Abstract
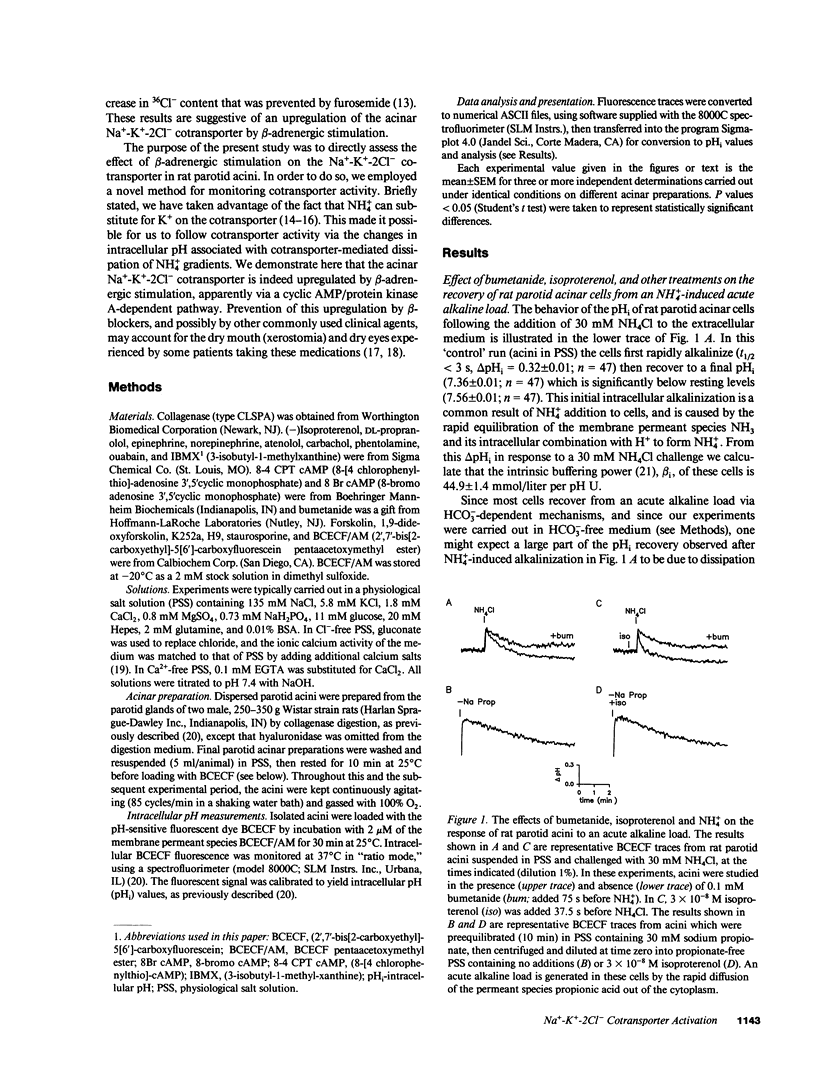
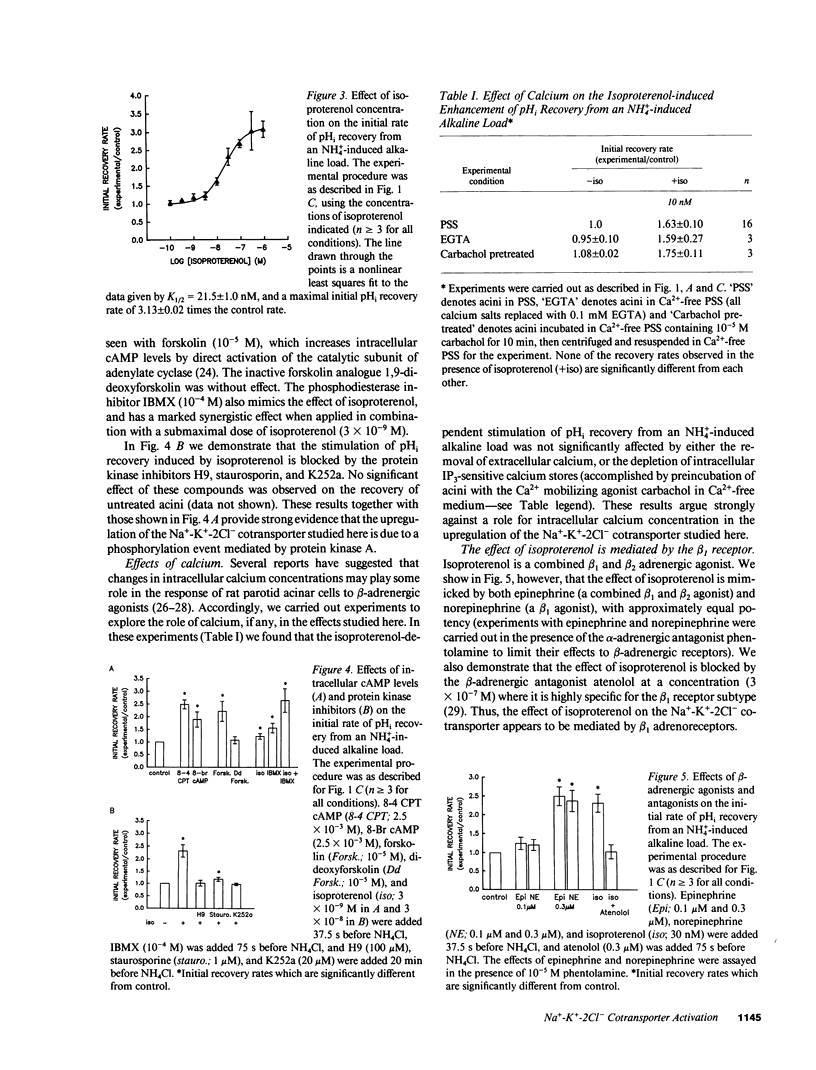
We used the pH-sensitive fluorescent dye 2',7'-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-5(6')-carboxyfluorescein to monitor the recovery of the intracellular pH (pHi) of rat parotid acini from an NH4(+)-induced alkaline load. This recovery was markedly inhibited by the loop diuretic bumetanide and by Cl- removal, indicating that it is largely due to NH4+ entry via the basolateral Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransporter. The rate of recovery of pHi was enhanced threefold by pretreatment (37.5 s) with isoproterenol (K1/2 = 21.5 nM) or norepinephrine (in the presence of phentolamine), and blocked by the beta 1-specific antagonist atenolol, indicating an upregulation of cotransport activity by beta 1-adrenergic stimulation. The effect of isoproterenol was prevented by protein kinase inhibitors and mimicked by cAMP analogues, and by maneuvers known to increase cytosolic cAMP levels in these cells, consistent with the involvement of protein kinase A. Physiologically, such an upregulation of the acinar Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransporter would lead to an increase in acinar chloride uptake across the basolateral membrane, and consequently, an increase in overall chloride and fluid secretion. Prevention of this upregulation by beta-blockers and possibly by other commonly used clinical agents may account for the dry mouth and dry eyes experienced by some patients taking these medications.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambudkar I. S., Melvin J. E., Baum B. J. Alpha 1-adrenergic regulation of Cl- and Ca2+ movements in rat parotid acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):75–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00583733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher F. R., Putney J. W., Jr Regulation of parotid gland function by cyclic nucleotides and calcium. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:215–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsö B., Danielsson A., Henriksson R., Idahl L. A. Characterization of the rat parotid beta-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):271–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Conigrave A. D., Novak I., Young J. A. Electrolyte and protein secretion by the perfused rabbit mandibular gland stimulated with acetylcholine or catecholamines. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:467–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreux C., Imhoff V., Huleux C., Busson S., Rossignol B. Forskolin, a tool for rat parotid secretion studies: 45Ca efflux is not related to cAMP. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):C754–C762. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.5.C754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. C., Atkinson J. C., Macynski A. A., Wolff A., Kung D. S., Valdez I. H., Jackson W., Delapenha R. A., Shiroky J., Baum B. J. Pilocarpine treatment of salivary gland hypofunction and dry mouth (xerostomia). Arch Intern Med. 1991 Jun;151(6):1149–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. M., Gallacher D. V. Beta-adrenergic receptor mechanisms in rat parotid glands: activation by nerve stimulation and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:335–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. Properties and diversity of (Na-K-Cl) cotransporters. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:443–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn V. J., Baum B. J., Ambudkar I. S. Beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation induces inositol trisphosphate production and Ca2+ mobilization in rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12454–12460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Does beta-adrenoceptor activation stimulate Ca2+ mobilization and inositol trisphosphate formation in parotid acinar cells? Cell Calcium. 1989 Nov-Dec;10(8):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Baum B. J., Roth G. S. Beta-adrenergic regulation of rat parotid gland exocrine protein secretion during aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 1981 Feb;15(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(81)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi M., Turner R. J., Baum B. J. 36Cl- and 86Rb+ uptake in rat parotid acinar cells. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31(10):679–683. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne R., Kinne-Saffran E., Schütz H., Schölermann B. Ammonium transport in medullary thick ascending limb of rabbit kidney: involvement of the Na+,K+,Cl(-)-cotransporter. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(3):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF01869723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne R., Koenig B., Hannafin J., Kinne-Saffran E., Scott D. M., Zierold K. The use of membrane vesicles to study the NaCl/KCl cotransporter involved in active transepithelial chloride transport. Pflugers Arch. 1985;405 (Suppl 1):S101–S105. doi: 10.1007/BF00581788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepper M. A., Packer R., Good D. W. Ammonium transport in the kidney. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):179–249. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O., Olgart L. The enhancement of carbachol-induced salivary secretion by VIP and CGRP in rat parotid gland is mimicked by forskolin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Oct;137(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. R., Cassity N. Cl- requirement for saliva secretion in the isolated, perfused rat submandibular gland. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):G464–G469. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.4.G464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. R., Cassity N., Reed P. Effects of isoproterenol on Cl transport in rat submandibular salivary-gland acini. Arch Oral Biol. 1988;33(7):505–509. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(88)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J. R., Reed P. Effect of alpha-receptor stimulation on Cl transport by rat submandibular acini. J Dent Res. 1988 Mar;67(3):561–564. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670030701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvin J. E., Kawaguchi M., Baum B. J., Turner R. J. A muscarinic agonist-stimulated chloride efflux pathway is associated with fluid secretion in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):754–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvin J. E., Moran A., Turner R. J. The role of HCO3- and Na+/H+ exchange in the response of rat parotid acinar cells to muscarinic stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19564–19569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Hedberg A., Molinoff P. B. Comparison of beta adrenergic receptor subtypes in mammalian tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Dec;211(3):502–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak I., Young J. A. Two independent anion transport systems in rabbit mandibular salivary glands. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):649–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00582647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady S. M., Palfrey H. C., Field M. Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C177–C192. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pewitt E. B., Hegde R. S., Haas M., Palfrey H. C. The regulation of Na/K/2Cl cotransport and bumetanide binding in avian erythrocytes by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Effects of kinase inhibitors and okadaic acid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20747–20756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P., Stoff J., Field M., Fine L., Forrest J. N., Epstein F. H. Mechanism of active chloride secretion by shark rectal gland: role of Na-K-ATPase in chloride transport. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F298–F306. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreebny L. M., Schwartz S. S. A reference guide to drugs and dry mouth. Gerodontology. 1986 Autumn;5(2):75–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-2358.1986.tb00055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Star R. A., Burg M. B., Knepper M. A. Bicarbonate secretion and chloride absorption by rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Role of chloride/bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H. Changes in cytosolic free calcium concentration in isolated rat parotid cells by cholinergic and beta-adrenergic agonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 30;131(3):1048–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., George J. N., Baum B. J. Evidence for a Na+/K+/Cl- cotransport system in basolateral membrane vesicles from the rabbit parotid. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF01871194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



