Abstract
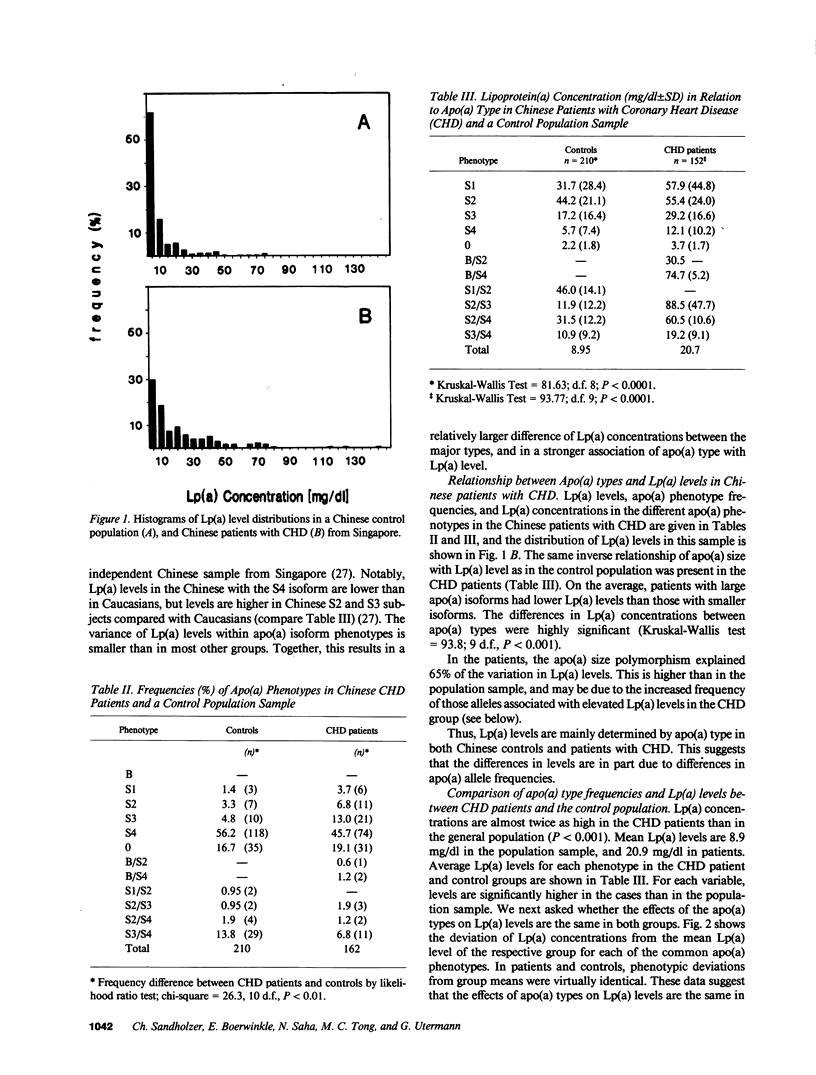
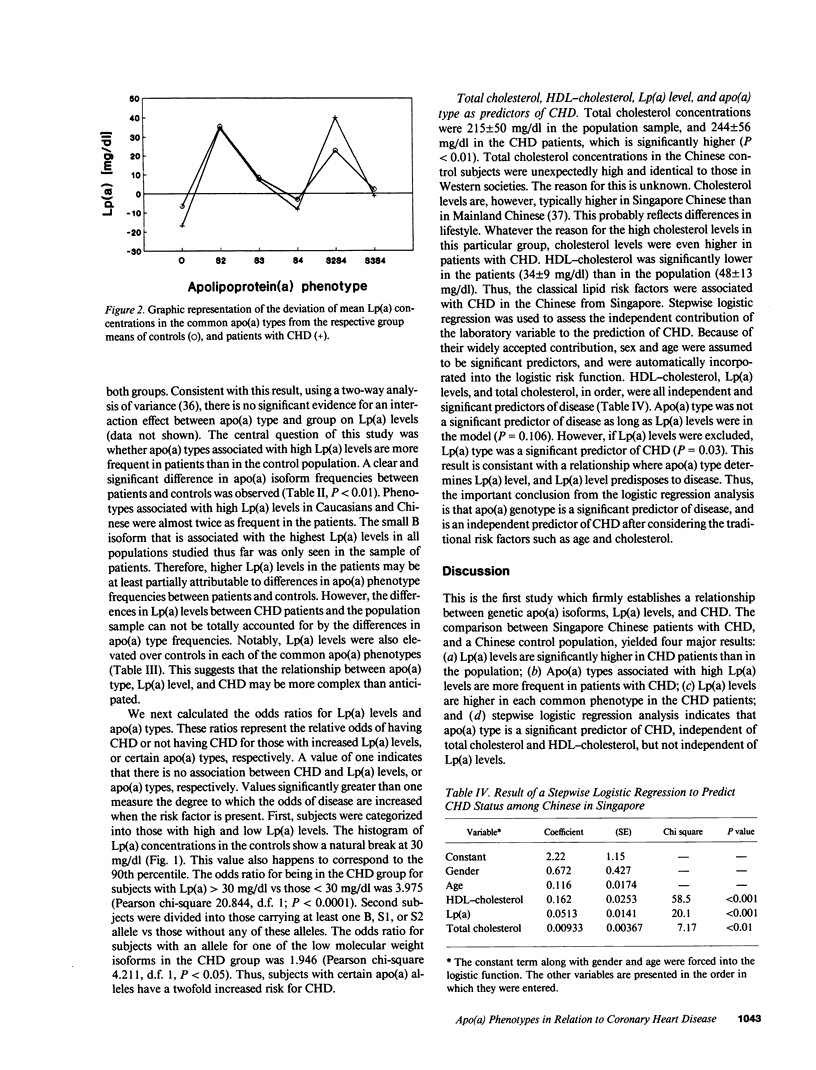
Elevated lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) concentrations are associated with premature coronary heart disease (CHD). In the general population, Lp(a) levels are largely determined by alleles at the hypervariable apolipoprotein(a) (apo[a]) gene locus, but other genetic and environmental factors also affect plasma Lp(a) levels. In addition, Lp(a) has been hypothesized to be an acute phase protein. It is therefore unclear whether the association of Lp(a) concentrations with CHD is primary in nature. We have analyzed apo(a) phenotypes, Lp(a) levels, total cholesterol, and HDL-cholesterol in patients with CHD, and in controls from the general population. Both samples were Chinese individuals residing in Singapore. Lp(a) concentrations were significantly higher in the patients than in the population (mean 20.7 +/- 23.9 mg/dl vs 8.9 +/- 12.9 mg/dl). Apo(a) isoforms associated with high Lp(a) levels (B, S1, S2) were significantly more frequent in the CHD patients than in the population sample (15.9% vs 8.5%, P less than 0.01). Higher Lp(a) concentrations in the patients were in part explained by this difference in apo(a) allele frequencies. Results from stepwise logistic regression analysis indicate that apo(a) type was a significant predictor of CHD, independent of total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol, but not independent of Lp(a) levels. The data demonstrate that alleles at the apo(a) locus determine the risk for CHD through their effects on Lp(a) levels, and firmly establish the role of Lp(a) as a primary genetic risk factor for CHD.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., Seidel D. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Dec;62(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K. A NEW SERUM TYPE SYSTEM IN MAN--THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckert E., Davidoff P., Grimaldi A., Truffert J., Giral P., Doumith R., Thervet F., De Gennes J. L. Increased serum levels of lipoprotein(a) in diabetes mellitus and their reduction with glycemic control. JAMA. 1990 Jan 5;263(1):35–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowle B., Giusti A. M., Waye J. S., Baechtel F. S., Fourney R. M., Adams D. E., Presley L. A., Deadman H. A., Monson K. L. Fixed-bin analysis for statistical evaluation of continuous distributions of allelic data from VNTR loci, for use in forensic comparisons. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):841–855. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 1986 Oct;74(4):758–765. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén G., Berg K., Gillnäs T., Ericson C. Lp(a) lipoprotein/pre-beta1-lipoprotein in Swedish middle-aged males and in patients with coronary heart disease. Clin Genet. 1975 Apr;7(4):334–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., Hegele R. A., Hass P. E., Emi M., Wu L. L., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M., Williams R. R., White R. L., Lalouel J. M. Genetic linkage between lipoprotein(a) phenotype and a DNA polymorphism in the plasminogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Oct;3(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Ghanem K. I., Guevara J., Jr, Nava M. L., Patsch W., Morrisett J. D. Polymorphic forms of human apolipoprotein[a]: inheritance and relationship of their molecular weights to plasma levels of lipoprotein[a]. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish D., Azrolan N., Breslow J. L. Plasma Ip(a) concentration is inversely correlated with the ratio of Kringle IV/Kringle V encoding domains in the apo(a) gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1172/JCI114395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genest J., Jr, Jenner J. L., McNamara J. R., Ordovas J. M., Silberman S. R., Wilson P. W., Schaefer E. J. Prevalence of lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] excess in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1991 May 15;67(13):1039–1145. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90862-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner S. M., Tuttle K. R., Rainwater D. L. Decrease of lipoprotein(a) with improved glycemic control in IDDM subjects. Diabetes Care. 1991 Apr;14(4):302–307. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.4.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Williams R. R. Three alleles for quantitative Lp(a). Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Wilson D. E., Edwards C. Q., Cannon W. N., Carmelli D., Williams R. R. The genetics of quantitative plasma Lp(a): analysis of a large pedigree. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn J. A., DeMaio S. J., Jr, Roubin G. S., Hammarstrom M., Sgoutas D. Predictive value of lipoprotein (a) and other serum lipoproteins in the angiographic diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Nov 15;66(17):1176–1180. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)91094-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iselius L., Dahlén G., de Faire U., Lundman T. Complex segregation analysis of the Lp(a)/pre-beta 1-lipoprotein trait. Clin Genet. 1981 Aug;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kervinen K., Savolainen M. J., Kesäniemi Y. A. A rapid increase in lipoprotein (a) levels after ethanol withdrawal in alcoholic men. Life Sci. 1991;48(22):2183–2188. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Marth E., Bittolo-Bon G., Qunici G. B. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner C., Boerwinkle E., Leffert C. C., Rahmig T., Hobbs H. H. Molecular basis of apolipoprotein (a) isoform size heterogeneity as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2153–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI115248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitsky L. L., Scanu A. M., Gould S. H. Lipoprotein(a) levels in black and white children and adolescents with IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1991 Apr;14(4):283–287. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.4.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Gersdorf E., Menzel H. J., Seed M., Humphries S., Utermann G. Variation in the size of human apolipoprotein(a) is due to a hypervariable region in the gene. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):563–567. doi: 10.1007/BF00210810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Abe A., Seishima M., Makino K., Noma A., Kawade M. Transient changes of serum lipoprotein(a) as an acute phase protein. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Aug;78(2-3):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Dieplinger H., Lackner C., Hoppichler F., Lloyd J. K., Muller D. R., Labeur C., Talmud P. J., Utermann G. Abetalipoproteinemia with an ApoB-100-lipoprotein(a) glycoprotein complex in plasma. Indication for an assembly defect. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):981–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Berg K., Dahlen G., Ferrell R. E., Rhoads G. G. Genetics of the Lp lipoprotein in Japanese-Americans. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai A., Miyahara T., Fujimoto N., Matsuda M., Kameyama M. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Feb;59(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra H. J., Mezdour H., Cachera C., Dracon M., Tacquet A., Fruchart J. C. Lp(a) lipoprotein in patients with chronic renal failure treated by hemodialysis. Clin Chem. 1987 May;33(5):721–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren A., Wilhelmsen L., Eriksson E., Risberg B., Wedel H. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease: a prospective case-control study in a general population sample of middle aged men. BMJ. 1990 Dec 1;301(6763):1248–1251. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6763.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha N. Serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoprotein A-I, A-II and B levels in Singapore ethnic groups. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Nov;68(1-2):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Császár A., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00201550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandkamp M., Funke H., Schulte H., Köhler E., Assmann G. Lipoprotein(a) is an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction at a young age. Clin Chem. 1990 Jan;36(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriewer H., Assmann G., Sandkamp M., Schulte H. The relationship of lipoprotein (a) (Lp(a)) to risk factors of coronary heart disease: initial results of the prospective epidemiological study on company employees in Westfalia. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1984 Sep;22(9):591–596. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1984.22.9.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Schultz J. S., Shreffler D. C. The genetics of the Lp antigen. II. A family study and proposed models of genetic control. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;38(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soma M., Fumagalli R., Paoletti R., Meschia M., Maini M. C., Crosignani P., Ghanem K., Gaubatz J., Morrisett J. D. Plasma Lp(a) concentration after oestrogen and progestagen in postmenopausal women. Lancet. 1991 Mar 9;337(8741):612–612. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91674-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegoshi T., Haba T., Hirai J., Kitoh C., Saga T., Yamazaki Y., Mabuchi H. Alterations of lipoprotein(a) in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Atherosclerosis. 1990 Jul;83(1):99–100. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(90)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Duba C., Menzel H. J. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):47–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00291233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hoppichler F., Dieplinger H., Seed M., Thompson G., Boerwinkle E. Defects in the low density lipoprotein receptor gene affect lipoprotein (a) levels: multiplicative interaction of two gene loci associated with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4171–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., Seitz C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00291232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



