-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Williams J. A. Multiple sources of 1,2-diacylglycerol in isolated rat pancreatic acini stimulated by cholecystokinin. Involvement of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate and phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14729–14734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt A. D., Clancy G., Welsh M. J. Mucosal adenosine stimulates chloride secretion in canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C167–C174. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Lowe C., Cornish J., Gray D. H., Skinner S. J. Adenylate cyclase blockers dissociate PTH-stimulated bone resorption from cAMP production. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):E708–E714. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.4.E708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridderstrale Y., Kashgarian M., Koeppen B., Giebisch G., Stetson D., Ardito T., Stanton B. Morphological heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1988 Nov;34(5):655–670. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan E. R., Mollinedo F. Diacylglycerol stimulates the Ca2(+)-dependent phospholipase A2 of ram spermatozoa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):294–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90923-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Bonsib S. M., Jennings M. L. Two types of collecting duct mitochondria-rich (intercalated) cells: lectin and band 3 cytochemistry. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C347–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Fejes-Tóth G., Naray-Fejes-Tóth A., Gluck S. Colocalization of H(+)-ATPase and band 3 anion exchanger in rabbit collecting duct intercalated cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):F506–F517. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.4.F506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert E. M., Light D. B., Fejes-Toth G., Naray-Fejes-Toth A., Stanton B. A. A GTP-binding protein activates chloride channels in a renal epithelium. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7725–7728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman W. S., Arend L. J. Adenosine receptors and signaling in the kidney. Hypertension. 1991 Feb;17(2):117–130. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinowitz B. S., Zadunaisky J. A. Action of adenosine on chloride active transport of isolated frog cornea. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F121–F127. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Adelsberg J., Edwards J. C., Herzlinger D., Cannon C., Rater M., al-Awqati Q. Isolation and culture of HCO3- -secreting intercalated cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):C1004–C1011. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.5.C1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yada Y., Nagao S., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Inhibition by cyclic AMP of guanine nucleotide-induced activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil Y. Interaction of adenosine with vasopressin in the inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F679–F687. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Sagi-Eisenberg R., Pines M., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. Multisite phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of transducin by the insulin receptor kinase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9294–9297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]